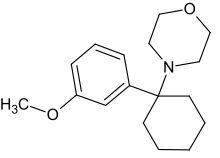
3-MeO-PCMo is a dissociative anesthetic drug which is similar in structure to phencyclidine[1][2] and been sold online as a designer drug.[3][4] The inhibitory effect of 3-MeO-PCMo on the reduction in the density of the drebrin clusters by NMDAR stimulation with glutamic acid is lower than that of PCP or 3-MeO-PCP, with half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values of 26.67 μM (3-MeO-PCMo), 2.02 μM (PCP) and 1.51 μM (3-MeO-PCP).[5]
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H25NO2 |
| Molar mass | 275.392 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Ahmadi A, Khalili M, Hajikhani R, Naserbakht M (April 2011). "New morpholine analogues of phencyclidine: chemical synthesis and pain perception in rats". Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior. 98 (2): 227–33. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2010.12.019. PMID 21215770. S2CID 24650035.
- ^ Abiero A, Botanas CJ, Custodio RJ, Sayson LV, Kim M, Lee HJ, et al. (March 2020). "4-MeO-PCP and 3-MeO-PCMo, new dissociative drugs, produce rewarding and reinforcing effects through activation of mesolimbic dopamine pathway and alteration of accumbal CREB, deltaFosB, and BDNF levels". Psychopharmacology. 237 (3): 757–772. doi:10.1007/s00213-019-05412-y. PMID 31828394. S2CID 209169410.
- ^ Colestock T, Wallach J, Mansi M, Filemban N, Morris H, Elliott SP, et al. (February 2018). "Syntheses, analytical and pharmacological characterizations of the 'legal high' 4-[1-(3-methoxyphenyl)cyclohexyl]morpholine (3-MeO-PCMo) and analogues". Drug Testing and Analysis. 10 (2): 272–283. doi:10.1002/dta.2213. PMID 28513099.
- ^ "3-MeO-PCMo". New Synthetic Drugs Database. Archived from the original on 2016-07-03. Retrieved 2016-02-09.
- ^ Mitsuoka T, Hanamura K, Koganezawa N, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Sekino Y, Shirao T (September–October 2019). "Assessment of NMDA receptor inhibition of phencyclidine analogues using a high-throughput drebrin immunocytochemical assay". Journal of Pharmacological and Toxicological Methods. 99: 106583. doi:10.1016/j.vascn.2019.106583. PMID 31082488.