Amardus or Mardus (Ancient Greek: Ἀμάρδος, Μάρδος, romanized: Amárdos, Márdos)[1] was a river of Media, mentioned by Ammianus Marcellinus in his confused description of the Persian provinces and [2] by Ptolemy places it in Media, and if we take his numbers as correct, its source is in the Zagrus.[3] The river flows north, and enters the southern coast of the Caspian. William Smith equates the river to the modern Sefīd-Rūd river.[4] As Ptolemy places the Amardi in Amol round the south coast of the Caspian and extending into the interior, we may suppose that they were once at least situated on and about this river.[4]
| Amardus | |
|---|---|
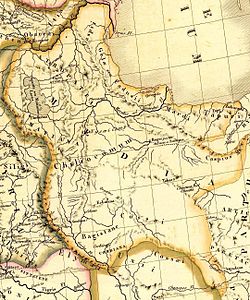 A map that shows the equality of the location of Amardus with Sefid-Rud. | |
| Location | |
| Region | Persian Media Region (currently Iran |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mouth | |
• coordinates | 37°28′09″N 49°56′32″E / 37.4692°N 49.9422°E |
References
edit- ^ Dionys. Perieg., 5.734
- ^ Ammianus Marcellinus. Res Gestae - The Later Roman Empire (AD 354–378). Vol. xxiii.6.
- ^ Ptolemy. The Geography. Vol. 6.2.2.
- ^ a b Smith, William, ed. (1854–1857). "Amardus". Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography. London: John Murray.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Smith, William, ed. (1854–1857). "Amardus". Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography. London: John Murray.