The Rote–Meto languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian language family spoken in the Lesser Sunda Islands. It includes Meto spoken on Timor and the languages of Rote Island.
| Rote–Meto | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | Indonesia (Rote, western Timor) East Timor (Oecusse) |
| Linguistic classification | Austronesian |
| Proto-language | Proto-Rote–Meto |
| Subdivisions |
|
| Language codes | |
| Glottolog | rote1234 |
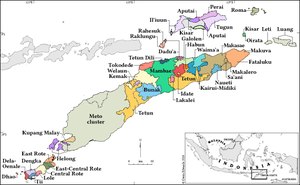 Linguistic map of the Timor area. Rote Island is bottom-left. Meto varieties (light olive) are spoken over most of western Timor. Helong (purple) and Kupang Malay (beige) spoken in the western tip of Timor do not belong to the Rote–Meto subgroup. | |
Languages
editMeto (also called Dawan, Atoni or Timorese) is a cluster of closely related dialects spoken in the Indonesian part of Timor and in the Oecusse district of East Timor. Rote–Meto varieties spoken on Rote Island can be divided into two groups, West Rote and Nuclear (or East) Rote:[1]
Classification
editA close relation between Meto and the languages of Rote was proposed in the 20th century by Jonker (1913) and Mills (1991).[2][3] Edwards (2018a, 2018b, 2021) studied the phonological history of the Rote–Meto languages and reconstructed the ancestral proto-language, Proto-Rote–Meto, based on internal evidence from the Rote–Meto languages, and also from the top-down by tracing the phonological changes that occurred in Rote–Meto reflexes of Proto-Austronesian and Proto-Malayo-Polynesian reconstructions.[1][4][5]
Inspite of being located at the opposite geopraphical ends of the Rote–Meto speech area, Meto and West Rote varieties share many common features in their lexicon and historical phonology.[2][4] This suggests that Proto-Rote–Meto first split into two branches, West Rote-Meto and Nuclear Rote.
| Rote–Meto |
| |||||||||||||||
Subsequently, Meto came into close contact with Nuclear Rote varieties and underwent some shared innovations with the latter. Most likely, speakers of an early form of the Meto cluster originally lived on Rote Islands in the vicinity of West Rote speakers, but later in history migrated to Timor, where they only remained in contact with speakers of Nuclear Rote varieties.[4]
On a higher level, the Rote–Meto languages group with the Austronesian languages spoken to the east.[3] Edwards (2021) includes them in a proposed Timor–Babar subgroup, that comprises all Austronesian languages languages spoken in an area that ranges from Rote Island across Timor and the Barat Daya Islands to Selaru (one of the Tanimbar Islands).[1]
Reconstruction
editComparison table
editThis comparison table (a small selection from Edwards (2021:88–403)) illustrates the correspondences between the Rote–Meto languages, including inherited vocabulary as well as Rote–Meto innovations.[1]
| Words inherited from Proto-Austronesian (PAn) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nuclear Rote (Termanu) |
West Rote (Dengka) |
Meto (Amarasi) |
Proto-Rote–Meto | PAn | Meaning |
| uda | uɗan | uran | *uɗan | *quzan | 'rain' |
| huni | hundi | uki | *hundi | *punti | 'banana' |
| dale-k | lala-ʔ | nana-ʔ | *dalə | *daləm | 'inside' |
| ledo | lelo | neno | *ledo | *qaləjaw | 'sun, day' |
| fee | fee | fee | *fee | *bəRay | 'give' |
| Rote–Meto innovations | |||||
| Nuclear Rote (Termanu) |
West Rote (Dengka) |
Meto (Amarasi) |
Proto-Rote–Meto | PAn | Meaning |
| hoka | hoka | hoka | *hoka | - | 'invite' |
| lui | lui | nui | *lui | - | 'remove' |
| ndui | ndui | kui | *ndui | - | 'draw water' |
| pinu | mbinu | pinu | *mbinu | - | 'snot' |
Lexical influence from non-Austronesian languages
editOne third of the basic lexicon reconstructed for Proto-Rote–Meto does not go back to a known Austronesian or Malayo-Polynesian etymon. Many of these reconstructed words have sounds that did not occur in the ancestral Proto-Malayo-Polynesian and Proto-Austronesian languages, such as prenasalized stops at the beginning of a word. Most likely, these words were borrowed from a non-Austronesian language spoken by earlier inhabitants of the area.[4][6]
References
edit- ^ a b c d Edwards, Owen (2021). Rote-Meto Comparative Dictionary (PDF). Canberra: ANU Press.
- ^ a b Jonker, J. C. G. (1913). "Bijdrage tot de kennis der Rottineesche tongvallen". Bijdragen tot de Taal-, Land- en Volkenkunde van Nederlandsch-Indië. 68: 521–622. JSTOR 20769734..
- ^ a b Mills, Roger F. (1991). "Tanimbar-Kei: An Eastern Indonesian Subgroup". In Robert Blust (ed.). Currents in Pacific Linguistics: Papers on Austronesian Languages and ethnolinguistics in Honour of George W. Grace. Pacific Linguistics, C-117. Canberra: Research School of Pacific and Asian Studies, Australian National University. pp. 241–263. doi:10.15144/PL-C117.241.
- ^ a b c d Edwards, Owen (2018a). "Parallel Histories in Rote-Meto". Oceanic Linguistics. 57 (2): 359–409. doi:10.1353/ol.2018.0016. hdl:1887/67592..
- ^ Edwards, Owen (2018b). "Top-Down Historical Phonology of Rote-Meto". Journal of the Southeast Asian Linguistics Society. 11 (1): 63–90. hdl:10524/52421.
- ^ Klamer, Marian; Moro, Francesca R. "Lexical Borrowing in Austronesian and Papuan Languages: Concepts, Methodology and Findings". In Klamer, Marian; Moro, Francesca R. (eds.). Traces of Contact in the Lexicon: Austronesian and Papuan Studies. Leiden: Brill. pp. 1–21. doi:10.1163/9789004529458_002.