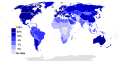
The Internet PortalThe Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a network of networks that consists of private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope, linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless, and optical networking technologies. The Internet carries a vast range of information resources and services, such as the interlinked hypertext documents and applications of the World Wide Web (WWW), electronic mail, internet telephony, and file sharing. The origins of the Internet date back to research that enabled the time-sharing of computer resources, the development of packet switching in the 1960s and the design of computer networks for data communication. The set of rules (communication protocols) to enable internetworking on the Internet arose from research and development commissioned in the 1970s by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) of the United States Department of Defense in collaboration with universities and researchers across the United States and in the United Kingdom and France. The ARPANET initially served as a backbone for the interconnection of regional academic and military networks in the United States to enable resource sharing. The funding of the National Science Foundation Network as a new backbone in the 1980s, as well as private funding for other commercial extensions, encouraged worldwide participation in the development of new networking technologies and the merger of many networks using DARPA's Internet protocol suite. The linking of commercial networks and enterprises by the early 1990s, as well as the advent of the World Wide Web, marked the beginning of the transition to the modern Internet, and generated sustained exponential growth as generations of institutional, personal, and mobile computers were connected to the internetwork. Although the Internet was widely used by academia in the 1980s, the subsequent commercialization of the Internet in the 1990s and beyond incorporated its services and technologies into virtually every aspect of modern life. (Full article...) Selected article
YouTube is a video sharing website where users can upload, view and share video clips. YouTube was created in mid-February 2005 by three former PayPal employees. The San Bruno-based service uses Adobe Flash technology to display a wide variety of video content, including movie clips, TV clips and music videos, as well as amateur content such as videoblogging and short original videos. In October 2006, Google Inc. announced that it had reached a deal to acquire the company for US$1.65 billion in Google stock. The deal closed on November 13, 2006. Unregistered users can watch most videos on the site, while registered users are permitted to upload an unlimited number of videos. Some videos are available only to users of age 18 or older (e.g. videos containing potentially offensive content). The uploading of pornography or videos containing nudity is prohibited. Related videos, determined by title and tags, appear onscreen to the right of a given video. In YouTube's second year, functions were added to enhance user ability to post video 'responses' and subscribe to content feeds. Few statistics are publicly available regarding the number of videos on YouTube. However, in July 2006 the company revealed that more than 100 million videos were being watched every day, and 2.5 billion videos were watched in June 2006.
Selected picture "All your base are belong to us" (often shortened to "All Your Base", "AYBABTU", or simply "AYB") is a broken English phrase (see Engrish) that sparked an Internet phenomenon in 2001 and 2002, with the spread of a Flash animation that depicted the slogan. The text is taken from the opening cut scene of the European Sega Mega Drive version of Zero Wing, a Japanese video game by Toaplan.  Beyond the First Amendment: The Politics of Free Speech and Pluralism is a book about freedom of speech and the First Amendment to the United States Constitution, written by author Samuel Peter Nelson. It was published by Johns Hopkins University Press in 2005. In it, Nelson discusses how the more general notion of free speech differs from that specifically applied to the First Amendment in American law. The book was positively received in reviews from academic and legal journals. Choice: Current Reviews for Academic Libraries recommended the book due to its thought-provoking propositions, and a review in The Journal of Politics described it as "a nice effort to explore free speech issues not covered by the First Amendment or constitutional law". A review in the journal Political Communication concluded of the author's argumentation: "His is indeed a theory fraught with possibilities both favorable and unfavorable to an expanded scope for the contents of free speech". Law and Politics Book Review concluded "Beyond the First Amendment is an intriguing and important contribution to the literature on free speech". (Full article...) WikiProjects
Did you know (auto-generated) -
Selected biography
Sergey Brin (Russian: Сергей Михайлович Брин; born August 21, 1973) is a Russian-born American entrepreneur who co-founded Google with Larry Page. Brin currently holds the position of President of Technology at Google and has a net worth estimated at $18.5 billion as of March 9, 2007, making him the 26th richest person in the world and the 5th richest person in the United States, together with Larry Page. He is also the fourth-youngest billionaire in the world. After graduating from the University of Maryland, Brin received a graduate fellowship from the National Science Foundation, which allowed him to study for his master's degree in computer science at Stanford University. Brin received his master's degree in August 1995 ahead of schedule in the process of his Ph.D. studies. Although he is still enrolled in the Stanford doctoral program, Brin has suspended his Ph.D. studies indefinitely while he is working at Google. Brin met Larry Page while they were both graduate students at Stanford, and they authored a paper together entitled a paper entitled "The Anatomy of a Large-Scale Hypertextual Web Search Engine."
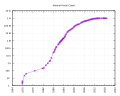
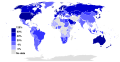
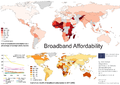
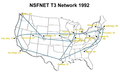
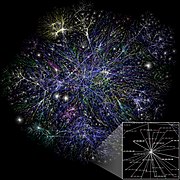
General images -The following are images from various internet-related articles on Wikipedia.
Selected quoteMain topics
Featured contentCategoriesRelated portalsThings you can do
Associated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Wikipedia's portals |