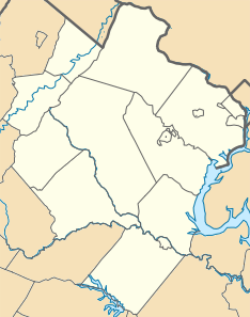
Kings Park is a census-designated place (CDP) in the eastern United States in Fairfax County, Virginia, southwest of Washington D.C. The population as of the 2010 census was 4,333.[1]
Kings Park, Virginia | |
|---|---|
 Houses in Kings Park in 2016 | |
| Coordinates: 38°48′12″N 77°14′36″W / 38.80333°N 77.24333°W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Virginia |
| County | Fairfax |
| Area | |
• Total | 1.33 sq mi (3.45 km2) |
| • Land | 1.31 sq mi (3.38 km2) |
| • Water | 0.02 sq mi (0.06 km2) |
| Elevation | 345 ft (105 m) |
| Population (2020) | |
• Total | 4,537 |
| • Density | 3,316/sq mi (1,280.4/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern (EST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| FIPS code | 51-42664[1] |
| GNIS feature ID | 1493167[2] |
A suburban community begun 64 years ago in early 1960, Kings Park is located a few miles west of the Capital Beltway and Annandale, near the junction of Braddock, Burke Lake, and Rolling roads in the Springfield area (ZIP code 22151). Richmarr Construction designed Kings Park as a planned community, with a park at its center, an elementary school, and an adjacent namesake shopping center.
History
editOwnership of the properties can be traced to Lord Culpeper who transferred the lands which now include Kings Park and Ravensworth Farm to William Fitzhugh in 1690. The land passed through Martha Custis, the wife of George Washington, to her son George Custis, then to his daughter, Mary Randolph Custis, who married Robert E. Lee at Arlington when he was a young officer in the U.S Army.
After the outbreak of the Civil War, Mary Custis Lee moved to relative safety at the Ravensworth Farm. Ownership of the property remained in the Lee family until World War I, when the land was sold to the Flatfelter Pulpwood Company. The company removed most of the softwood trees but retrained the hardwood, many of which are still in abundance in Kings Park.
In the early 1950s the properties were sold to a Baltimore investment firm, and those which were to become Kings Park were later sold to Richmarr Construction Corporation. Kings Park, as we know it today, began in March 1960 with a 200-acre (81 ha) wooded entrance of Kings Park Drive from Braddock Road.
A number of landmarks in and around Kings Park still retain vestiges of their early history.
Geography
editKings Park is located southeast of the center of Fairfax County, northwest of Springfield, southwest of Annandale, and southeast of the city of Fairfax. The Kings Park CDP is bordered to the east by Ravensworth and North Springfield, to the north by Wakefield, to the west by Burke, and to the south by West Springfield. It is 1.5 miles (2.4 km) west of the Braddock Road interchange with the Capital Beltway and 17 miles (27 km) southwest of downtown Washington, D.C. The CDP border follows Braddock Road to the north, Accotink Creek to the east, the VRE Manassas Line to the south, and Rolling Road to the west.[3]
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the Kings Park CDP has a total area of 1.33 square miles (3.45 km2), of which 1.31 square miles (3.38 km2) is land and 0.02 square miles (0.06 km2), or 1.78%, is water.[1]
Education
editFairfax County Public Schools operates Kings Park Elementary School in Kings Park CDP.[4][5]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ a b c "Geographic Identifiers: 2010 Demographic Profile Data (G001): Kings Park CDP, Virginia". U.S. Census Bureau, American Factfinder. Retrieved October 6, 2016.[dead link]
- ^ U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Kings Park, Virginia
- ^ "TIGERweb". TIGER Web Viewer. United States Census Bureau. Retrieved December 14, 2019.
- ^ "2010 CENSUS - CENSUS BLOCK MAP: Kings Park CDP, VA" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved December 5, 2020.
- ^ "Home". Kings Park Elementary School. Retrieved December 5, 2020.
5400 Harrow Way Springfield, VA 22151