You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Portuguese. (February 2019) Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|
The Republic of Salé, also known as the Bou Regreg Republic and the Republic of the Two Banks, was a city-state maritime corsair republic based at Salé in Morocco during the 17th century, located at the mouth of the Bou Regreg river. It was founded by Moriscos from the town of Hornachos, in western Spain. The Moriscos were the descendants of Muslims who were nominally converted to Christianity, and were subject to mass deportation during Philip III's reign, following the expulsion of the Moriscos decrees. The republic's main commercial activities were the Barbary slave trade and piracy during its brief existence in the 17th century.[4][5]
Bou Regreg Republic | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1627–1668 | |||||||||
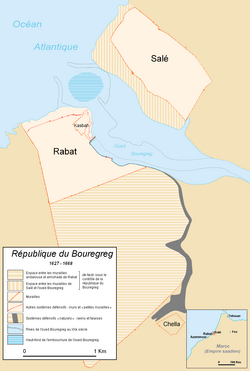 Rabat-Salé, where the republic was located. | |||||||||
| Status | Under the suzerainty of the Zawiya Dila'iya (1641–1661) | ||||||||
| Capital | Kasbah | ||||||||
| Common languages | Arabic Spanish Spanish-based lingua franca[1][2] | ||||||||
| Government | Corsair republic | ||||||||
| Commander | |||||||||
• 1627–1641 | Sidi al-Ayachi | ||||||||
| Governor | |||||||||
• 1651–1661 | Abdullah ibn Mohammed al-Hajj | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• Established | 1627 | ||||||||
• Disestablished | 1668 | ||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
| 1624–1668[3] | 0.91 km2 (0.35 sq mi) | ||||||||
| Population | |||||||||
| 13,000 | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | Morocco | ||||||||
History
editArrival of the Moriscos
editThe republic traces its origins back to the beginning of the 17th century, with the arrival of approximately 3,000 wealthy Moriscos from Hornachos in Extremadura, who anticipated the 1609 expulsion edicts ordered by Philip III of Spain.[6] After 1609, approximately 10,000 down-and-out expelled Moriscos arrived from Spain.[7] Cultural and language differences between the native Salétin people and the Morisco refugees led the newcomers to settle in the old medina of Rabat, on the opposite bank of the Bou Regreg.[8][4]
In 1614 Brahim Vargas became the first governor of the Republic of Salé,[9] a famous corsair who made the old medina of Rabat rich and prosperous by engaging in piracy and trade with Spain and other countries bordering the Mediterranean, for which he had a powerful fleet of galleons (feared by many at the time).[10] Pirates based on the western bank thrived and expanded their operations throughout the Mediterranean and the Atlantic Ocean.[11] In 1624, the Dutchman Jan Janszoon, also known as Murad Reis, became the "Grand Admiral" of the Corsair Republic of Salé.[12] He hired a fellow countryman from the Netherlands, Mathys van Bostel Oosterlinck, who would serve as his Vice-Admiral.[13] The Saadi Sultan Zidan Abu Maali acknowledged Janszoon's election by formally appointing him as his ceremonial governor.[13]
Independence
editIn April 1627, with the support of Sidi al-Ayachi, the Hornacheros expelled the Sherif's governor and constituted themselves a virtually independent republic.[14] The English diplomat John Harrison negotiated a treaty with Sidi al-Ayachi in May, a month after their coup d'état.[14] After Janszoon left Salé in 1627, the Moriscos ceased to recognize the authority of the Sultan Zidan Abu Maali, and refused to pay his tithe on their incomes.[15] They proclaimed a republic, in the image of medieval Italian city-states like Venice or Genoa,[16] ruled by a council or Diwan, a sort of government cabinet formed by 12 to 14 notable people whose members annually elected a Governor and a Captain General of the Fortalesa during the month of May. In the early years of the republic, between 1627 and 1630, the Diwan was controlled only by the Hornacheros, whose grip on power was resented by the growing population of non-Hornachero Moriscos, called Andalusians.[17] After bloody clashes in 1630, an agreement was reached: the election of a Qaid by Andalusians and a new Diwan of 16 members of whom 8 were Andalusians and 8 Hornacheros.[18] The members of the Divan elected a governor or captain general of the fortress every May. All of its documentation was done in the Spanish of the time.
Internal dissension and the failed delivery of the republic to Spain
editIt is in this context of internal confrontation that the initiative of the Hornacheros to hand over the republic to the Hispanic Monarchy of Philip IV must be placed. The Hornacheros sent the draft treaty in 1631 to the Duke of Medina Sidonia so that he could convey it to the king. In it they proposed, "because of the great love they have for Spain, since they have longed for it since they left," to hand over the city with the following conditions:[19]
Let them return to Hornachos, taking charge of compensating the neighbors who had replaced them.
That the municipal authorities be from the same nation, "so that they do not receive the wrongs that they have received in other times." That there were no more old Christians among them than the priests and friars necessary to indoctrinate them; and that the Inquisition does not punish for twenty years those who were born in Barbary and are not imposed on the Catholic religion. That the old privileges they had will be preserved, without making a difference between them and the other vassals in matters of tribute. Their estates would be respected, giving them certificates about it, and the same assurances would be given to the other Andalusians who wanted to return, "because there are many in Tetouan and Algiers who, knowing that they can come, will come." To verify that they were Christians, they would send information supported by Christian captives about how many Moriscos had been martyred and killed for the faith of Christ. They offer to reach Seville with their privateering ships, which will remain the property of H.M. They asked for the return of the children that had been taken from them as a result of the expulsion. They offered to deliver the fortress of Salé with its 68 cannons, for which it would be enough to send a company of one hundred men. They would also deliver the correspondence they had exchanged with the king of England...; also the papers they had from the burgomasters of Amsterdam. "Before departure they will strip the Jewish quarter, which is very rich, waiting for the time when the Cafilas and the Jews from Flanders come with very interested ships, and they will hand everything over to Your Majesty; and the other estates of Dutch and French merchants, which are usually of consideration". In exchange for this loot and their ships the king would give them 200 pounds of gold.
The document was signed by four main horncheros who, in Moorish style, mixed Christian and Arabic names: Mahamet ben Abdelkader, governor of the Kasbah, the caid Bexer Brahin of Bargas and the scribes Mumamet Blanco and Musa Santiago.
Negotiations were initiated but these did not prosper, among other reasons because in 1636 internal fighting returned, in which the kingdom of England intervened, whose ships bombarded the Kasbah in 1637 in support of the indigenous faction of the Marabutus. After 1640 the republic fell under the control of the Dilaites, Berbers from the upper Muluya valley.[19]
Decline
editIn 1641 the Zawiya Dila'iya, which controlled much of Morocco, imposed a religious hegemony over Salé and its parent republic.[20] By the early 1660s the republic was embroiled in war with the Zawiya, and eventually, in June 1668, Sultan Moulay al-Rashid of the Alaouite dynasty, which still rules Morocco into the 21st century, vanquished the Dilaites and Khadir Ghaïlan's influence and ended the republic's independence.[21]
Piracy
editPiracy in Salé began with the arrival of the Moors from Spain, whose wealth allowed them to acquire some ships. With them they traveled the seas, approaching mainly Spanish ships, giving 10% of their loot (both riches and captives) to the Saadians, before they successfully rebelled against the authority of the Emperor of Morocco.[22]
Murad Reis led an expedition into the English Channel in 1622.[23] In 1625 the Salé Rovers carried off captives from Plymouth in England;[24][25] in 1626 five ships were seized off the coast of Wales;[24][25] in 1627 they reached Iceland and sacked the city of Reykjavik[24][26] and raided the fishing village of Grindavík, in what is known as the Turkish Abductions.[27] Their ships then sailed to Bessastaðir, home of the Danish-Norwegian governor of Iceland, to raid but were unable to make a landing.[28] They also captured the island of Lundy in the Bristol Channel and held it for five years, using it as a base for raiding expeditions.[29] A great deal of activity was centered in the waters between England and Ireland.[25] In the Newfoundland banks the Salétin fleet captured more than 40 fishing vessels in the space of two years, and in 1624 a dozen or so ships from Salé appeared on the coasts off Acadia or Nova Scotia.[24][30] In 1631 Murad Reis led the Sack of Baltimore in Ireland.[31]
European agents, sent mostly to deal with questions arising from piracy or connected with commerce, dealt directly with the Andalusians, From 1643 there was a Dutch consul in Salé, and in 1648 the French government appointed a substantive consul to reside there, after having been satisfied since 1629 with having a merchant living in Marseille act as consul while having an agent in Salé.[32]
Legacy
editPiracy, although in decline as was the commercial activity of the city, remained in Salé long after the republic ceased to exist.[33] The attempt of Sidi Mohammed III (1757–1790) to officially revive piracy only accelerated the decline of the city and its corsair activity. The foundation of Mogador in 1760, as a better equipped city to the needs of modern piracy, was a fatal blow to the port of the Bou Regreg.[34] In 1818 Sultan Moulay Slimane officially renounced the holy war and liquidated the Sherifian Navy, definitively putting an end to Salé as a corsair city.[34]
The descendants of Brahim Vargas are the current Bargach of Rabat, which was, and continues to be, an influential family in the Moroccan capital.[10] The Vargas/Bargach saga has remained linked to the government of Rabat for nearly four hundred years.[9]
In popular culture
editThe character Robinson Crusoe, in Daniel Defoe's novel of the same name, spends time in captivity of the local pirates and at last sails off to liberty from the mouth of the Salé river.[35]
The anarchist writer Peter Lamborn Wilson devotes to the Republic of Salé a major part of his 1995 book Pirate Utopias: Moorish Corsairs & European Renegadoes.[36] In Wilson's view, such pirate enclaves as Salé were early forms of autonomous proto-anarchist societies in that they operated beyond the reach of governments and embraced unrestricted political freedom.
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Coindreau 2006, p.43-44
- ^ Barnaby Rogerson, « The Sallee Rovers » Archived 29 December 2012 at the Wayback Machine, in travelintelligence.com
- ^ a b Maziane 2007, p.116
- ^ a b c (in French) Leïla Maziane, « Salé au XVIIe siècle, terre d’asile morisque sur le littoral Atlantique marocain », in Cahiers de la Méditerranée, no 79, 2009
- ^ Saïd Mouline (August 2008). "Rabat, Salé – Holy Cities of the Two Banks". In Salma K. Jayyusi (ed.). The City in the Islamic World, Volume 94/1 & 94/2. Vol. 1. Renata Holod, Attilio Petruccioli, Andre Raymond. BRILL. pp. 652–653. ISBN 978-90-04-16240-2.
- ^ Coindreau 2006, p.42
- ^ Coindreau 2006, p.43
- ^ Leïla Maziane (2008). Salé et ses corsaires, 1666-1727 (in French). Publication Univ Rouen Havre. pp. 69–70. ISBN 978-2-87775-832-1.
- ^ a b "Rabat/Salé, la conquête pirate - LeMonde.fr". Le Monde (in French). Archived from the original on 19 January 2011. Retrieved 19 May 2023.
- ^ a b "Moriscos de Hornachos y República de Rabat". archive.wikiwix.com. Retrieved 19 May 2023.
- ^ "Voyage - Actualités, vidéos et infos en direct". Le Monde.fr (in French). Retrieved 28 February 2023.
- ^ Wilson, Peter Lamborn (2003). Pirate Utopias: Moorish Corsairs & European Renegadoes. Autonomedia. ISBN 978-1-57027-158-8.
- ^ a b "Murad Rais", p. 98
- ^ a b Andrews, Kenneth R. (26 April 1991). Ships, Money and Politics: Seafaring and Naval Enterprise in the Reign of Charles I. CUP Archive. ISBN 978-0-521-40116-6.
- ^ Maziane 2007, p.59
- ^ Hachim, Mouna (9 November 2017). "L'insolite république indépendante du Bouregreg". L'Economiste. Archived from the original on 9 November 2017. Retrieved 19 May 2023.
- ^ Coindreau 2006, p.48
- ^ Coindreau 2006, p.44-45 & 49-50
- ^ a b Domínguez Ortiz, Antonio; Vincent, Bernard (1993). Historia de los moriscos: vida y tragedia de una minoría. Alianza Universidad. Madrid: Alianza ed. ISBN 978-84-206-2415-0.
- ^ Mojuetan, B. A. (1995). History and Underdevelopment in Morocco: The Structural Roots of Conjuncture. Lit. ISBN 978-3-89473-697-2.
- ^ Roger Coindreau, 2006, p. 53
- ^ Dan 1649, p. 205-206
- ^ Pennell, C. R. (2003). Morocco: From Empire to Independence. Oneworld. p. 95. ISBN 978-1-85168-634-6.
- ^ a b c d "Murad Rais", p.151
- ^ a b c Coindreau 2006, p.132
- ^ Coindreau 2006, p.76
- ^ Þorsteinn Helgason. "Hvað gerðist í Tyrkjaráninu?". Vísindavefurinn (in Icelandic). Retrieved 10 June 2019.
- ^ Þorsteinn Helgason. "Hvað gerðist í Tyrkjaráninu?". Vísindavefurinn (in Icelandic). Retrieved 10 June 2019.
- ^ Konstam, Angus (2008). Piracy: The Complete History. Osprey Publishing. pp. 90–91. ISBN 978-1-84603-240-0. Retrieved 29 April 2011.
- ^ Coindreau 2006, p.133
- ^ Ó Domhnaill, Rónán Gearóid (2015). Fadó Fadó: More Tales of Lesser-Known Irish History. Troubador Publishing Ltd. p. 34. ISBN 9781784622305. Retrieved 15 June 2015.
The truth soon emerged and he was hanged from the cliff top outside the village for his conspiracy
- ^ Abun-Nasr, Jamil M. (1987). A History of the Maghrib in the Islamic Period. Cambridge University Press. pp. 224–225. ISBN 9780521337670.
- ^ Coindreau 2006, p.57
- ^ a b Coindreau 2006, p.58
- ^ "Robinson's Captivity at Sallee", The life and surprising adventures of Robinson Crusoe, p. 14, Retrieved 30 September 2009.
- ^ Wilson, Peter (2003). Pirate Utopias: Moorish Corsairs & European Renegadoes. Autonomedia. ISBN 1-57027-158-5.
Bibliography
edit- (in French) Leïla Maziane, « Salé et ses corsaires, 1666-1727: un port de course marocain au XVIIe siècle », Publication Université de Rouen Havre, 2007 (ISBN 978-2-84133-282-3)
- (in French) Pierre Dan, Histoire de Barbarie et de ses corsaires, Pierre Rocolet, 1649
- (in French) Roger Coindreau, « Les Corsaires de Salé », La Croisée des chemins, 2006 (orig. ed. 1948) (ISBN 978-9981-896-76-5)
