The western hoolock gibbon (Hoolock hoolock) is a primate from the gibbon family, Hylobatidae. The species is found in Assam, Mizoram, and Meghalaya in India, Bangladesh, and Myanmar west of the Chindwin River.[4]
| Western hoolock gibbon | |
|---|---|

| |
| A female in the foreground, and a male in the background | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Primates |
| Suborder: | Haplorhini |
| Infraorder: | Simiiformes |
| Family: | Hylobatidae |
| Genus: | Hoolock |
| Species: | H. hoolock
|
| Binomial name | |
| Hoolock hoolock | |
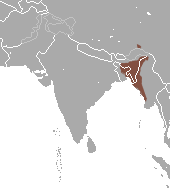
| |
| Western hoolock gibbon range | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Simia hoolock protonym | |
Classification
editMootnick and Groves[5] stated that hoolock gibbons do not belong in the genus Bunopithecus, and placed them in a new genus, Hoolock. This genus was argued to contain two and later three distinct species, which were previously thought to be subspecies: H. hoolock, H. leuconedys, and H. tianxing. A larger evolutionary distance was later found to exist between these three species and the white-handed gibbons than between bonobos and chimpanzees.[6]
A new subspecies of the western hoolock gibbon has been described recently from northeastern India, which has been named the Mishmi Hills hoolock gibbon, H. h. mishmiensis.[7]
Vocalisation
editLike other gibbons, hoolock gibbon pairs produce a loud, elaborate song, usually as a duet from the forest canopy, in which younger individuals of the family group may join. The song includes an introductory sequence, an organising sequence, and a great call sequence, with the male also contributing to the latter (unlike in some other gibbon species).[8]
Habitat and Diet
editIn India and Bangladesh, the western hoolock gibbon is found where the canopy is contiguous, broad-leaved, wet evergreen and mixed evergreen forests, including dipterocarp forests and often in mountainous terrain. The species is an important seed disperser; its diet includes mostly ripe fruits, with some flowers, leaves, and shoots.[9] The western hoolock gibbon also feeds on non-plant items such as silkworms, ants, and various other insect species.[9] During the monsoon season of northeast India, insects are recorded to be this species' second preferred food item, behind Artocarpus chaplasha, a fruit bearing tree in the same genus of jack fruit.[10][11]
Conservation
editNumerous threats exist for western hoolock gibbons in the wild, and they are now entirely dependent on human action for their survival. Threats include habitat encroachment by humans, forest clearance for tea cultivation, the practice of jhuming (slash-and-burn cultivation), hunting for food and "medicine", capture for trade, and forest degradation.[1]
Since the 1980s, western hoolock gibbon numbers are estimated to have dropped from more than 100,000 (Assam alone was estimated to have around 80,000 in the early 1970s) to less than 5,000 individuals (a decline of more than 90%).[12] In 2009 it was considered to be one of the 25 most endangered primates,[13] though it has been dropped from the later editions of the list,[14] and is rated as endangered by the IUCN.[1]
There are multiple conservation agencies that work to protect the western hoolock gibbon's habitat. A few organizations that help to fund the protection of their habitats are World Land Trust [15] and Gibbon Conservation Alliance.[16]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ a b c Brockelman, W.; Molur, S.; Geissmann, T. (2019). "Hoolock hoolock". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T39876A17968083. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T39876A17968083.en. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ^ "Appendices | CITES". cites.org. Retrieved 14 January 2022.
- ^ Harlan, Richard (1834). "Description of a Species of Orang, from the North-Eastern Province of British East India, Lately the Kingdom of Assam". Transactions of the American Philosophical Society. 4: 52–59. doi:10.2307/1004829. JSTOR 1004829.
- ^ Groves, C. P. (1967). "Geographic variation in the hoolock or white-browed gibbon (Hylobates hoolock harlan 1834)". Folia Primatologica. 7 (3–4): 276–283. doi:10.1159/000155125. PMID 5626313.
- ^ Mootnick, A. R. & C. P. Groves (2005). "A new generic name for the hoolock gibbon (Hylobatidae)". Int. J. Primatol. 26 (4): 971–976. doi:10.1007/s10764-005-5332-4. S2CID 8394136.
- ^ Mootnick, A. R. (2006). "Gibbon (Hylobatidae) species identification recommended for rescue or breeding centers". Primate Conserv. 21: 103–138. doi:10.1896/0898-6207.21.1.103. S2CID 86331056.
- ^ Choudhury, A. U. (2013). "Description of a new subspecies of hoolock gibbon Hoolock hoolock from North East India". The Newsletter & Journal of the Rhino Foundation for Nat. In NE India. 9: 49–59.
- ^ Kakati, Kashmira; Alfred, J. R. B.; Sati, J. P. (2013). "Hoolock gibbon". In Johnsingh, A. J. T.; Manjrekar, N. (eds.). Mammals of South Asia. Vol. 1. Hyderabad: Universities Press. pp. 332–354. ISBN 978-81-7371-590-7.
- ^ a b Borah, Mrigakhi; Devi, Ashalata; Kumar, Awadhesh (11 September 2017). "Diet and feeding ecology of the western hoolock gibbon (Hoolock hoolock) in a tropical forest fragment of Northeast India". Primates. 59 (1): 31–44. doi:10.1007/s10329-017-0627-6. ISSN 0032-8332. PMID 28894949. S2CID 12152723.
- ^ Borah; Mrigakhi; Asglata, Devi; Awadhesh, Kumar (2014). "Feeding on Non-Plant Food Items by Western Hoolock Gibbon (Hoolock Hoolock)" (PDF). Current Science (Bangalore). 107 (10): 1657–660 – via Current Science.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Ray, Parimal Chandra; Kumar, Awadhesh; Devi, Ashalata; Krishna, Murali C.; Khan, M. L.; Brockelman, W. Y. (2015). "Habitat Characteristics and Their Effects on the Density of Groups of Western Hoolock Gibbon (Hoolock hoolock) in Namdapha National Park, Arunachal Pradesh, India". International Journal of Primatology. 36 (3): 445–459. doi:10.1007/s10764-015-9834-4. ISSN 0164-0291. S2CID 7098362.
- ^ "Western Hoolock Gibbon, Hoolock hoolock". Retrieved 10 March 2008.
- ^ Mittermeier, R.A.; Wallis, J.; Rylands, A.B.; Ganzhorn, J.U.; Oates, J.F.; Williamson, E.A.; Palacios, E.; Heymann, E.W.; Kierulff, M.C.M.; Long, Yongcheng; Supriatna, J.; Roos, C.; Walker, S.; Cortés-Ortiz, L.; Schwitzer, C., eds. (2009). Primates in Peril: The World's 25 Most Endangered Primates 2008–2010 (PDF). Illustrated by S.D. Nash. Arlington, VA: IUCN/SSC Primate Specialist Group (PSG), International Primatological Society (IPS), and Conservation International (CI). pp. 1–92. ISBN 978-1-934151-34-1.
- ^ Mittermeier, R.A.; Schwitzer, C.; Rylands, A.B.; Taylor, L.A.; Chiozza, F.; Williamson, E.A.; Wallis, J., eds. (2012). Primates in Peril: The World's 25 Most Endangered Primates 2012–2014 (PDF). Illustrated by S.D. Nash. IUCN/SSC Primate Specialist Group (PSG), International Primatological Society (IPS), Conservation International (CI), and Bristol Conservation and Science Foundation. pp. 1–40. ISBN 978-1-934151-69-3.
- ^ Farrows. "WESTERN HOOLOCK GIBBON". World Land Trust. Retrieved 11 December 2023.
- ^ "Gibbon Conservation Alliance - Projects". www.gibbonconservation.org. Retrieved 11 December 2023.
