The American Hockey Association (AHA) was a minor professional hockey league that operated between 1926 and 1942. It had previously operated as the Central Hockey League, and before that as part of the United States Amateur Hockey Association. The AHA was the first professional hockey league to field teams in the Southern United States. The founding president was Alvin Warren, who also owned the St. Paul Saints.
| Countries | |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1926 |
| First season | 1926–27 |
| Folded | 1942 |
| Most successful club | St. Louis Flyers (5) |
Other founding owners included William Grant, league secretary and owner of the Duluth Hornets (and Warren's successor as president in 1930), Paul Loudon of the Minneapolis Millers, and William Holmes, owner of the league's only Canadian franchise, the Winnipeg Maroons, and also owner of the Winnipeg Auditorium.
History
editThe United States Amateur Hockey Association split into two sections in 1925. The western-based teams formed a new league, which was initially called the "Central Hockey Association" before ultimately re-naming itself the "American Hockey Association."[1]
Eddie Livingstone, banished by National Hockey League team owners in 1917, owned the Chicago Cardinals. Eager to sign a new interleague agreement with the NHL in 1927, the AHA revoked Livingstone's franchise after one season when NHL president Frank Calder threatened that no deal would be signed with the league as long as it was associated with Livingstone.
The Oklahoma-based Tulsa Oilers and Missouri-based St. Louis Flyers took the ice in 1928, predating the NHL's short-lived St. Louis Eagles franchise by six years. The Kansas City Greyhounds were added to the league in 1933. The Oilers and Flyers were also joined in the early 1940s by two Texas-based teams, the Dallas Texans and Fort Worth Rangers.
By 1930, some AHA owners, led by Walter Whiteside of the Tulsa Oilers, were questioning the league's relationship with the NHL. They approved the creation of a new Chicago franchise, the Chicago Shamrocks, owned by James E. Norris, bringing the league into an NHL market. Renaming the league the American Hockey League, they also established a franchise in Buffalo, New York, an IHL city, which would have been prohibited under the previous agreement with the NHL.[2] In October 1930, Calder declared the AHL to be an outlaw league and threatened never to allow any AHL players into the NHL. The NHL carried out its threat and denied the applications of former AHL players to join NHL teams for the 1931–32 season. In the fall of 1931, the AHL applied to the Stanley Cup trustees to challenge for the trophy, but was unsuccessful in its attempts to force the NHL into a series.
The AHL struggled through two seasons in opposition to the NHL. The Buffalo Majors folded halfway through the 1931–32 season, leaving 12 players who unsuccessfully tried to sue team owners to recover $12,000 in unpaid salaries.[3] By the summer of 1932, the AHL was willing to sign another affiliation agreement with the NHL and officially return to minor league status.[4] The NHL insisted that the AHL leave Chicago, and the Shamrocks were shut down, despite having won the league championship. Norris was told that he would be welcomed into the NHL and acquired the Detroit franchise in 1933. The AHL went back to being known as the American Hockey Association.
The AHA, led by acting president Lyle Wright of the Omaha Knights, voted to shut the league down in the fall of 1942. It returned after World War II as the United States Hockey League, starting with the 1945–46 season.
Teams
edit- Buffalo Majors (1930–31 to 1931–32)
- Chicago Americans / Cardinals (1926–27)
- Chicago Shamrocks (1930–31 to 1931–32)
- Dallas Texans (1941–42; joins USHL in 1945)
- Detroit Greyhounds (1926–27)
- Duluth Hornets (1926–27 to 1932–33)
- Fort Worth Rangers (1941–42; joins USHL in 1945)
- Kansas City Americans (1940–42; joins USHL in 1945)
- Kansas City Greyhounds (1933–40)
- Kansas City Pla-Mors (1927–33)
- Minneapolis Millers (1926–27 to 1930–31; 1936–37 to 1941–42; joins USHL in 1945)
- Minneapolis Warriors (1936)
- Oklahoma City Warriors (1933–34 to 1935–36)
- Omaha Knights (1939–40 to 1941–42; joins USHL in 1945)
- St. Louis Flyers (1928–29 to 1941–42)
- St. Paul Saints (1926–27 to 1929–30; 1932–33; 1935–36 to 1941–42; joins USHL in 1945)
- St. Paul Greyhounds (1932–33)
- Tulsa Indians (1933–34)
- Tulsa Oilers (1928–29 to 1931–32; 1932–33 to 1941–42; joins USHL in 1945)
- Wichita Blue Jays (1932–33)
- Wichita Skyhawks (1935–36 to 1939–40)
- Wichita Vikings (1933–34)
- Winnipeg Maroons (1926–27 to 1927–28)
Timeline
edit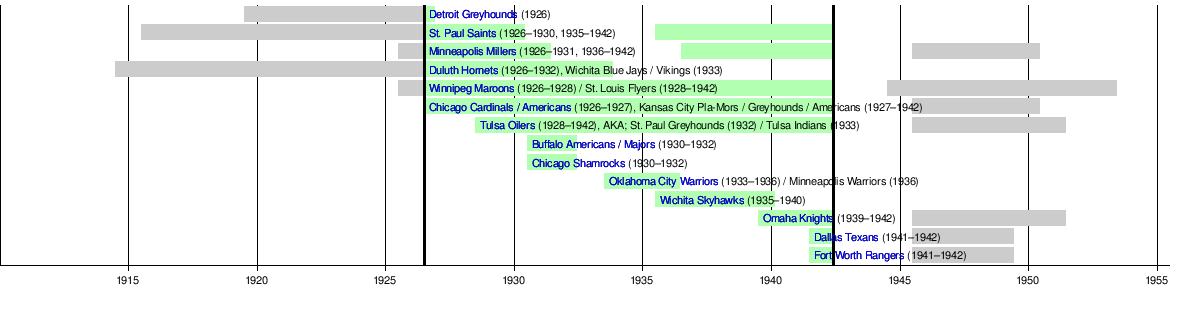
Champions
editThe Harry F. Sinclair Trophy was awarded to the league champions.
- 1926–27 — Duluth Hornets
- 1927–28 — Minneapolis Millers
- 1928–29 — Tulsa Oilers
- 1929–30 — Kansas City Pla-Mors
- 1930–31 — Tulsa Oilers
- 1931–32 — Chicago Shamrocks
- 1932–33 — Kansas City Pla-Mors
- 1933–34 — Kansas City Greyhounds
- 1934–35 — St. Louis Flyers
- 1935–36 — St. Louis Flyers
- 1936–37 — Minneapolis Millers
- 1937–38 — St. Louis Flyers
- 1938–39 — St. Louis Flyers
- 1939–40 — St. Paul Saints
- 1940–41 — St. Louis Flyers
- 1941–42 — Omaha Knights
References
edit- ^ Ross 2015, pp. 128–129
- ^ "Regard American as an outlaw league," Toronto Star, October 10, 1930, p. 14.
- ^ "Hockey players fail to recover salaries," Toronto Star, July 13, 1932, p. 12.
- ^ "Hockey league feud brought to an end," Toronto Star, September 16, 1932, p. 13.
Bibliography
edit- Holzman, Morey; Nieforth, Joseph (2002), Deceptions and Doublecross: How the NHL Conquered Hockey, Toronto: Dundurn Press, ISBN 1-55002-413-2
- Ross, J. Andrew (2015), Joining the Clubs: The Business of the National Hockey League to 1945, Syracuse, New York: Syracuse University Press, ISBN 978-0-8156-3383-9
- Wong, John Chi-Kit (2005), Lords of the Rinks: The Emergence of the National Hockey League 1875–1936, Toronto: University of Toronto Press, ISBN 0-8020-8520-2