The 1992 United States Senate election in New York took place on November 3, 1992, alongside other elections to the United States Senate in other states, as well as elections to the United States House of Representatives and various state and local elections. Incumbent Senator Al D'Amato narrowly won re-election to a third term. As of 2024, this is the last time Republicans won a U.S. Senate election in New York, and the last time that the winning presidential and U.S. Senate candidates in New York were of different political parties.
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
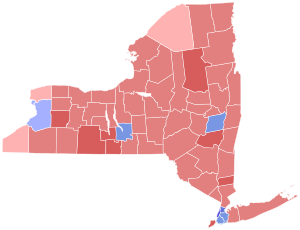 County results D'Amato: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% Abrams: 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
Republican primary
editCandidates
editDeclared
edit- Al D'Amato, incumbent Senator
Withdrew
edit- Laurance Rockefeller Jr., environmental attorney and nephew of former New York Governor and Vice President Nelson Rockefeller (failed to submit signatures)[1]
Results
editSenator D'Amato was unopposed for re-nomination.
Democratic primary
editCandidates
editDeclared
edit- Robert Abrams, New York Attorney General
- Geraldine Ferraro, former U.S. Representative, and Democratic nominee for vice president in 1984
- Elizabeth Holtzman, New York City Comptroller, and nominee for the U.S. Senate in 1980
- Al Sharpton, Baptist minister and civil rights activist
Withdrew
edit- Robert Mrazek, U.S. Representative from Suffolk County
Declined
edit- Mark Green, New York City Commissioner of Consumer Affairs; Democratic nominee for Senate in 1986[2]
Campaign
editThe Democratic primary campaign featured State Attorney General Robert Abrams, former U.S. Congresswoman and 1984 vice presidential candidate Geraldine Ferraro, Reverend Al Sharpton, and New York City Comptroller and former Congresswoman Elizabeth Holtzman. Congressman Robert J. Mrazek was also an early candidate, but withdrew from the race after being named in the House banking scandal.[3] Abrams was considered the initial front-runner.[4]
Ferraro emphasized her career as a teacher, prosecutor, congresswoman, and mother, and positioned herself as being tough on crime.[5] She soon took the lead in the polls, additionally capitalizing on her name recognition from 1984.[6] However, she drew attacks from the media and her opponents over her husband John Zaccaro's finances and business relationships.[6] Initially, Ferraro used the attacks in an attempt to galvanize the feminist vote, but her lead began to dwindle under the criticism, and she released additional tax returns in an attempt to defray the attacks.[7][8][9] Holtzman ran a negative ad accusing Ferraro and Zaccaro of taking more than $300,000 in rent in the 1980s from a pornographer with purported ties to organized crime.[10]
Results
edit- Abrams—40–50%
- Abrams—30–40%
- Ferraro—30–40%
- Ferraro—40–50%
- Ferraro—50–60%
- Ferraro—60–70%
- Ferraro—70–80%
In the primary, Abrams won by less than one percentage point, winning 37 percent of the vote to Ferraro's 36 percent.[8] Ferraro did not concede the election for two weeks.[11]
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Robert Abrams | 426,904 | 37.02% | |
| Democratic | Geraldine Ferraro | 415,650 | 36.04% | |
| Democratic | Al Sharpton | 166,665 | 14.45% | |
| Democratic | Elizabeth Holtzman | 144,026 | 12.49% | |
| Total votes | 1,153,245 | 100.00% | ||
General election
editCampaign
editAfter Abrams emerged as the nominee, the Democrats remained divided. In particular, Abrams spent much of the remainder of the campaign trying to get Ferraro's endorsement.[13] Ferraro, enraged and bitter after the nature of the primary,[7][11] ignored Abrams, and accepted Bill Clinton's request to campaign for his presidential bid instead. She was eventually persuaded by state party leaders into giving an unenthusiastic endorsement, with just three days to go before the general election, in exchange for an apology by Abrams for the tone of the primary.[13]
Abrams was also accused of engaging in ethnically charged attacks against the Italian ancestry of both Ferraro and D'Amato. Ahead of the primary, Ferraro sought to defend herself against accusations that she received financial support from organized crime in her 1978 congressional campaign, claiming that, "If I were not Italian American, this whole thing would never have been brought up."[14] In October, Abrams was again accused of anti-Italian political attacks, after calling D'Amato a "fascist" at a campaign event and alleging that he had engaged in the "big lie techniques" of Nazi propaganda officers.[15] At a Columbus Day parade the following day, D'Amato accused Abrams of engaging in ethnic insults on his Italian ancestry, and in a subsequent campaign ad featured images of Italian fascist leader Benito Mussolini to depict the word "fascist" as an anti-Italian slur.[16] Abrams narrowly lost the general election, partially as a result of these controversies.[17]
Polling
editThis article's use of external links may not follow Wikipedia's policies or guidelines. (August 2016) |
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size |
Margin of error |
Alfonse D'Amato (R) |
Robert Abrams (D) |
Other/Neither | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffalo News/Political-Media Research Inc.[18] | October 30, 1992 | 833 | ± 3.5% | 42% | 44% | - | 14% |
Results
edit| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Al D'Amato (incumbent) | 2,652,822 | 41.07% | |
| Conservative | Al D'Amato (incumbent) | 289,258 | 4.48% | |
| Right to Life | Al D'Amato (incumbent) | 224,914 | 3.48% | |
| Total | Al D'Amato (incumbent) | 3,166,994 | 49.03% | |
| Democratic | Robert Abrams | 2,943,001 | 45.57% | |
| Liberal | Robert Abrams | 143,199 | 2.22% | |
| Total | Robert Abrams | 3,086,200 | 47.78% | |
| Libertarian | Norma Segal | 108,530 | 1.68% | |
| New Alliance | Mohammad T. Mehdi | 56,631 | 0.88% | |
| Natural Law | Stanley Nelson | 23,747 | 0.37% | |
| Socialist Workers | Eddie Warren | 16,724 | 0.26% | |
| Republican hold | ||||
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Purdum, Todd S. (July 12, 1992). "JULY 5-11: Rockefeller vs. D'Amato; A Powerful Political Name Reappears in New York". The New York Times.
- ^ Schwartz, Maralee; Kurtz, Howard (June 9, 1991). "D'AMATO FOE GREEN RULES OUT REMATCH IN NEW YORK IN '92". Washington Post.
- ^ Pear, Robert (March 20, 1992). "Mrazek Is Said to Be Ready to Quit Senate Race". The New York Times. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ Kolbert, Elizabeth (October 21, 1991). "In Senate Campaign, Ferraro Picks Up Where She Left Off". The New York Times.
- ^ Braden, Maria (1996). Women Politicians and the Media. Lexington, Kentucky: The University Press of Kentucky. p. 135. ISBN 0-8131-1970-7.
- ^ a b Mitchell, Alison (September 1, 1992). "For Ferraro, Cheers of '84 Are Still Resonating". The New York Times.
- ^ a b Lurie, Leonard (1994). Senator Pothole: The Unauthorized Biography of Al D'Amato. Birch Lane Press. pp. 465, 467. ISBN 1-55972-227-4.
- ^ a b Purdum, Todd S. (September 16, 1992). "Abrams, In Tight Senate Vote, Appears to Edge Out Ferraro". The New York Times.
- ^ Blumenthal, Ralph (September 11, 1992). "Ferraro Releases Tax Returns for 2 Missing Years to Offset Attacks by Rivals". The New York Times.
- ^ Mitchell, Alison (August 27, 1992). "Holtzman Draws Criticism From Feminists Over Ads". The New York Times.
- ^ a b Verhovek, Sam Howe (October 1, 1992). "Abrams Gets A Concession From Ferraro". The New York Times.
- ^ "NY US Senate D Primary Race - September 15, 1992". Our Campaigns. Retrieved June 24, 2018.
- ^ a b Manegold, Catherine S. (November 1, 1992). "Ferraro Gets An Apology From Abrams". The New York Times.
- ^ Treadwell, David (September 15, 1992). "'92 POLITICAL PERSPECTIVE : A Family Feud Comes to a Close - at Ballot Box: N.Y. Senate primary today ends Democratic fight over Ferraro. But GOP could benefit". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ Mouat, Lucia (October 22, 1992). "D'Amato, Abrams Splatter Road To US Senate With Lots of Mud". Christian Science Monitor. Retrieved August 18, 2018.
- ^ Stanley, Alessandra (November 5, 1992). "THE 1992 ELECTIONS: NEW YORK STATE - U.S. SENATE RACE; D'Amato: Combining Money, Attacks, and Foe's Blunders". New York Times. Retrieved August 18, 2018.
- ^ Attorney General Abrams to Quit To Join a Law Firm in Manhattan. New York Times. September 9, 1993.
- ^ Buffalo News/Political-Media Research Inc.
- ^ "Our Campaigns - NY US Senate Race - Nov 03, 1992".
- ^ Clerk of the House of Representatives (1993). "Statistics of the Presidential and Congressional election of November 3, 1992" (PDF). U.S. Government Printing Office.
Further reading
edit- Navasky, Victor (January–February 1993). "Degrees of Sleaze". Columbia Journalism Review.

