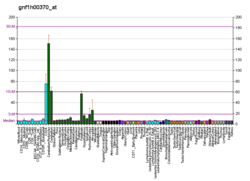
Alsin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ALS2 gene.[5][6] ALS2 orthologs[7] have been identified in all mammals for which complete genome data are available.
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000003393 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000026024 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Hadano S, Hand CK, Osuga H, Yanagisawa Y, Otomo A, Devon RS, Miyamoto N, Showguchi-Miyata J, Okada Y, Singaraja R, Figlewicz DA, Kwiatkowski T, Hosler BA, Sagie T, Skaug J, Nasir J, Brown RH Jr, Scherer SW, Rouleau GA, Hayden MR, Ikeda JE (Oct 2001). "A gene encoding a putative GTPase regulator is mutated in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 2". Nat Genet. 29 (2): 166–73. doi:10.1038/ng1001-166. PMID 11586298. S2CID 52828189.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: ALS2 amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 2 (juvenile)".
- ^ "OrthoMaM phylogenetic marker: ALS2 coding sequence". Archived from the original on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2009-12-09.
Further reading
edit- Hadano S (2002). "[Causative genes for familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis]". Seikagaku. 74 (6): 483–9. PMID 12138710.
- Nakajima D, Okazaki N, Yamakawa H, et al. (2003). "Construction of expression-ready cDNA clones for KIAA genes: manual curation of 330 KIAA cDNA clones". DNA Res. 9 (3): 99–106. doi:10.1093/dnares/9.3.99. PMID 12168954.
- Hadano S, Nichol K, Brinkman RR, et al. (1999). "A yeast artificial chromosome-based physical map of the juvenile amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS2) critical region on human chromosome 2q33-q34". Genomics. 55 (1): 106–12. doi:10.1006/geno.1998.5637. PMID 9889004.
- Hosler BA, Sapp PC, Berger R, et al. (2000). "Refined mapping and characterization of the recessive familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis locus (ALS2) on chromosome 2q33". Neurogenetics. 2 (1): 34–42. doi:10.1007/s100480050049. PMID 9933298. S2CID 33368578.
- Nagase T, Kikuno R, Nakayama M, et al. (2001). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. XVIII. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which code for large proteins in vitro". DNA Res. 7 (4): 273–81. doi:10.1093/dnares/7.4.271. PMID 10997877.
- Yang Y, Hentati A, Deng HX, et al. (2001). "The gene encoding alsin, a protein with three guanine-nucleotide exchange factor domains, is mutated in a form of recessive amyotrophic lateral sclerosis". Nat. Genet. 29 (2): 160–5. doi:10.1038/ng1001-160. PMID 11586297. S2CID 9036123.
- Birkenhäger R, Otto E, Schürmann MJ, et al. (2001). "Mutation of BSND causes Bartter syndrome with sensorineural deafness and kidney failure". Nat. Genet. 29 (3): 310–4. doi:10.1038/ng752. PMID 11687798. S2CID 5892001.
- Eymard-Pierre E, Lesca G, Dollet S, et al. (2002). "Infantile-Onset Ascending Hereditary Spastic Paralysis Is Associated with Mutations in the Alsin Gene". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 71 (3): 518–27. doi:10.1086/342359. PMC 379189. PMID 12145748.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Lesca G, Eymard-Pierre E, Santorelli FM, et al. (2004). "Infantile ascending hereditary spastic paralysis (IAHSP): clinical features in 11 families". Neurology. 60 (4): 674–82. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000048207.28790.25. PMID 12601111. S2CID 20968387.
- Otomo A, Hadano S, Okada T, et al. (2003). "ALS2, a novel guanine nucleotide exchange factor for the small GTPase Rab5, is implicated in endosomal dynamics". Hum. Mol. Genet. 12 (14): 1671–87. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddg184. PMID 12837691.
- Nagano I, Murakami T, Shiote M, et al. (2003). "Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in uncoding regions of ALS2 gene of Japanese patients with autosomal-recessive amyotrophic lateral sclerosis". Neurol. Res. 25 (5): 505–9. doi:10.1179/016164103101201733. PMID 12866199. S2CID 42350605.
- Devon RS, Helm JR, Rouleau GA, et al. (2004). "The first nonsense mutation in alsin results in a homogeneous phenotype of infantile-onset ascending spastic paralysis with bulbar involvement in two siblings". Clin. Genet. 64 (3): 210–5. doi:10.1034/j.1399-0004.2003.00138.x. PMID 12919135. S2CID 27423316.
- Yamanaka K, Vande Velde C, Eymard-Pierre E, et al. (2004). "Unstable mutants in the peripheral endosomal membrane component ALS2 cause early-onset motor neuron disease". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100 (26): 16041–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.2635267100. PMC 307689. PMID 14668431.
- Hand CK, Devon RS, Gros-Louis F, et al. (2004). "Mutation screening of the ALS2 gene in sporadic and familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis". Arch. Neurol. 60 (12): 1768–71. doi:10.1001/archneur.60.12.1768. PMID 14676054.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Kanekura K, Hashimoto Y, Niikura T, et al. (2004). "Alsin, the product of ALS2 gene, suppresses SOD1 mutant neurotoxicity through RhoGEF domain by interacting with SOD1 mutants". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (18): 19247–56. doi:10.1074/jbc.M313236200. PMID 14970233.
External links
edit- GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on ALS2-Related Disorders
- OMIM entries on ALS2-Related Disorders
- Genetics Home Reference- US National Library of Medicine
- Human ALS2 genome location and ALS2 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.