The tropical and subtropical dry broadleaf forest is a habitat type defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature and is located at tropical and subtropical latitudes.[1] Though these forests occur in climates that are warm year-round, and may receive several hundred millimeters of rain per year, they have long dry seasons that last several months and vary with geographic location. These seasonal droughts have great impact on all living things in the forest.
Deciduous trees predominate in most of these forests, and during the drought a leafless period occurs, which varies with species type. Because trees lose moisture through their leaves, the shedding of leaves allows trees such as teak and mountain ebony to conserve water during dry periods. The newly bare trees open up the canopy layer, enabling sunlight to reach ground level and facilitate the growth of thick underbrush. Trees on moister sites and those with access to ground water tend to be evergreen. Infertile sites also tend to support evergreen trees. Three tropical dry forest ecoregions, the East Deccan dry evergreen forests, the Sri Lanka dry-zone dry evergreen forests, and the Southeastern Indochina dry evergreen forests, are characterized by evergreen trees.[1]
Though less biologically diverse than rainforests, tropical dry forests are home to a wide variety of wildlife including monkeys, deer, large cats, parrots, various rodents, and ground dwelling birds. Mammalian biomass tends to be higher in dry forests than in rain forests, especially in Asian and African dry forests. Many of these species display extraordinary adaptations to the difficult climate.[1]
This biome is alternately known as the tropical and subtropical dry forest biome or the tropical and subtropical deciduous forest biome.
Geographical variation
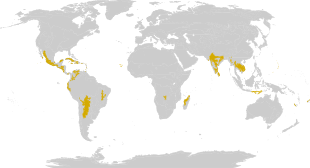
editDry forests tend to exist in the drier areas north and south of the tropical rainforest belt, south or north of the subtropical deserts, generally in two bands: one between 10° and 20°N latitude and the other between 10° and 20°S latitude. The most diverse dry forests in the world occur in western and southern Mexico and in the Bolivian lowlands.[2] The dry forests of the Pacific Coast of northwestern South America support a wealth of unique species due to their dry climate. The Maputaland-Pondoland bushland and thickets along the east coast of South Africa are diverse and support many endemic species. The dry forests of central India and Indochina are notable for their diverse large vertebrate faunas. Madagascar dry deciduous forests and New Caledonia dry forests are also highly distinctive (pronounced endemism and a large number of relictual taxa) for a wide range of taxa and at higher taxonomic levels.[1] Trees use underground water during the dry seasons.
Biodiversity patterns and requirements
editSpecies tend to have wider ranges than moist forest species, although in some regions many species do display highly restricted ranges; most dry forest species are restricted to tropical dry forests, particularly in plants; beta diversity and alpha diversity high but typically lower than adjacent moist forests.[1]
Effective conservation of dry broadleaf forests requires the preservation of large and continuous areas of forest. Large natural areas are required to maintain larger predators and other vertebrates, and to buffer sensitive species from hunting pressure. The persistence of riparian forests and water sources is critical for many dry forest species. Large swathes of intact forest are required to allow species to recover from occasional large events, like forest fires.[1]
Dry forests are highly sensitive to excessive burning and deforestation; overgrazing and invasive species can also quickly alter natural communities; restoration is possible but challenging, particularly if degradation has been intense and persistent.[1]
Ecoregions
editAfrotropical realm
editAustralasian realm
edit- Lesser Sundas deciduous forests
- New Caledonia dry forests
- Sumba deciduous forests
- Timor and Wetar deciduous forests
Indomalayan realm
edit- Central Deccan Plateau dry deciduous forests
- Central Indochina dry forests
- Chota Nagpur Plateau
- East Deccan dry evergreen forests
- Irrawaddy dry forests
- Khathiar–Gir dry deciduous forests
- Narmada Valley dry deciduous forests
- Northern dry deciduous forests
- South Deccan Plateau dry deciduous forests
- Southeastern Indochina dry evergreen forests
- Southern Vietnam lowland dry forests
- Sri Lanka dry-zone dry evergreen forests
Nearctic realm
editNeotropical realm
edit- Apure–Villavicencio dry forests
- Atlantic dry forests
- Bahamian dry forests
- Bajío dry forests
- Balsas dry forests
- Bolivian montane dry forests
- Cayman Islands dry forests
- Central American dry forests
- Chiapas Depression dry forests
- Chiquitano dry forests
- Cuban dry forests
- Ecuadorian dry forests
- Gran Chaco
- Hispaniolan dry forests
- Jalisco dry forests
- Jamaican dry forests
- Lara–Falcón dry forests
- Leeward Islands dry forests
- Magdalena Valley dry forests
- Maracaibo dry forests
- Marañón dry forests
- Panamanian dry forests
- Patía Valley dry forests
- Puerto Rican dry forests
- Revillagigedo Islands
- Sierra de la Laguna dry forests
- Sinaloan dry forests
- Sinú Valley dry forests
- Southern Pacific dry forests
- Trinidad and Tobago dry forests
- Tumbes–Piura dry forests
- Veracruz dry forests
- Windward Islands dry forests
- Yucatán dry forests
Oceanian realm
editSee also
editReferences
edit- ^ a b c d e f g This article incorporates text available under the CC BY-SA 3.0 license. World Wide Fund for Nature. "Tropical and Subtropical Dry Broadleaf Forest Ecoregions". Archived from the original on 2012-04-25. Retrieved 2012-09-25.
- ^ Gentry, A (1993). "Diversity and floristic composition of Neotropical dry forests". In Mooney, H; Bullock, S; Medina, E (eds.). Tropical deciduous forest ecosystems. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. pp. 146–194.
- "Deep-rooted Plants Have Much Greater Impact On Climate Than Experts Thought". Science Daily. 2006-01-13.
External links
edit- Media related to Tropical & Subtropical Dry Broadleaf Forests Biome at Wikimedia Commons
- The Tropical Dry Forest of Costa Rica