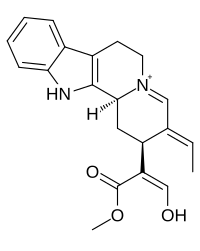
4,21-Dehydrogeissoschizine is a terpene indole alkaloid.[1] It is believed to be the precursor leading to the formation of the aspidosperma, corynanthe, and iboga classes of terpene indole alkaloids.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(16Z)-17-Hydroxy-16-(methoxycarbonyl)-4,16,17,19,20,21-hexadehydro-17,18-seco-4λ5-yohimban-4-ylium
| |
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2S,3E,12bS)-3-Ethylidene-2-[(1Z)-1-hydroxy-3-methoxy-3-oxoprop-1-en-2-yl]-2,3,6,7,12,12b-hexahydro-1H-5λ5-indolo[2,3-a]quinolizin-5-ylium | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H23N2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 351.426 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
References
edit- ^ Rueffer, Martina; Kan-Fan, Christiane; Husson, Henri-Phillipe; Stöckigt, Joachim; Zenk, Meinhart H (1979). "4,21-Dehydrogeissoschizine, an intermediate in heteroyohimbine alkaloid biosynthesis". J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. (22): 1016–1018. doi:10.1039/C39790001016.