The 1944 Irish general election to the 12th Dáil was held on Tuesday, 30 May, having been called on 9 May by President Douglas Hyde on the advice of Taoiseach Éamon de Valera. The general election took place in 34 parliamentary constituencies for 138 seats in Dáil Éireann, the house of representatives of the Oireachtas. Fianna Fáil won an overall majority. The outgoing 11th Dáil was dissolved on 7 June.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
138 seats in Dáil Éireann[a] 70 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 69.2% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
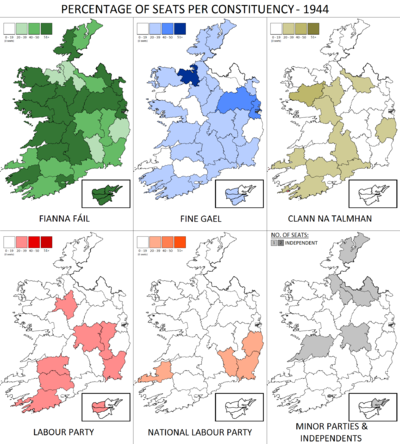 Percentage of seats gained by each of the five biggest parties, and number of seats gained by smaller parties and independents. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 12th Dáil met at Leinster House on 9 June to nominate the Taoiseach for appointment by the president and to approve the appointment of a new government of Ireland on the nomination of the Taoiseach. Outgoing Taoiseach Éamon de Valera was re-appointed leading a single-party Fianna Fáil government.
Calling the election
editThe outgoing Fianna Fáil government, formed on 1 July 1943, was a minority government. On 9 July 1944, it suffered a defeat for the second reading of its Transport Bill.[3] Taoiseach Éamon de Valera sought a snap election, just one year after the previous election, in hopes of getting an overall majority.
It was the second election called under the General Elections (Emergency Provisions) Act 1943.[4][5][6] The Act, intended to increase national security by minimising the interval during which no Dáil is in existence, subvented the requirement under the Constitution for the president to dissolve the Dáil before a general election took place, and was permitted under the state of emergency in effect during the Second World War.[5] The election was called on 9 May but the Dáil met as scheduled on the following day, when an adjournment debate was held in which the opposition TDs condemned the decision to hold an election in wartime as unnecessary and reckless.[6] The 11th Dáil was dissolved on 7 June 1944.[7]
Campaign
editThe campaign was not wanted by the opposition parties. Fianna Fáil fought the election on its record in government and also in the hope of securing a fresh mandate for its policies. During the campaign Fine Gael put forward the proposal of forming a coalition government with the Labour Party and Clann na Talmhan; however, this was ridiculed by Fianna Fáil as untenable. National Labour had split from Labour in January 1944.
Due to the fractured nature of the opposition, Éamon de Valera's tactic of calling a snap general election succeeded, with Fianna Fáil increasing its share of seats, as it had in the previous snap elections of 1933 and 1938.
Result
edit| Election to the 12th Dáil – 30 May 1944[8][9][10][11] | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Leader | Seats | ± | % of seats |
First pref. votes |
% FPv | ±% | |
| Fianna Fáil | Éamon de Valera | 76[a] | +9 | 55.1 | 595,259 | 48.9 | +7.0 | |
| Fine Gael | Richard Mulcahy | 30 | –2 | 21.8 | 249,329 | 20.5 | –2.6 | |
| Clann na Talmhan | Joseph Blowick | 9 | –1 | 6.5 | 122,745 | 10.1 | +0.3 | |
| Labour | William Norton | 8 | –9 | 5.8 | 106,767 | 8.8 | –6.9 | |
| National Labour Party | James Everett | 4 | New | 2.9 | 32,732 | 2.7 | – | |
| Monetary Reform | Oliver J. Flanagan | 1 | 0 | 0.7 | 9,856 | 0.8 | +0.5 | |
| Ailtirí na hAiséirghe | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5,809 | 0.5 | +0.3 | ||
| Independent | N/A | 10 | 0 | 7.2 | 94,852 | 7.8 | –0.9 | |
| Spoilt votes | 12,790 | — | — | |||||
| Total | 138 | 0 | 100 | 1,230,139 | 100 | — | ||
| Electorate/Turnout | 1,816,142 | 69.2% | — | |||||
Voting summary
editSeats summary
editGovernment formation
editFianna Fáil formed the 4th government of Ireland, a majority government.
Changes in membership
editFirst-time TDs
edit- Thomas Brennan
- Harry Colley
- Eamonn Coogan
- Walter Furlong
- Michael Lydon
- Patrick McAuliffe
- John S. O'Connor
- Mary Ryan
Re-elected TDs
edit- John A. Costello
- Frank Loughman
- Peter O'Loghlen
- Eamonn O'Neill
- Laurence Walsh
- Richard Walsh (regained seat)
Outgoing TDs
editRetiring TDs
editSeanad election
editThe election was followed by an election to the 5th Seanad.
Notes
edit- ^ a b Including Frank Fahy (FF), returned automatically for Galway East as outgoing Ceann Comhairle, under Art. 16.6 of the Constitution and the Electoral (Chairman of Dáil Éireann) Act 1937.[1][2]
References
edit- ^ Electoral (Chairman of Dail Eireann) Act 1937, s. 3: Re-election of outgoing Ceann Comhairle (No. 25 of 1937, s. 3). Enacted on 1 November 1937. Act of the Oireachtas. Retrieved from Irish Statute Book.
- ^ "12th Dáil 1944: Galway East". ElectionsIreland.org. Retrieved 9 July 2022.
- ^ "Transport Bill, 1944—Second Stage—(Resumed). Dáil Éireann - 09 May 1944". Houses of the Oireachtas. Retrieved 16 December 2022.
- ^ "Constitution of Ireland". Irish Statute Book. Article 16.3. Archived from the original on 3 May 2019. Retrieved 27 March 2018.; General Elections (Emergency Provisions) Act 1943 (No. 11 of 1943). Act of the Oireachtas. Retrieved from Irish Statute Book on 27 March 2018.
- ^ a b "General Elections (Emergency Provisions) Bill, 1943—Second Stage". Dáil Éireann debates. Oireachtas. 14 April 1943. Archived from the original on 15 June 2020. Retrieved 15 June 2020.
- ^ a b de Valera, Éamon (10 May 1944). "Adjournment of the Dáil". Vol.93 No.15 p.3 c.2497–2498. Archived from the original on 23 September 2021. Retrieved 15 June 2020.
I did not ask for a dissolution of the Dáil. This Dáil would not have been meeting to-day if there had been a dissolution. ... I did not ask for a dissolution, because we passed an Act last year to enable the Dáil, during this critical period, to be brought together at any time that there was need for doing so, so that the Executive at any time would have to assemble the Dáil in case there was any national issue that demanded its assembly. ... when the Dáil adjourns now it will not meet again unless there is some national issue which makes it necessary to call the Dáil together.
- ^ "Dáil dissolved". The Irish Times. 8 June 1944. p. 3.
- ^ "12th Dáil 1944 General Election". ElectionsIreland.org. Archived from the original on 3 June 2009. Retrieved 2 May 2009.
- ^ "Dáil elections since 1918". ARK Northern Ireland. Archived from the original on 27 November 2020. Retrieved 2 May 2009.
- ^ Maurice Manning (1972) notes that the Clann na Talmhan figure is often listed in error, due to the inclusion of Independent Farmer TDs in the CnaT total.
- ^ Nohlen, Dieter; Stöver, Philip (2010). Elections in Europe: A data handbook. pp. 1009–1017. ISBN 978-3-8329-5609-7.
Sources
edit- Manning, Maurice (1972). Irish Political Parties: An Introduction. Dublin: Gill & Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-7171-0536-6.



