In finance, an inverted yield curve is a yield curve in which short-term debt instruments (typically bonds) have a greater yield than longer term bonds. An inverted yield curve is an unusual phenomenon; bonds with shorter maturities generally provide lower yields than longer term bonds.[2][3]
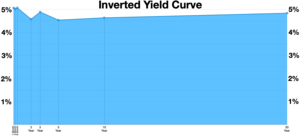


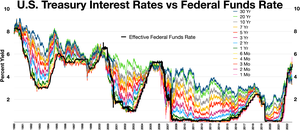
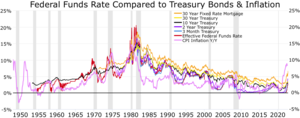
To determine whether the yield curve is inverted, it is a common practice to compare the yield on the 10-year U.S. Treasury bond to either a 2-year Treasury note or a 3-month Treasury bill. If the 10-year yield is less than the 2-year or 3-month yield, the curve is inverted.[4][5][6][7]
History
editThe term "inverted yield curve" was coined by the Canadian economist Campbell Harvey in his 1986 PhD thesis at the University of Chicago.[8]
Causes and significance
editThere are several explanations of why the yield curve becomes inverted. The "expectations theory" holds that long-term rates depicted in the yield curve are a reflection of expected future short-term rates,[9] which in turn reflect expectations about future economic conditions and monetary policy. In this view, an inverted yield curve implies that investors expect lower interest rates at some point in the future – for example, when the economy is expected to enter a recession and the Federal Reserve reduces interest rates to stimulate the economy and pull it out of recession. In that scenario, expected future short-term rates fall below current short-term rates, and the yield curve inverts.[10][11]
A related explanation holds that when investors who value interest income expect recession, a shift in Federal Reserve policy and lower interest rates, they try to lock in long-term yields to protect their income stream. The resulting demand for longer-term bonds drives up their prices, reducing long-term yields.[11]: 87
Business cycles
editThe inverted yield curve is the contraction phase in the Business cycle or Credit cycle when the federal funds rate and treasury interest rates are high to create a hard or soft landing in the cycle. When the Federal funds rate and interest rates are lowered after the economic contraction (to get price and commodity stabilization) this is the growth and expansion phase in the business cycle. The Federal Reserve only indirectly controls the money supply and it is the banks themselves that create new money when they make loans (Debt based monetary system). By manipulating interest rates with the Federal funds rate and Repurchase agreement (Repo Market) the Fed tries to control how much new money banks create.[12][13]
As a leading indicator
editIt has often been said that the inverted yield curve has been one of the most reliable leading indicators for economic recession during the post–World War II era. Proponents of this position maintain that inversion tends to predate a recession 7 to 24 months in advance.[2]: 318 [10][14][15][16][17] Others are skeptical, for example stating that the inverted yield curve is "not necessarily" a reliable metric for predicting recession, or that it has predicted "nine of the past five" recessions.[11]: 86 [18]
In 2023, inversion during a labor shortage and low indebtedness raised questions over whether widespread awareness of its predictive power made it less predictive.[19]
The longest and deepest Treasury yield curve inversion in history began in July 2022, as the Federal Reserve sharply increased the fed funds rate to combat the 2021–2023 inflation surge. Despite widespread predictions by economists and market analysts of an imminent recession, none had materialized by July 2024, economic growth remained steady, and a Reuters survey of economists that month found they expected the economy to continue growing for the next two years. An earlier survey of bond market strategists found a majority no longer believed an inverted curve to be a reliable recession predictor. The curve began re-steepening toward positive territory in June 2024, as it had at other points during that inversion; in every previous inversion they examined, Deutsche Bank analysts found the curve had re-steepened before a recession began.[20][21][22]
Inverted yield curves outside the US
editGerman bonds Inverted yield curve in 2008 and Negative interest rates 2014–2022 30 year 10 year 2 year 1 year 3 month |
50 year 20 year 10 year 2 year 1 year 3 month 1 month |
30 year 10 year 2 year 1 year 3 month 1 month |
30 year bond 10 year bond 5 year bond 1 year bond 3 month bond |
15 year bond 10 year bond 5 year bond 3 year bond |
20 year bond 10 year bond 1 year bond 3 month bond |
Inverted yield curve in the first half of 2022 during Sri Lankan economic crisis 15 year bonds 10 year bonds 5 year bonds 1 year bonds 6 month bonds |
10 year bond 5 year bond 1 year bond |
10 year bonds 5 year bonds 2 year bonds |
Inverted yield curve in 1990 Zero interest-rate policy starting in 1999[24] Negative interest rate policy started in 2014 30 year 20 year 10 year 5 year 2 year 1 year |
Inverted yield curve in 1994–1998 and 2004–2008 20 year 10 year 2 year 3 month 1 month |
See also
edit- Austrian business cycle theory
- Friedman's k-percent rule
- Zero interest-rate policy
- 1970s commodities boom
- 2000s commodities boom
- 2020s commodities boom
- Sahm rule - Economic indicator predicting recessions
- Yield curve control
- Taylor rule
References
edit- ^ "US Treasurys". CNBC. September 25, 2012.
- ^ a b Bodie, Zvi; Kane, Alex; Marcus, Alan J. (2010). Essentials of Investments (Eighth ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Irwin. pp. 315–317. ISBN 978-0-07-338240-1.
- ^ Melicher, Ronald W.; Welshans, Merle T. (1988). Finance: Introduction to Markets, Institutions and Management (7th ed.). Cincinnati OH: South-Western Publishing Co. p. 493. ISBN 0-538-06160-X.
- ^ "Bond Yields Reliably Predict Recessions. Why?". The Economist. 26 July 2018. Retrieved 31 May 2023.
- ^ Randall, David; Barbuscia, Davide (March 7, 2023). "Explainer: U.S. yield curve reaches deepest inversion since 1981: What is it telling us?". Reuters. Retrieved 27 May 2023.
- ^ Strauss, Lawrence C. "Yield-Curve Inversion Widens, Signaling More Recession Worries". Barron's. Dow Jones. Retrieved 28 May 2023.
- ^ "10-Year Treasury Constant Maturity Minus 2-Year Treasury Constant Maturity". Federal Reserve Economic Data.
- ^ Cox, Jeff (2019-10-08). "The father of the yield curve indicator says now is the time to prepare for a recession". CNBC. Retrieved 2024-03-27.
- ^ Melicher, Ronald; Welshans, Merle (1988). Finance: Introduction to Markets, Institutions & Management (1988 ed.). Cincinnati OH: South-Western Publishing Co. p. 493. ISBN 0-538-06160-X.
- ^ a b Rosenberg, Joshua; Maurer, Samuel. "Signal or Noise? Implications of the Term Premium for Recession Forecasting". Federal Reserve Bank of New York. Retrieved 27 May 2023.
- ^ a b c Thau, Annette (2001). The Bond Book (Second ed.). New York: McGraw Hill. p. 86. ISBN 0-07-135862-5.
- ^ "Here We Go Again: The Fed is Causing Another Recession". 21 June 2022.
- ^ "Reference Rates - FEDERAL RESERVE BANK of NEW YORK".
- ^ Campbell, Harvey R. "Yield Curve Inversions and Future Economic Growth" (PDF). Duke University. Retrieved 29 May 2023.
- ^ "What Is an Inverted Yield Curve?". Investopedia.com.
- ^ Bruce-Lockhart, Chelsea; Lewis, Emma; Stubbington, Tommy (6 April 2022). "An inverted yield curve: why investors are watching closely". Ig.ft.com.
- ^ Kock, Ned; Tarkom, Augustine (2023). "How many times until a coincidence becomes a pattern? The case of yield curve inversions preceding recessions and the magical number 7". Communications in Statistics - Theory and Methods: 1–8. doi:10.1080/03610926.2023.2232908.
- ^ Andolfatto, David; Spewack, Andrew (2018). "Does the Yield Curve Really Forecast Recession?". Economic Synopses. 2018 (30). doi:10.20955/es.2018.30. S2CID 158795961. Retrieved 27 May 2023.
- ^ Darian Woods; Adrian Ma (April 14, 2023). "An indicator that often points to recession could be giving a false signal this time". All Things Considered.
- ^ Peck, Emily (December 22, 2023). "Why everyone was so wrong about the 2023 economy". Axios.
- ^ Barbuscia, Davide (July 29, 2024). "US yield curve nears flip with jury out on recession signal". Reuters.
- ^ "10-Year Treasury Constant Maturity Minus 2-Year Treasury Constant Maturity". Federal Reserve Economic Data.
- ^ "a. Irish yield curve dynamics around 2011 loan amendments. b. Portuguese yield curve around 2011 loan amendments". ResearchGate.
- ^ https://www.weforum.org/stories/2024/03/japan-ends-negative-interest-rates-economy-monetary-policy/#:~:text=%E2%80%9CBOJ%2520decided%2520to%2520implement%2520a,%252C%2520namely%25200.25%2520to%25200.5%2525.
External links
edit- Daily yield curve data. U.S. Department of the Treasury.
- Daily yield spread data: 10-year vs. 2-year Treasury securities. Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis.
- Reference Rates. Federal Reserve Bank of New York.
- Here We Go Again: The Fed Is Causing Another Recession. Mises Institute. June 21, 2022.