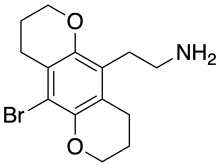
2C-B-BUTTERFLY (2C-B-MOTH, 2C-B-BFLY) is a conformationally-restricted derivative of the phenethylamine hallucinogen 2C-B, which was discovered in 1999 by Michael S. Whiteside and Aaron Monte.[1] It is a ring-expanded homologue of the better known compound 2C-B-FLY, and has similar properties as an agonist for serotonin receptors, but with more selectivity for 5-HT2C over 5-HT2A.[2][3]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H18BrNO2 |
| Molar mass | 312.207 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Analogues and derivatives
editAnalogues and derivatives of 2C-B:
25-N:
- 25B-NB
- 25B-NB23DM
- 25B-NB25DM
- 25B-NB3OMe
- 25B-NB4OMe
- 25B-NBF
- 25B-NBMD
- 25B-NBOH
- 25B-NBOMe (NBOMe-2CB)
- 2C-B-FLY
- 2CBFly-NBOMe (NBOMe-2CB-Fly)
- DOB-FLY
- DOB-2-DRAGONFLY-5-BUTTERFLY
Other:
- BOB
- BOH-2C-B, β-Hydroxy-2C-B, βOH-2CB[6][7]
- BMB
- 2C-B-5-hemifly
- 2C-B-aminorex (2C-B-AR)
- 2C-B-AN
- 2C-B-BZP
- 2C-B-FLY-NB2EtO5Cl
- 2C-B-PP
- 2CB-Ind
- βk-2C-B (beta-keto 2C-B)
- N-Ethyl-2C-B
- TCB-2 (2C-BCB)
Legal Status
edit2C-B-BUTTERFLY is illegal in Latvia.[8]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Whiteside MS (1999). "Synthesis of hexahydrobenzodipyrans as ring-expanded analogues of potent serotonin 5-HT2A/2C receptor probes". UW-LaCrosseJUR. 2: 61–68. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.688.4722.
- ^ Whiteside MS, Kurrasch-Orbaugh D, Marona-Lewicka D, Nichols DE, Monte A (October 2002). "Substituted hexahydrobenzodipyrans as 5-HT2A/2C receptor probes". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 10 (10): 3301–6. doi:10.1016/S0968-0896(02)00209-2. PMID 12150876.
- ^ Schultz DM, Prescher JA, Kidd S, Marona-Lewicka D, Nichols DE, Monte A (June 2008). "'Hybrid' benzofuran-benzopyran congeners as rigid analogs of hallucinogenic phenethylamines". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 16 (11): 6242–51. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2008.04.030. PMC 2601679. PMID 18467103.
- ^ "Explore N-(2C-B)-Fentanyl | PiHKAL · info". isomerdesign.com.
- ^ "Explore N-(2C-FLY)-Fentanyl | PiHKAL · info". isomerdesign.com.
- ^ Glennon, Richard A.; Bondarev, Mikhail L.; Khorana, Nantaka; Young, Richard; May, Jesse A.; Hellberg, Mark R.; McLaughlin, Marsha A.; Sharif, Najam A. (November 2004). "β-Oxygenated Analogues of the 5-HT2ASerotonin Receptor Agonist 1-(4-Bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-aminopropane". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 47 (24): 6034–6041. doi:10.1021/jm040082s. ISSN 0022-2623. PMID 15537358.
- ^ Beta-hydroxyphenylalkylamines and their use for treating glaucoma
- ^ "Noteikumi par Latvijā kontrolējamajām narkotiskajām vielām, psihotropajām vielām un prekursoriem" [Regulations Regarding Narcotic Drugs, Psychotropic Substances and Precursors Controlled in Latvia]. Methodological Guidelines for the Application of Annex 1 to the Cabinet Regulation No. 847 (in Latvian). Ministry of Health of the Republic of Latvia. 8 November 2005. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 8 October 2015.