The sun bear (Helarctos malayanus) is a bear species in the family Ursidae (the only species in the genus Helarctos) occurring in the tropical forests of Southeast Asia. It is the smallest bear species, standing nearly 70 cm (28 in) at the shoulder and weighing 25–65 kg (55–143 lb). It is stockily built, with large paws, strongly curved claws, small, rounded ears and a short snout. The fur is generally short and jet black, but can vary from grey to red. The sun bear gets its name from its characteristic orange to cream-coloured chest patch. Its unique morphology—inward-turned front feet, flattened chest, powerful forelimbs with large claws—suggests adaptations for climbing.
| Sun bear Temporal range: Middle Pleistocene–recent,[1]
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Sun bear in Kaeng Krachan National Park | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Ursidae |
| Subfamily: | Ursinae |
| Genus: | Helarctos Horsfield, 1825 |
| Species: | H. malayanus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Helarctos malayanus (Raffles, 1821)
| |
| Subspecies[3] | |
| |
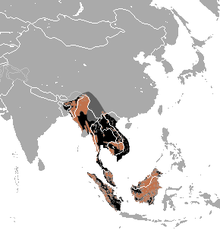
| |
| Distribution of the sun bear (2010)[2] (brown – extant, black – former, dark grey – presence uncertain) | |
| Synonyms[4] | |
|
List
| |
The most arboreal (tree-living) of all bears, the sun bear is an excellent climber and sunbathes or sleeps in trees 2 to 7 m (7 to 23 ft) above the ground. It is mainly active during the day, though nocturnality might be more common in areas frequented by humans. Sun bears tend to remain solitary, but sometimes occur in twos (such as a mother and her cub). They do not seem to hibernate, possibly because food resources are available the whole year throughout the range. Being omnivores, sun bears' diet includes ants, bees, beetles, honey, termites, and plant material such as seeds and several kinds of fruits; vertebrates such as birds and deer are also eaten occasionally. They breed throughout the year; individuals become sexually mature at two to four years of age. Litters comprise one or two cubs that remain with their mother for around three years.
The range of the sun bear is bounded by northeastern India to the north then south to southeast through Bangladesh, Cambodia, Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, and Vietnam in mainland Asia to Brunei, Indonesia, and Malaysia to the south. These bears are threatened by heavy deforestation and illegal hunting for food and the wildlife trade; they are also harmed in conflicts with humans when they enter farmlands, plantations, and orchards. The global population is estimated to have declined by 35% since the 1990s. The IUCN has listed this species as vulnerable.
Etymology
editThe sun bear is named so for its characteristic orange- to cream-coloured, crescent-like chest patch.[5] The generic name Helarctos comes from two Greek words: ήλιος (hēlios, related to the sun) and αρκτος (arctos, bear).[4][6] Another name is honey bear, beruang madu in Malay and Indonesian, in reference to its habit of feeding on honey from honeycombs.[7][8] "Honey bear" can also refer to the kinkajou.[9]
Taxonomy and phylogeny
editThe scientific name Ursus malayanus was proposed by Stamford Raffles in 1821; he first described a sun bear from Sumatra.[10] In 1825, Thomas Horsfield placed the species in a genus of its own, Helarctos, when describing a sun bear from Borneo.[11]
Subspecies and distribution
edit| Image | Name | Distribution | Description/Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Malayan sun bear (H. m. malayanus) | The Malayan sun bear occurs on the Asian mainland and Sumatra.[12][13] | Smallest member of the bear family.[14] | |
| Bornean sun bear (H. m. euryspilus) | The Bornean sun bear occurs only in Borneo.[15] | Its skull is smaller than that of the Malayan sun bear.[8][16] |
H. annamiticus, described by Pierre Marie Heude in 1901 from Annam, is not considered a distinct species, but is subordinated as a junior synonym to H. m. malayanus.[12] In 1906, Richard Lydekker proposed another subspecies by the name H. m. wardii for a sun bear skull, noting its similarities to a skull from Tibet with a thicker coat, but the Tibetan specimen was later found to be an Asian black bear (Ursus thibetanus).[17][18] Genetic differences between the two subspecies are obscure[19] and some authorities consider the species monotypic.[4]
Phylogeny
editThe phylogenetic relationships among ursid species have remained ambiguous over the years.[20] Noting the production of fertile hybrids between sun bears and sloth bears (Melursus ursinus), it was proposed that Helarctos be treated as a synonym of Melursus.[21][22] However, studies differed on whether the two species were closely related.[23][24] The brown bear/polar bear genetic lineage was estimated to have genetically diverged from the two black bears/sun bear lineage around 6.72 to 5.54 million years ago (mya); the sun bear appears to have diverged from the two black bears between 6.26 and 5.09 mya.[25] and 5.89–3.51 mya.[26] Nuclear gene sequencing of bear species revealed that the sloth bear and the sun bear were the first Ursinae bears that radiated and are not included in the monophyletic Ursus group; moreover, all relationships between the bears were well resolved.[27]
| A possible phylogeny based on complete mitochondrial DNA sequences from Yu et al. (2007).[28] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The polar bear and the brown bear form a close grouping, while the relationships of the other species are not very well resolved.[29] |
| A more recent phylogeny based on the genetic study of Kumar et al. (2017).[30] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The study concludes that Ursine bears originated around five million years ago and show extensive hybridization of species in their lineage.[30] |
Characteristics
editThe sun bear is the smallest of all bear species.[4][8][31] It is stockily built, with large paws, strongly curved claws, small rounded ears and a short snout. The head-and-body length is between 100 and 140 cm (39 and 55 in), and the shoulder height is nearly 70 cm (28 in). Adults weigh 25–65 kg (55–143 lb). The snout is grey, silver, or orange. The fur is generally jet black, but can vary from grey to red. The hair is silky and fine, and is the shortest of all bear species, suiting its hot tropical habitat.[4][32] The characteristic chest patch, typically U-shaped, but sometimes circular or spotlike, varies from orange or ochre-yellow to buff or cream, or even white. Some individuals may even lack the patch.[4][31] Sun bears can expose the patch while standing on their hind feet as a threat display against enemies.[8][4] Infants are greyish black with a pale brown or white snout and the chest patch is dirty white; the coat of older juveniles may be dark brown. The underfur is particularly thick and black in adults, while the guard hairs are lighter.[4] Two whorls occur on the shoulders, from whence the hair radiates in all directions. A crest is seen on the sides of the neck and a whorl occurs in the centre of the breast patch.[33] The edges of the paws are tan or brown, and the soles are fur-less, which possibly is an adaptation for climbing trees.[4][31][34] The claws are sickle-shaped; the front claws are long and heavy. The tail is 3–7 cm (1.2–2.8 in) long.[35] The sympatric Asian black bear has cream-coloured chest markings of a similar shape as those of sun bears and different claw markings.[5][36]
During feeding, the sun bear can extend its exceptionally long tongue to extract insects and honey.[32][37] The teeth are very large, especially the canines, and the bite force quotient is high relative to its body size for reasons not well understood; a possible explanation could be its frequent opening of tropical hardwood trees with its powerful jaws and claws in pursuit of insects, larvae, or honey.[38] The bite force is high for its size: a 50 Kg sun bear bites with a maximum force of 1907.3–2020.6 Newtons on the rear molar.[39] The head is large, broad and heavy in proportion to the body, but the ears are proportionately smaller; the palate is wide in proportion to the skull.[5][31] The overall unique morphology of this bear, such as its inward-turned front feet, flattened chest, and powerful fore limbs with large claws, indicates adaptations for extensive climbing.[31]
Ecology and behaviour
editSun bears lead the most arboreal (tree-living) lifestyle among all bears.[4][40] They are mainly active during the day, although nocturnality might be more common in areas frequented by humans.[8][41][42] The sun bear is an excellent climber; it sunbathes or sleeps in trees 2 to 7 m (6 ft 7 in to 23 ft 0 in) above the ground. Bedding sites consist mainly of fallen hollow logs, but they also rest in standing trees with cavities, in cavities underneath fallen logs or tree roots, and in tree branches high above the ground.[8][43][44] It is also an efficient swimmer.[5] Sun bears are noted for their intelligence; a captive bear observed sugar being stored in a cupboard locked by a key, and later used its claw to open the lock.[44] A study published in 2019 described skillful mimicry of facial expressions by sun bears, with precision comparable to that seen in gorillas and humans.[45][46]
Sun bears are shy and reclusive animals, and usually do not attack humans unless provoked to do so, or if they are injured or with their cubs; their timid nature led these bears to be often tamed and kept as pets in the past.[4][32] Other sources, though, state that sun bears are known as very fierce animals when surprised in the forest.[47] They are typically solitary but are sometimes seen in pairs (such as mothers and cubs).[8][44] Sun bears stand on their hind feet for a broader view of their surroundings or smell far-off objects; they try to intimidate their enemies by displaying their chest patch if threatened.[4][8] Vocalisations include grunts and snuffles while foraging for insects, and roars similar to those of a male orangutan during the breeding season; less commonly, they may give out short barks (like a rhinoceros) when they are surprised.[4][8] Sun bears do not seem to hibernate, possibly because food resources are available the whole year throughout the range.[2] They occupy home ranges of varying sizes in different areas, ranging from 7 to 27 km2 (2.7 to 10.4 sq mi) in Borneo and peninsular Malaysia; and 8.7 to 20.9 km2 (3.4 to 8.1 sq mi) in Ulu Segama Forest Reserve in Sabah.[43] Tigers are their major predators; dholes and leopards have also been recorded preying on sun bears, but cases are relatively few.[48] In one incident, a tiger-sun bear interaction resulted in a prolonged altercation and in the death of both animals.[49] In another incident, a wild female sun bear was swallowed by a large reticulated python in East Kalimantan.[50]
Diet
editSun bears are omnivores and feed on a broad variety of items, such as ants, bees, beetles, honey, termites, and plant material such as seeds and several kinds of fruits.[8][51] Vertebrates such as birds, deer,[failed verification] eggs, and reptiles may be eaten occasionally.[52][53][page needed] They forage mostly at night. Sun bears tear open hollow trees with their long, sharp claws and teeth in search of wild bees and honey. They also break termite mounds and quickly lick and suck the contents, holding pieces of the broken mound with their front paws.[8][44] They consume figs in large amounts and eat them whole.[54] In a study in the forests of Kalimantan, the fruits of Moraceae, Burseraceae, and Myrtaceae species made up more than 50% of the fruit diet; in times of fruit scarcity, sun bears switched to a more insectivorous diet.[55] A study in Central Borneo revealed that sun bears play an important role in the seed dispersal of Canarium pilosum (a tree in the family Burseraceae).[56] Sun bears eat the centre of coconut palms, and crush oil-rich seeds such as acorns.[44] Oil palms are nutritious but not enough for subsistence.[57]
Reproduction
editSun bears are polyoestrous; births occur throughout the year.[58][59] Oestrus lasts five to seven days. Sun bears become sexually mature at two to four years of age.[4][40] Reported lengths for pregnancies vary from 95 to 240 days; pregnancy tends to be longer in zoos in temperate climate possibly due to delay in implantation or fertilisation.[40] Births occur inside hollow tree cavities.[2] A litter typically comprises one or two cubs weighing around 325 g (11.5 oz) each.[44] Cubs are born deaf with eyes closed. The eyes open at nearly 25 days, but they remain blind till 50 days after birth; the sense of hearing improves over the first 50 days. Cubs younger than two months are dependent on external stimulation for defecation. Cubs are kept on buttress roots at the base of trees until they learn how to walk and climb properly. Mothers protect their cubs aggressively. Offspring remain with their mother for nearly the first three years of their lives. Lifespan in captivity is generally over 20 years; one individual has lived for 34 years.[4][44][60]
Distribution and habitat
editThe sun bear is native to the tropical forests of Southeast Asia; its range is bound by northeastern India to the north and extends south to Bangladesh, Myanmar, Thailand, Cambodia, Laos, and Vietnam to Brunei, Indonesia, and Malaysia to the south.[2][4] Its presence in China was confirmed in 2017 when it was sighted in Yingjiang County of Yunnan Province.[61] It is extinct in Singapore.[2]
These bears dwell primarily in two main types of forests throughout their range - deciduous and seasonally evergreen forests to the north of the Isthmus of Kra, and nonseasonal evergreen forests in Indonesia and Malaysia. They are typically found at low altitudes, such as below 1,200 m (3,900 ft) in western Thailand and peninsular Malaysia, but this varies widely throughout the range; in India, larger numbers have been recorded at elevations up to 3,000 m (9,800 ft) than in low-lying areas, probably due to habitat loss at ground level. They occur in montane areas in northeast India, but may not extend farther north into the unfavourable and colder Himalayan region; their distribution might be restricted to the northwest due to competition with sloth bears. The sun bear is sympatric with the Asian black bear throughout the remaining areas in the mainland range featuring a mix of seasonal forest types, with monthly rainfall below 100 mm (3.9 in) for a long spell of 3–7 months. In mountainous areas, Asian black bears are more common than sun bears, probably due to scarcity of invertebrates on which to feed. The major habitats in southern Thailand and peninsular Malaysia are moist evergreen forests, with more or less unvarying climate and heavy rainfall throughout the year, and low-lying or montane dipterocarp forests. Mangroves may be inhabited, but usually only when they are close to preferred habitat types.[2][4]
The sun bear tends to avoid heavily logged forests and areas close to human settlement.[62][63][64] However, sun bears have been seen in farmlands, plantations and orchards, where they may be considered vermin.[65][66] A survey in Lower Kinabatangan Segama Wetlands showed that sun bears were feared but were not common in oil palm plantations; Bornean bearded pigs, elephants and macaques were far more damaging to crops.[57] Sun bears have been reported preying on poultry and livestock.[67]
Fossil remains suggest its occurrence farther north during the Pleistocene; it may have occurred as far south as Java in the middle to Late Pleistocene. Fossils also known from the Middle Pleistocene of Thailand along with Stegodon, gaur, wild water buffalo, and other living and extinct mammals.[68] Today, it has been eliminated from the majority of its erstwhile range, especially in Thailand; populations are declining in most of the range countries. It disappeared from Singapore during the 1800s and 1900s, possibly due to extensive deforestation. Sun bear populations appear to decrease in size northward from Sundaland, and numbers are especially low in the northern and western extremes of the range. This has possibly been the case since prehistoric times, and is not a result of human interference.[2] The population density varies from 4.3 and 5.9 individuals/km2 (11 and 15 individuals/sq mi) in Khao Yai National Park to 26 individuals/km2 (67 individuals/sq mi) in the Harapan Rainforest in southern Sumatra.[2][69]
Threats
editAccording to the IUCN Bear Specialist Group, sun bear populations have fallen by an estimated 35% since the 1990s. Numbers are especially low in Bangladesh and China, and populations in Vietnam are feared to decline severely by 50–80% in the next 30 years. Habitat fragmentation is on the rise, particularly in Borneo, Sumatra, and some areas of the mainland range. Heavy deforestation (due to agriculture, logging, and forest fires) and hunting for wildlife trade are severe threats throughout the range; human-bear conflicts are a relatively minor threat.[2][31] Compared to other continents, Southeast Asia has undergone severe depletion in forest cover over the past few decades (by almost 12% between 1990 and 2010); this has resulted in substantial habitat loss for forest-dependent species such as sun bears.[70][71] A 2007 study in East Borneo recorded severe loss of habitat and food resources due to droughts and forest fires brought about by the El Niño.[72] With lack of research in predation, sources have documented very few predation events. In the island of Borneo sun bears were found to be hunted by python in their most vulnerable state.[73] Pythons are successfully able to attack by taking advantage of the nighttime when the sun bears are sleep or nursing their cub. In Southeast Asia, a male leopard (Panthera pardus) has been photographed with a sun bear cub being held by the throat. This reported case has been reported to be the second confirmed predator as of 2019.[74] During surveys in Kalimantan between 1994 and 1997, interviewees admitted to hunting sun bears and indicated that sun bear meat is eaten by indigenous people in several areas there. Studies have found evidence of pet trade and sale of sun bear parts such as gall bladders in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) shops in Sabah and Sarawak.[75] In 2018 and 2019, 128 TCM outlets in 24 locations across Sabah and Sarawak were surveyed and bear parts and derivatives were recorded for sale in 25% of the outlets surveyed, many of which would have been derived from locally sourced sun bears.[76] Sun bears were killed by shooting or administering poison to protect coconut and snakefruit plantations in east Kalimantan.[77] A report published by TRAFFIC in 2011 showed that sun bears, along with Asian black bears and brown bears, are specifically targeted for the bear bile trade in Southeast Asia, and are kept in bear farms in Laos, Vietnam, and Myanmar. Poaching is common in several countries in the region.[78] Hunting pressure is rising even in some protected areas; in the Nam Ha National Protected Area in Laos, hunter snares have been found that specifically target bears.[79] A study in Nagaland (northeastern India) recorded a sparse distribution of sun bears in the Fakim and Ntangki National Parks, and reported extensive illegal hunting for food and trade in bear parts.[80] Protective laws have shown little success in controlling these threats, especially due to poor execution and high potential for gains by the trade.[78][81]
Conservation measures
editThe sun bear is listed as vulnerable on the IUCN Red List, and is included in CITES Appendix I.[2] With the exception of Sarawak (Malaysia) and Cambodia, the sun bear is legally protected from hunting in its whole range. A 2014 report documented rampant poaching and trade in sun bear parts in Sarawak, more than anywhere else in Malaysia; the researchers recommended stricter legislations in the state to protect local sun bears.[82]
The Bornean Sun Bear Conservation Centre, founded by Wong Siew Te in Sabah (Malaysia) in 2008, aims to work for the welfare of sun bears rescued from poor conditions in captivity and spread awareness about their conservation.[83] The Malayan sun bears are part of an international captive-breeding program and a species survival plan under the Association of Zoos and Aquariums since late 1994.[84] Since that same year, the European breed registry for sun bears is kept in the Cologne Zoological Garden, Germany.[85]
References
edit- ^ J. H. Schwartz, T. H. Vu, L. C. Nguyen, K. T. Le, and I. Tattersall. 1994. A diverse hominoid fauna from the late middle Pleistocene breccia cave of Tham Khuyen, Socialist Republic of Vietnam. Anthropological Papers of the American Museum of Natural History 73:1-11
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Scotson, L.; Fredriksson, G.; Augeri, D.; Cheah, C.; Ngoprasert, D. & Wai-Ming, W. (2018) [errata version of 2017 assessment]. "Helarctos malayanus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T9760A123798233. Retrieved 16 January 2022.
- ^ Wozencraft, W. C. (2005). "Order Carnivora". In Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 587. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Fitzgerald, C. S.; Krausman, P. R. (2002). "Helarctos malayanus". Mammalian Species. 696: 1–5. doi:10.1644/1545-1410(2002)696<0001:HM>2.0.CO;2. S2CID 198969265.
- ^ a b c d Kemmerer, L. (2015). "Bear basics". In Kemmerer, L. (ed.). Bear Necessities: Rescue, Rehabilitation, Sanctuary, and Advocacy. Boston: Brill. pp. 17–34. ISBN 978-90-04-29309-0. Archived from the original on 2022-04-12. Retrieved 2023-02-10.
- ^ Liddell, H. G. & Scott, R. (1889). An Intermediate Greek–English Lexicon. Oxford: Clarendon Press. pp. 117, 350.
- ^ Lai, F.; Olesen, B. (2016). A Visual Celebration of Borneo's Wildlife. Singapore: Bjorn Olesen Wildlife Photography. p. 323. ISBN 978-0-7946-0787-6. Archived from the original on 2022-05-25. Retrieved 2023-02-10.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Phillipps, Q. (2016). "Sun bear". Phillipps' Field guide to the Mammals of Borneo: Sabah, Sarawak, Brunei, and Kalimantan. Princeton: Princeton University Press. pp. 246–249. ISBN 978-0-691-16941-5. Archived from the original on 2022-03-19. Retrieved 2023-02-10.
- ^ de la Rosa, C. L.; Nocke, C. C. (2000). "Kinkajou Potos flavus". A Guide to the Carnivores of Central America: Natural History, Ecology, and Conservation. Texas: University of Texas Press. pp. 100–109. ISBN 0-292-71605-2. Archived from the original on 2022-04-26. Retrieved 2023-02-10.
- ^ Raffles, T. S. (1821). "XVII. Descriptive catalogue of a zoological collection, made on account of the honourable East India Company, in the island of Sumatra and its vicinity, under the direction of Sir Thomas Stamford Raffles, Lieutenant-Governor of Fort Marlborough; with additional notices illustrative of the natural history of those countries". Transactions of the Linnean Society of London. 13 (1): 239–274. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8339.1821.tb00064.x.
- ^ Horsfield, T. (1825). "Description of the Helarctos euryspilus exhibiting in the bear from the island of Borneo, the type of a subgenus of Ursus". The Zoological Journal. 2 (6): 221–234.
- ^ a b Ellerman, J. R.; Morrison-Scott, T. C. S. (1966). "Genus Helarctos Horsfield, 1825". Checklist of Palaearctic and Indian mammals 1758 to 1946 (2nd ed.). London: British Museum of Natural History. p. 241.
- ^ Santiapillai, A. & Santiapillai, C. (1996). "The status, distribution and conservation of the Malayan sun bear (Helarctos malayanus) in Indonesia". Tigerpaper. 23 (1): 11–16.
- ^ "Malayan Sun Bear". Malaysian Wildlife. Retrieved 2023-10-30.
- ^ Meijaard, E. (2004). "Craniometric differences among Malayan sun bears (Ursus malayanus); evolutionary and taxonomic implications" (PDF). Raffles Bulletin of Zoology. 52 (2): 665–672. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2012-07-15. Retrieved 2013-02-07.
- ^ Chasen, F. N. (1940). "A handlist of Malaysian mammals: A systematic list of the mammals of the Malay Peninsula, Sumatra, Borneo and Java, including the adjacent small islands". Bulletin of the Raffles Museum. 15: 89–90.
- ^ Lydekker, R. (1906). "On the occurrence of the bruang in the Tibetan Province". Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London. 66: 997–999.
- ^ Pocock, R. I. (1932). "The black and brown bears of Europe and Asia". Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society. 36: 101–138.
- ^ Zhang, Y.-P. (1996). "Genetic variability and conservation relevance of the sun bear as revealed by DNA sequences". Zoological Research. 17 (4): 459–468.
- ^ Waits, L.; Paetkau, D.; Strobeck, C. (1999). "Genetics of the bears of the world". In Servheen, C.; Herrero, S.; Peyton, B. (eds.). Bears: Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan. Gland: IUCN/SSC Bear and Polar Bear Specialist Groups. pp. 25–32. ISBN 2-8317-0462-6. Archived from the original on 2022-04-10. Retrieved 2023-02-10.
- ^ Asakura, S. (1969). "A note on a bear hybrid Melursus ursinus × Helarctos malayanus at Tama Zoo, Tokyo". International Zoo Yearbook. 9 (1): 88. doi:10.1111/j.1748-1090.1969.tb02631.x.
- ^ Van Gelder, R. G. (1977). "Mammalian hybrids and generic limits" (PDF). American Museum Novitates (2635): 1–25. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2020-08-08. Retrieved 2020-05-04.
- ^ Goldman, D.; Giri, P. R.; O'Brien, S. J. (1989). "Molecular genetic-distance estimates among the Ursidae as indicated by one- and two-dimensional protein electrophoresis". Evolution. 43 (2): 282–295. doi:10.1111/j.1558-5646.1989.tb04228.x. JSTOR 2409208. PMID 28568545. S2CID 40420496.
- ^ Bininda-Emonds, O. R. P.; Gittleman, J. L.; Purvis, A. (1999). "Building large trees by combining phylogenetic information: a complete phylogeny of the extant Carnivora (Mammalia)". Biological Reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society. 74 (2): 143–175. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.328.7194. doi:10.1111/j.1469-185X.1999.tb00184.x. PMID 10396181.
- ^ Yu, L.; Li, Y.-W.; Ryder, O. A.; Zhang, Y.-P. (2007). "Analysis of complete mitochondrial genome sequences increases phylogenetic resolution of bears (Ursidae), a mammalian family that experienced rapid speciation". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 7 (198): 198. Bibcode:2007BMCEE...7..198Y. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-7-198. PMC 2151078. PMID 17956639.
- ^ Krause, J.; Unger, T.; Noçon, A.; Malaspinas, A. S.; Kolokotronis, S. O.; Stiller, M.; Soibelzon, L.; Spriggs, H.; Dear, P. H.; Briggs, A. W.; Bray, S. C.; O'Brien, S. J. & Rabeder, G. (2008). "Mitochondrial genomes reveal an explosive radiation of extinct and extant bears near the Miocene-Pliocene boundary". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 8 (220): 220. Bibcode:2008BMCEE...8..220K. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-8-220. PMC 2518930. PMID 18662376.
- ^ Pagès, M.; Calvignac, S.; Klein, C.; Paris, M.; Hughes, S.; Hänni, C. (2008). "Combined analysis of fourteen nuclear genes refines the Ursidae phylogeny". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 47 (1): 73–83. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2007.10.019. PMID 18328735. Archived from the original on 2021-09-27. Retrieved 2021-09-09.
- ^ Yu, Li; Li, Yi-Wei; Ryder, Oliver A.; Zhang, Ya-Ping (2007). "Analysis of complete mitochondrial genome sequences increases phylogenetic resolution of bears (Ursidae), a mammalian family that experienced rapid speciation". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 7 (198): 198. Bibcode:2007BMCEE...7..198Y. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-7-198. PMC 2151078. PMID 17956639.
- ^ Servheen, C.; Herrero, S.; Peyton, B. (1999). Bears: Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan (PDF). IUCN. pp. 26–30. ISBN 978-2-8317-0462-3. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-10-09.
- ^ a b Kumar, V.; Lammers, F.; Bidon, T.; Pfenninger, M.; Kolter, L.; Nilsson, M. A.; Janke, A. (2017). "The evolutionary history of bears is characterized by gene flow across species". Scientific Reports. 7: 46487. Bibcode:2017NatSR...746487K. doi:10.1038/srep46487. PMC 5395953. PMID 28422140.
- ^ a b c d e f Servheen, C. (1999). "Sun bear conservation action plan". In Servheen, C.; Herrero, S.; Peyton, B. (eds.). Bears: Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan. Gland: IUCN/SSC Bear and Polar Bear Specialist Groups. pp. 219–224. ISBN 2-8317-0462-6. Archived from the original on 2022-04-10. Retrieved 2023-02-10.
- ^ a b c Woods, J. G. (1885). "Sun bears". Animate Creation: Popular Edition of "Our Living World", a Natural History. Vol. 1. New York: Selmar Press. pp. 324–325. Archived from the original on 2022-03-28. Retrieved 2023-02-10.
- ^ Pocock, R. I. (1941). "Helarctos malayanus". The Fauna of British India, including Ceylon and Burma. Vol. Mammalia 2. London: Taylor and Francis. pp. 224–232.
- ^ Servheen, C. (1993). "The Sun Bear". In Stirling, I.; Kirshner, D.; Knight, F. (eds.). Bears, Majestic Creatures of the Wild. Pennsylvania: Rodale Press. p. 124. Archived from the original on 2013-07-23. Retrieved 2013-02-07.
- ^ Brown, G. (1996). Great Bear Almanac. The Lyons Press. p. 340. ISBN 978-1-55821-474-3.
- ^ Steinmetz, R.; Garshelis, D. L. (2008). "Distinguishing Asiatic black bears and sun bears by claw marks on climbed trees". Journal of Wildlife Management. 72 (3): 814–821. doi:10.2193/2007-098. S2CID 86179807.
- ^ Meijaard, E. (1997). The Malayan sun bear on Borneo, with special emphasis on its conservation status in Kalimantan, Indonesia (Report). International Ministry of Forestry – Tropendos Kalimantan Project and World Society for the Protection of Animals, London. pp. 1–51.
- ^ Christiansen, P. (2007). "Evolutionary implications of bite mechanics and feeding ecology in bears". Journal of Zoology. 272 (4): 423–443. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.2006.00286.x.
- ^ van der Meijden, Arie; González-Gómez, Julio César; Pulido-Osorio, María D.; Herrel, Anthony (2023). "Measurement of voluntary bite forces in large carnivores using a semi-automated reward-driven system". Journal of Experimental Biology. 226 (7). doi:10.1242/jeb.245255. ISSN 0022-0949.
- ^ a b c Humphrey, S. R.; Bain, J. R. (1990). "Malayan sun bear". Endangered Animals of Thailand. Florida: Sandhill Crane Press. pp. 313–315. ISBN 1-877743-07-0. Archived from the original on 2022-03-26. Retrieved 2023-02-10.
- ^ Griffiths, M.; Schaik, C. P. (1993). "The impact of human traffic on the abundance and activity periods of Sumatran rain forest wildlife". Conservation Biology. 7 (3): 623–626. Bibcode:1993ConBi...7..623G. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1739.1993.07030623.x.
- ^ Guharajan, R.; Arnold, T. W.; Bolongon, G.; Dibden, G. H.; Abram, N. K.; Teoh, S. W.; Magguna, M. A.; Goossens, B.; Wong, S. T.; Nathan, S. K. S. S.; Garshelis, D. L. (2018). "Survival strategies of a frugivore, the sun bear, in a forest-oil palm landscape" (PDF). Biodiversity and Conservation. 27 (14): 3657–3677. Bibcode:2018BiCon..27.3657G. doi:10.1007/s10531-018-1619-6. S2CID 52274809. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-08-07. Retrieved 2020-05-30.
- ^ a b Wong, S. T.; Servheen, C. W.; Ambu, L. (2004). "Home range, movement and activity patterns, and bedding sites of Malayan sun bears Helarctos malayanus in the Rainforest of Borneo" (PDF). Biological Conservation. 119 (2): 169–181. Bibcode:2004BCons.119..169T. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2003.10.029. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-05-11. Retrieved 2013-02-07.
- ^ a b c d e f g Nowak, R. M. (2005). "Ursus malayanus Malayan sun bear". Walker's Carnivores of the World. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 127–128. ISBN 0-8018-8032-7.
- ^ Taylor, D.; Hartmann, D.; Dezecache, G.; Te Wong, S.; Davila-Ross, M. (2019). "Facial complexity in sun bears: Exact facial mimicry and social sensitivity". Scientific Reports. 9 (1): 4961. Bibcode:2019NatSR...9.4961T. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-39932-6. PMC 6428817. PMID 30899046.
- ^ Solly, M. (2019). "Sun bears mimic each other's facial expressions to communicate". Smithsonian Magazine. Archived from the original on 2020-05-30. Retrieved 2020-05-25.
- ^ Servheen, C.; Salter, R. E. (1999). "Chapter 11: Sun Bear Conservation Action Plan" (PDF). In Servheen, C.; Herrero, S.; Peyton, B. (eds.). Bears: Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan. Gland: International Union for Conservation of Nature. pp. 219–224. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2014-12-21. Retrieved 2014-12-21.
- ^ Naing, H.; Htun, S.; Kamler, J. F.; Burnham, D.; Macdonald, D. W. (2020). "Large carnivores as potential predators of sun bears". Ursus. 2019 (30e4): 51. doi:10.2192/URSU-D-18-0022.2. S2CID 204151870.
- ^ Bickmore, A.S. (1868). "April 27th". Travels in the East Asian Archipelago. London: John Murray. p. 510. Archived from the original on 2023-02-10. Retrieved 2015-06-11.
- ^ Fredriksson, G. M. (2005). "Predation on sun bears by reticulated python in East Kalimantan, Indonesian Borneo" (PDF). Raffles Bulletin of Zoology. 53 (1): 165–168. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-08-11.
- ^ Sethy, J.; Chauhan, N. P. S. (2018). "Dietary preference of Malayan sun bear Helarctos malayanus in Namdapha Tiger Reserve, Arunachal Pradesh, India". Wildlife Biology. 2018 (1): 1–10. doi:10.2981/wlb.00351.
- ^ Wong, S. T.; Servheen C.; Ambu, L. (2002). "Food habits of Malayan Sun Bears in lowland tropical forests of Borneo" (PDF). Ursus. 13: 127–136. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-07-23. Retrieved 2013-02-07.
- ^ Augeri, D. M. (2005). On the biogeographic ecology of the Malayan sun bear (PDF) (Thesis). Cambridge: Darwin College. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2013-05-14. Retrieved 2013-02-07.
- ^ Wong, S. T.; Servheen C.; Ambu, L. (2002). "Food habits of Malayan sun bears in lowland tropical forests of Borneo" (PDF). Ursus. 13: 127–136. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2013-07-23. Retrieved 2013-02-07.
- ^ Fredriksson, G. M.; Trisno, S. A. W. (2006). "Frugivory in sun bears (Helarctos malayanus) is linked to El Niño-related fluctuations in fruiting phenology, East Kalimantan, Indonesia". Biological Journal of the Linnean Society. 89 (3): 489–508. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8312.2006.00688.x.
- ^ McConkey, K.; Galetti, M. (1999). "Seed dispersal by the sun bear Helarctos malayanus in Central Borneo". Journal of Tropical Ecology. 15 (2): 237–241. doi:10.1017/S0266467499000784. hdl:11449/37442. S2CID 53694341.
- ^ a b Guharajan, R.; Abram, N. K.; Magguna, M. A.; Goossens, B.; Wong, S. T.; Nathan, S. K. S. S.; Garshelis, D. L. (2017). "Does the vulnerable sun bear Helarctos malayanus damage crops and threaten people in oil palm plantations?". Oryx. 53 (4): 611–619. doi:10.1017/S0030605317001089. S2CID 90111598.
- ^ Frederick, C.; Hunt, K. E.; Kyes, R.; Collins, D.; Wasser, S. K. (2012). "Reproductive timing and aseasonality in the sun bear (Helarctos malayanus)". Journal of Mammalogy. 93 (2): 522–531. doi:10.1644/11-MAMM-A-108.1.
- ^ Schwarzenberger, F.; Fredriksson, G.; Schaller, K.; Kolter, L. (2004). "Fecal steroid analysis for monitoring reproduction in the sun bear (Helarctos malayanus)". Theriogenology. 62 (9): 1677–1692. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.556.2474. doi:10.1016/j.theriogenology.2004.03.007. PMID 15511554.
- ^ Self, Matthew (27 May 2024). "Topeka Zoo's Hoho the sun bear gains internet following for cute looks". ksnt.com. Retrieved 16 August 2024.
- ^ Li, F.; Zheng, X.; Jiang, X. L.; Chan, B. P. L. (2017). "Rediscovery of the sun bear (Helarctos malayanus) in Yingjiang County, Yunnan Province, China". Zoological Research. 38 (4): 206–207. doi:10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2017.044. PMC 5571478. PMID 28825452.
- ^ Nazeri, M.; Kumar, L.; Jusoff, K.; Bahaman, A. R. (2014). "Modeling the potential distribution of sun bear in Krau Wildlife Reserve, Malaysia". Ecological Informatics. 20: 27–32. doi:10.1016/j.ecoinf.2014.01.006.
- ^ Wong, W.-M.; Linkie, M. (2013). "Managing sun bears in a changing tropical landscape". Diversity and Distributions. 19 (7): 700–709. Bibcode:2013DivDi..19..700W. doi:10.1111/ddi.12020. S2CID 84703680.
- ^ Nazeri, M.; Jusoff, K.; Madani, N.; Mahmud, A. R.; Bahman, A. R. (2012). "Predictive modeling and mapping of Malayan sun bear (Helarctos malayanus) distribution using maximum entropy". PLOS ONE. 7 (10): e48104. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...748104N. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0048104. PMC 3480464. PMID 23110182.
- ^ Nomura, F.; Higashi, S.; Ambu, L.; Mohamed, M. (2004). "Notes on oil palm plantation use and seasonal spatial relationships of sun bears in Sabah, Malaysia". Ursus. 15 (2): 227–231. doi:10.2192/1537-6176(2004)015<0227:NOOPPU>2.0.CO;2. JSTOR 3872976. S2CID 85727749.
- ^ Te Wong, S.; Servheen, C.; Ambu, L.; Norhayati, A. (2005). "Impacts of fruit production cycles on Malayan sun bears and bearded pigs in lowland tropical forest of Sabah, Malaysian Borneo". Journal of Tropical Ecology. 21 (6): 627–639. doi:10.1017/S0266467405002622. S2CID 83777246.
- ^ Fredriksson, G. (2005). "Human-sun bear conflicts in East Kalimantan, Indonesian Borneo". Ursus. 16 (1): 130–137. doi:10.2192/1537-6176(2005)016[0130:HBCIEK]2.0.CO;2. JSTOR 3873066. S2CID 26961091.
- ^ K. Suraprasit, J.-J. Jaegar, Y. Chaimanee, O. Chavasseau, C. Yamee, P. Tian, and S. Panha (2016). "The Middle Pleistocene vertebrate fauna from Khok Sung (Nakhon Ratchasima, Thailand): biochronological and paleobiogeographical implications". ZooKeys (613): 1–157. Bibcode:2016ZooK..613....1S. doi:10.3897/zookeys.613.8309. PMC 5027644. PMID 27667928.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Ngoprasert, D.; Reed, D. H.; Steinmetz, R.; Gale, G. A. (2012). "Density estimation of Asian bears using photographic capture–recapture sampling based on chest marks". Ursus. 23 (2): 117–133. doi:10.2192/URSUS-D-11-00009.1. S2CID 86278189.
- ^ Sodhi, N. S.; Koh, L. P.; Brook, B. W.; Ng, P. K.L. (2004). "Southeast Asian biodiversity: an impending disaster". Trends in Ecology & Evolution. 19 (12): 654–660. doi:10.1016/j.tree.2004.09.006. PMID 16701328.
- ^ Stibig, H.-J.; Achard, F.; Carboni, S.; Raši, R.; Miettinen, J. (2014). "Change in tropical forest cover of Southeast Asia from 1990 to 2010". Biogeosciences. 11 (2): 247–258. Bibcode:2014BGeo...11..247S. doi:10.5194/bg-11-247-2014.
- ^ Fredriksson, G. M.; Danielsen, L. S.; Swenson, J. E. (2006). "Impacts of El Niño related drought and forest fires on sun bear fruit resources in lowland dipterocarp forest of East Borneo". Biodiversity and Conservation. 16 (6): 1823–1838. doi:10.1007/s10531-006-9075-0. S2CID 33022260.
- ^ Fredriksson, GM (2005). "Predation on Sun Bears by Reticulated Python in East Kalimantan, Indonesian Borneo". Raffles Bulletin of Zoology. 53 (1): 165, 168.
- ^ Naing, Hla; Htun, Saw; Kamler, Jan F.; Burnham, Dawn; Macdonald, David W. "Large carnivores as potential predators of sun bears. Ursus". 30 (E4): 51, 57. doi:10.2192/URSU-D-18-0022.2. S2CID 204151870.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Gomez, L; Shepherd, C. R.; Khoo, M (2020-03-12). "Illegal trade of sun bear parts in the Malaysian states of Sabah and Sarawak". Endangered Species Research. 41: 279–287. doi:10.3354/esr01028. ISSN 1863-5407. S2CID 213779453. Archived from the original on 2022-06-17. Retrieved 2022-06-25.
- ^ Gomez, Lalita; Shepherd, Chris R.; Khoo, Min Sheng (2020-03-12). "Illegal trade of sun bear parts in the Malaysian states of Sabah and Sarawak". Endangered Species Research. 41: 279–287. doi:10.3354/esr01028. ISSN 1863-5407. S2CID 213779453. Archived from the original on 2022-06-17. Retrieved 2022-06-25.
- ^ Meijaard, E. (1999). "Human imposed threats to sun bears in Borneo" (PDF). Ursus. 11 (A Selection of Papers from the Eleventh International Conference on Bear Research and Management, Graz, Austria, September 1997, and Gatlinburg, Tennessee, April 1998): 185–192. JSTOR 3873000. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2013-07-23. Retrieved 2013-02-07.
- ^ a b Foley, K. E.; Stengel, C. J.; Shepherd, C. R. (2011). Pills, powders, vials and flakes: the bear bile trade in Asia (PDF) (Report). TRAFFIC Southeast Asia, Petaling Jaya, Selangor, Malaysia. pp. 1–79. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-09-25. Retrieved 2020-05-05.
- ^ Scotson, L.; Hunt, M. (2012). "Dismantling the "wall of death": emergency bear snare-line patrol in the Nam Kan National Protected Area, Lao PDR". International Bear News. 21 (4): 17–19.
- ^ Sethy, J.; Chauhan, N. P. S. (2012). "Conservation status of sun bear (Helarctos malayanus) in Nagaland state, north-east India" (PDF). Asian Journal of Conservation Biology. 1 (2): 103–109. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-05-30. Retrieved 2020-05-05.
- ^ Asher, C. (1 August 2016). "Malayan sun bear: bile trade threatens the world's smallest bear". Mongabay. Archived from the original on 26 April 2020. Retrieved 5 May 2020.
- ^ Krishnasamy, K.; Shepherd, C. R. (2014). "A review of the sun bear trade in Sarawak, Malaysia" (PDF). TRAFFIC Bulletin. 26 (1): 37–40. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-05-30. Retrieved 2020-05-05.
- ^ Li, T. C. (5 May 2014). "Sun bears: At home in the forest". The Star. Archived from the original on 7 August 2020. Retrieved 5 May 2020.
- ^ Ball, J. (2000). Sun bear fact sheet (PDF) (Report). Association of Zoos and Aquariums. pp. 1–2. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 August 2008.
- ^ Kok, J., ed. (2008). EAZA Bear TAG Annual Report 2007–2008 (Report). European Association of Zoos and Aquaria.
External links
edit- ARKive: Malayan Sun Bear (Helarctos malayanus) (archived 7 May 2006)
- San Diego Zoo's Animal Bytes: Sun Bear
- Bornean Sun Bear Conservation (archived 18 February 2014)
- The effects of selective logging on Malayan sun bears in lowland tropical rainforest of Borneo (archived 28 June 2010)
