This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2014) |
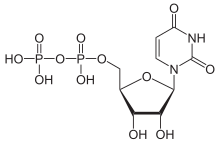
Uridine diphosphate, abbreviated UDP, is a nucleotide diphosphate. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleoside uridine. UDP consists of the pyrophosphate group, the pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase uracil.
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Uridine 5′-(trihydrogen diphosphate)
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(2,4-Dioxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-1(2H)-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl trihydrogen diphosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.372 |
| MeSH | Uridine+diphosphate |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H14N2O12P2 | |
| Molar mass | 404.161 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
UDP is an important factor in glycogenesis. Before glucose can be stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles, the enzyme UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase forms a UDP-glucose unit by combining glucose 1-phosphate with uridine triphosphate, cleaving a pyrophosphate ion in the process. Then, the enzyme glycogen synthase combines UDP-glucose units to form a glycogen chain. The UDP molecule is cleaved from the glucose ring during this process and can be reused by UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase.[1][2]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Glycogen Biochemistry
- ^ "Biochemistry Pathways: Polysaccharide Synthesis". Archived from the original on 2015-04-10. Retrieved 2014-09-20.