The white-bearded hermit (Phaethornis hispidus) is a species of hummingbird in the family Trochilidae. It is found in Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and Venezuela.[3][4]
| White-bearded hermit | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Clade: | Strisores |
| Order: | Apodiformes |
| Family: | Trochilidae |
| Genus: | Phaethornis |
| Species: | P. hispidus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Phaethornis hispidus (Gould, 1846)
| |
| |
Taxonomy and systematics
editThe white-bearded hermit is monotypic.
Description
editThe white-bearded hermit is about 13 to 14 cm (5.1 to 5.5 in) long and weighs 4 to 6 g (0.14 to 0.21 oz). This medium-sized hermit has bronzy green upperparts with gray margins on the uppertail coverts. The underparts are gray. The face has a black "mask" with a white supercilium and malar stripe; the center of the throat has a white stripe. The female has identical plumage but shorter wings and a shorter and more decurved bill than the male.[5]
Distribution and habitat
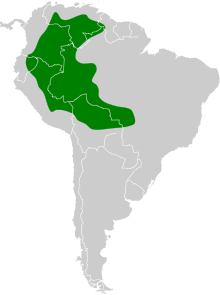
editThe white-bearded hermit is found in Amazonia, from the Andean foothills of western and southern Venezuela south through eastern Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru to northeastern Bolivia, and east throughout western Amazonian Brazil. In elevation it usually ranges as high as 850 m (2,800 ft) but has been recorded up to 1,200 m (3,900 ft) in Peru. It is a bird of humid landscapes. In the lowlands it mostly inhabits regularly inundated areas, such as along rivers and in várzea forest. At higher elevations if favors gallery forest in the cerrado and llanos.[5]
Behavior
editMovement
editNo information about the white-bearded hermit's movements has been published.[5]
Feeding
editThe white-bearded hermit is a "trap-line" feeder like other hermit hummingbirds, visiting a circuit of a wide variety of flowering plants for nectar. It also consumes small arthropods.[5]
Breeding
editThe breeding seasons of the white-bearded hermit vary throughout its large range but have not been defined in detail. Like many hermits, it builds a cone-shaped nest suspended from the underside of drooping leaf. The clutch size is two eggs.[5]
Vocalization
editThe white-bearded hermit's song is "a continuous series of high-pitched single notes 'seep'. It is typically sung from a low perch while gathered at a lek with other males. Its call is "a short explosive 'pip!'."[5]
Status
editThe IUCN has assessed the white-bearded hermit as being of Least Concern though its population size is unknown and believed to be decreasing.[1] It occurs in several protected areas and its "[w]ide distribution and adaptability probably mean that species is not threatened."[5]
References
edit- ^ a b BirdLife International (2018). "White-bearded Hermit Phaethornis hispidus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T22686952A130114646. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22686952A130114646.en. Retrieved 1 December 2021.
- ^ "Appendices | CITES". cites.org. Retrieved 2022-01-14.
- ^ Gill, F.; Donsker, D.; Rasmussen, P. (July 2021). "IOC World Bird List (v 11.2)". Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Remsen, J. V., Jr., J. I. Areta, E. Bonaccorso, S. Claramunt, A. Jaramillo, D. F. Lane, J. F. Pacheco, M. B. Robbins, F. G. Stiles, and K. J. Zimmer. Version 24 August 2021. Species Lists of Birds for South American Countries and Territories. https://www.museum.lsu.edu/~Remsen/SACCCountryLists.htm retrieved August 24, 2021
- ^ a b c d e f g Hinkelmann, C., G. M. Kirwan, and P. F. D. Boesman (2020). White-bearded Hermit (Phaethornis hispidus), version 1.0. In Birds of the World (J. del Hoyo, A. Elliott, J. Sargatal, D. A. Christie, and E. de Juana, Editors). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.2173/bow.whbher1.01 retrieved December 1, 2021
