This article needs additional citations for verification. (January 2021) |
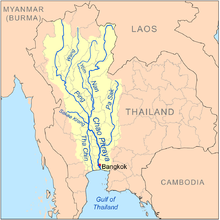
The Pa Sak River (Thai: แม่น้ำป่าสัก, RTGS: Maenam Pa Sak, IPA: [mɛ̂ːnáːm pàː sàk], Pronunciation) is a river in central Thailand. The river originates in the Phetchabun Mountains, Dan Sai District, Loei Province, and passes through Phetchabun Province as the backbone of the province. It then passes through the eastern part of Lopburi Province and Saraburi Province, until it joins the Lopburi River northeast of Ayutthaya Island, before it runs into the Chao Phraya River southeast of Ayutthaya near Phet Fortress. It has a length of 513 km (319 mi) and drains a watershed of 16,291 km2 (6,290 sq mi). The annual discharge is 2.4 km3 (0.58 cu mi).
| Pa Sak River (แม่น้ำป่าสัก) | |
|---|---|
 The Pa Sak River flowing east of Ayuttaya's old city | |
 | |
| Location | |
| Country | Thailand |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | Phetchabun Mountains |
| Mouth | |
• location | Chao Phraya River at Ayutthaya Island |
| Length | 513 km (319 mi) |
| Basin size | 16,291 km2 (6,290 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| • average | 2.4 km3 (0.58 cu mi)/yr |
The valley of the Pa Sak through the Phetchabun mountains is a dominant feature of Phetchabun Province. Water levels vary seasonally. To address drought problems in the lower Pa Sak valley, in 1994 the construction of the Pa Sak Cholasit Dam (เขื่อนป่าสักชลสิทธิ์) in Lopburi Province was built. The 4,860-meter (15,940 ft) wide and 36.5-meter (120 ft) high dam retains 0.785 km3 (0.188 cu mi) of water. The dam also supplies about 6.7 MW of electricity.
Tributaries
editTributaries of the Pa Sak include the Lopburi River, Khlong Muak Lek, Huai Nam Phung, Huai Pa Daeng, Khlong Lam Kong, Lam Sonthi, Khlong Wang Chomphu, Khlong Huai Na, Huai Nam Chun, Huai Nam Duk, Huai Khon Kaen, Huai Yai, Khlong Saduang Yai, Khlong Ban Bong, Khlong Tarang, and Lam Phaya Klang.
Pa Sak Basin
editThe Pa Sak drains an area of 16,291 square kilometres (6,290 sq mi).[1] The Pa Sak Basin is part of the Chao Phraya watershed.
Tied with people in terms of lifestyle
editIn addition to being used as a waterway, course of the Pa Sak River, no less than 60 years ago, especially in Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya Province, it was well known for its Khanom chin, traditional Thai vermicelli. So, that it was aso known as Khlong Khanom chin. Additionally, the water in the canal was clean and clear, suitable for consumption and use. It was habitat to the zig-zag eel, an eel-like freshwater fish that were a delicacy.[2]
Around the same time, Wat Mondop across from the Hua Ro quarter was an important pier because people would board boats here for Bangkok. All around this spot, there were many rafts and boats selling Khanom chin as well as other Khanom Thai, Thai snacks and sweets, including Khanom thuai, Khanom thuai fu, Khanom mo kaeng, Khanom tan, Khanom kluai, Khao lam, Khao mak, Lot chong, Pakrim khai tao, Thong yip and Thong yod, etc. Many of these were made by people living along the river, where it was referred to as Khlong Hantra.
Moreover, in terms of folk traditions, there is a natural khlong that links Khlong Bang Kaeo at Maha Rat District and the river at Nakhon Luang District. Set on its banks are two very important Buddhist temples, Wat Khot Khema Pitaram and Wat Tan En, which are actually gathering places for flying foxes. During the 11th and 12th Thai lunar months, following the Buddhist retreat, Wan Ok Phansa, when the waters are high and the paddies flood, it used to be a time for courting, or boat song festivals along with boat races between the two temples. Now, though, only the boat racing tradition is still preserved annually.
References
edit- ^ "Basins of Thailand". Retrieved 2008-03-29.[dead link]
- ^ "ฟื้นชีวิต 'คลองขนมจีน' เนสท์เล่ น้ำรักษ์น้ำ ตามหาปลากระทิงที่หายไป" [Revive ‘Khlong Khanom chin’ Nestle, a water conservationist, searches for the lost zig-zag eel]. Matichon (in Thai). 2024-12-03. Retrieved 2023-12-01.