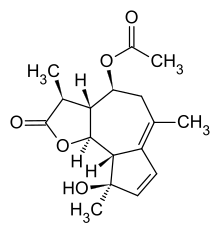
Matricin is a sesquiterpene. It can be extracted from flower of chamomille (Matricaria chamomilla).[1] Matricin is colorless.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(11S)-4-Hydroxy-12-oxo-6α,12-epoxyguaia-1(10),2-dien-8α-yl acetate
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(3S,3aR,4S,9R,9aS,9bS)-9-Hydroxy-3,6,9-trimethyl-2-oxo-2,3,3a,4,5,9,9a,9b-octahydroazuleno[4,5-b]furan-4-yl acetate | |
| Other names
Proazulene; Prochamazulene
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.044.881 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H22O5 | |
| Molar mass | 306.358 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Chamazulene, a blue-violet derivative of azulene, found in a variety of plants including in chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla), wormwood (Artemisia absinthium) and yarrow (Achillea millefolium) is biosynthesized from matricin.

Biosynthesis of chamazulene (3) from matricin (1) via a decarboxylative pathway.
References
edit- ^ Ramadan M, Goeters S, Watzer B, Krause E, Lohmann K, Bauer R, Hempel B, Imming P (2006). "Chamazulene carboxylic acid and matricin: a natural profen and its natural prodrug, identified through similarity to synthetic drug substances". J Nat Prod. 69 (7): 1041–1045. doi:10.1021/np0601556. PMID 16872141.
