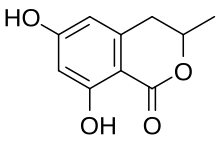
6-Hydroxymellein is a dihydroisocoumarin, a phenolic compound found in carrots.[1] It has also been isolated in Aspergillus terreus and shows an inhibition of pollen development in Arabidopsis thaliana.[2]
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(3R)-6,8-Dihydroxy-3-methyl-3,4-dihydro-1H-2-benzopyran-1-one | |
| Other names
(R)-6-hydroxymellein
(−)-6-Hydroxymellein | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H10O4 | |
| Molar mass | 194.18 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Biosynthesis
edit6-Methoxymellein is formed from S-adenosyl methionine and 6-hydroxymellein by the enzyme 6-hydroxymellein O-methyltransferase with secondary production of S-adenosylhomocysteine.[3]
References
edit- ^ Kurosaki, F.; Nishi, A. (1988). "A methyltransferase for synthesis of the phytoalexin 6-methoxymellein in carrot cells". FEBS Letters. 227 (2): 183. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(88)80894-9. S2CID 86402868.
- ^ Shimada, A.; Kusano, M.; Takeuchi, S.; Fujioka, S.; Inokuchi, T.; Kimura, Y. (2002). "Aspterric acid and 6-hydroxymellein, inhibitors of pollen development in Arabidopsis thaliana, produced by Aspergillus terreus". Zeitschrift für Naturforschung C. 57 (5–6): 459–464. doi:10.1515/znc-2002-5-610. PMID 12132685. S2CID 37714214.
- ^ 6-Hydroxymellein biosynthesis pathway on www.biocyc.org