A cytotoxic T cell (also known as TC, cytotoxic T lymphocyte, CTL, T-killer cell, cytolytic T cell, CD8+ T-cell or killer T cell) is a T lymphocyte (a type of white blood cell) that kills cancer cells, cells that are infected by intracellular pathogens (such as viruses or bacteria), or cells that are damaged in other ways.[1]
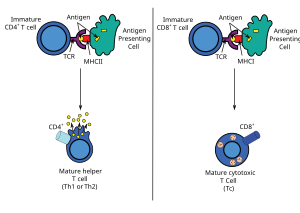
Most cytotoxic T cells express T-cell receptors (TCRs) that can recognize a specific antigen. An antigen is a molecule capable of stimulating an immune response and is often produced by cancer cells, viruses, bacteria or intracellular signals. Antigens inside a cell are bound to class I MHC molecules, and brought to the surface of the cell by the class I MHC molecule, where they can be recognized by the T cell. If the TCR is specific for that antigen, it binds to the complex of the class I MHC molecule and the antigen, and the T cell destroys the cell.
In order for the TCR to bind to the class I MHC molecule, the former must be accompanied by a glycoprotein called CD8, which binds to the constant portion of the class I MHC molecule. Therefore, these T cells are called CD8+ T cells.
The affinity between CD8 and the MHC molecule keeps the TC cell and the target cell bound closely together during antigen-specific activation. CD8+ T cells are recognized as TC cells once they become activated and are generally classified as having a pre-defined cytotoxic role within the immune system. However, CD8+ T cells also have the ability to make some cytokines, such as TNF-α and IFN-γ, with antitumour and antimicrobial effects.
Development
editThe immune system must recognize millions of potential antigens. There are fewer than 30,000 genes in the human body, so it is impossible to have one gene for every antigen. Instead, the DNA in millions of white blood cells in the bone marrow is shuffled to create cells with unique receptors, each of which can bind to a different antigen. Some receptors bind to tissues in the human body itself, so to prevent the body from attacking itself, those self-reactive white blood cells are destroyed during further development in the thymus, in which iodine is necessary for its development and activity.[2]
TCRs have two parts, usually an alpha and a beta chain. (Some TCRs have a gamma and a delta chain. They are inherent to act against stress and form part of the epithelial barrier[3]). Hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow migrate into the thymus, where they undergo V(D)J recombination of their beta-chain TCR DNA to form a developmental form of the TCR protein, known as pre-TCR. If that rearrangement is successful, the cells then rearrange their alpha-chain TCR DNA to create a functional alpha-beta TCR complex. This highly-variable genetic rearrangement product in the TCR genes helps create millions of different T cells with different TCRs, helping the body's immune system respond to virtually any protein of an invader. The vast majority of T cells express alpha-beta TCRs (αβ T cells), but some T cells in epithelial tissues (like the gut) express gamma-delta TCRs (gamma delta T cells), which recognize non-protein antigens. The latter are characterised by their ability to recognise antigens that are not presented. In addition, they can recognise microbial toxic shock proteins and self-cell stress proteins.[4] T γδ cells possess a wide functional plasticity after recognising infected or transformed cells, as they are able to produce cytokines (IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-17) and chemokines (IP-10, lymphotactin), trigger cytolysis of target cells (perforins, granzymes...), and interact with other cells, such as epithelial cells, monocytes, dendritic cells, neutrophils and B cells. In some infections, such as human cytomegalovirus, there is a clonal expansion of peripheral γδ T cells that have specific TCRs, indicating the adaptive nature of the immune response mediated by these cells.[5]
T cells with functionally stable TCRs express both the CD4 and CD8 co-receptors and are therefore termed "double-positive" (DP) T cells (CD4+CD8+). The double-positive T cells are exposed to a wide variety of self-antigens in the thymus and undergo two selection criteria:
- positive selection, in which those double-positive T cells that bind to foreign antigen in the presence of self MHC. They will differentiate into either CD4+ or CD8+ depending on which MHC is associated with the antigen presented (MHC1 for CD8, MHC2 for CD4). In this case, the cells would have been presented antigen in the context of MHC1. Positive selection means selecting those TCRs capable of recognizing self MHC molecules.
- negative selection, in which those double-positive T cells that bind too strongly to MHC-presented self antigens undergo apoptosis because they could otherwise become autoreactive, leading to autoimmunity.
Only those T cells that bind to the MHC-self-antigen complexes weakly are positively selected. Those cells that survive positive and negative selection differentiate into single-positive T cells (either CD4+ or CD8+), depending on whether their TCR recognizes an MHC class I-presented antigen (CD8) or an MHC class II-presented antigen (CD4). It is the CD8+ T-cells that will mature and go on to become cytotoxic T cells following their activation with a class I-restricted antigen.
Activation
editThis section may be confusing or unclear to readers. (August 2023) |
Mature T cells go through different stages, depending on the number of times they have been in contact with the antigen. In the first place, naïve T-lymphocytes are an initial stage of T cell residing in the thymus which have not yet encountered an antigen with affinity for its TCR. T cells that have been in contact with the antigen at least once but have subsequently returned to a quiescent or inactive state, are known as memory T cells. This particular stage remains ready to respond again to the specific antigen against which they were stimulated. Finally, when an immune response is triggered, these naive and memory T cells are activated, giving rise to effector T cells that have the capacity to kill pathogens or tumor cells.[6][7]
The threshold for activation of these cells is very high, and the process can occur via two pathways: thymus-independent (by infected APCs) or thymus-dependent (by CD4+ T cells). In the thymus-independent pathway, because the APC is infected, it is highly activated and expresses a large number of co-receptors for coactivation. If APCs are not infected, CD4 cells need to be involved: either to activate the APC by co-stimulation (more common) or to directly activate the Tc cell by secreting IL-2.
If activation occurs, the lymphocyte polarizes its granules towards the site of the synapse and releases them, producing a "lethal hit". At this point, it separates from the target cell, and can move on to another, and another. The target cell dies in about 6 hours, usually by apoptosis.[8]
Class I MHC is expressed by all host cells, except for non-nucleated ones, such as erythrocytes. When these cells are infected with a intracellular pathogen, the cells degrade foreign proteins via antigen processing. These result in peptide fragments, some of which are presented by MHC Class I to the T cell antigen receptor (TCR) on CD8+ T cells.
The activation of cytotoxic T cells is dependent on several simultaneous interactions between molecules expressed on the surface of the T cell and molecules on the surface of the antigen-presenting cell (APC). For instance, consider the two signal model for TC cell activation.
| Signal | T cell | APC | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| First Signal | TCR | peptide-bound MHC class I molecule | There is a second interaction between the CD8 coreceptor and the class I MHC molecule to stabilize this signal. |
| Second Signal | CD28 molecule on the T cell | either CD80 or CD86 (also called B7-1 and B7-2) | CD80 and CD86 are known as costimulators for T cell activation. This second signal can be assisted (or replaced) by stimulating the TC cell with cytokines released from T helper cells. |
A simple activation of naive CD8+ T cells requires the interaction with professional antigen-presenting cells, mainly with matured dendritic cells. To generate longlasting memory T cells and to allow repetitive stimulation of cytotoxic T cells, dendritic cells have to interact with both, activated CD4+ helper T cells and CD8+ T cells.[9][7] During this process, the CD4+ helper T cells "license" the dendritic cells to give a potent activating signal to the naive CD8+ T cells.[10] This licensing of antigen-presenting cells by the CD4+ T helper cells proceeds by signaling between CD154/CD40L on the T helper cell and the CD40 receptor on the antigen-presenting cell during immunological synapse formation.[11]
While in most cases activation is dependent on TCR recognition of antigen, alternative pathways for activation have been described. For example, cytotoxic T cells have been shown to become activated when targeted by other CD8 T cells leading to tolerization of the latter.[12]
Once activated, the TC cell undergoes clonal expansion with the help of the cytokine interleukin 2 (IL-2), which is a growth and differentiation factor for T cells. This increases the number of cells specific for the target antigen that can then travel throughout the body in search of antigen-positive somatic cells.
Effector functions
editWhen exposed to infected/dysfunctional somatic cells, TC cells release the cytotoxins perforin, granzymes, and granulysin. Through the action of perforin, granzymes enter the cytoplasm of the target cell and their serine protease function triggers the caspase cascade, which is a series of cysteine proteases that eventually lead to apoptosis (programmed cell death). This is called a "lethal hit” and allows to observe a wave-like death of the target cells.[13] Due to high lipid order and negatively charged phosphatidylserine present in their plasma membrane, TC cells are resistant to the effects of their perforin and granzyme cytotoxins.[14]
A second way to induce apoptosis is via cell-surface interaction between the TC and the infected cell. When a TC is activated it starts to express the surface protein FAS ligand (FasL)(Apo1L)(CD95L), which can bind to Fas (Apo1)(CD95) molecules expressed on the target cell. However, this Fas-Fas ligand interaction is thought to be more important to the disposal of unwanted T lymphocytes during their development or to the lytic activity of certain TH cells than it is to the cytolytic activity of TC effector cells. Engagement of Fas with FasL allows for recruitment of the death-induced signaling complex (DISC).[15] The Fas-associated death domain (FADD) translocates with the DISC, allowing recruitment of procaspases 8 and 10.[15] These caspases then activate the effector caspases 3, 6, and 7, leading to cleavage of death substrates such as lamin A, lamin B1, lamin B2, PARP (poly ADP ribose polymerase), and DNA-PKcs (DNA-activated protein kinase). The final result is apoptosis of the cell that expressed Fas. CD8 T cells can also show Activation Induced Cell Death or AICD which is mediated by CD3 receptor complex. Recently, a platelet released protein TLT-1 has been shown to induce AICD like cell death in CD8 T cells[16]
The transcription factor Eomesodermin is suggested to play a key role in CD8+ T cell function, acting as a regulatory gene in the adaptive immune response.[17] Studies investigating the effect of loss-of-function Eomesodermin found that a decrease in expression of this transcription factor resulted in decreased amount of perforin produced by CD8+ T cells.[17]
Role in disease pathogenesis
editUnlike antibodies, which are effective against both viral and bacterial infections, cytotoxic T cells are mostly effective against viruses.[18]
During hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, cytotoxic T cells kill infected cells and produce antiviral cytokines capable of purging HBV from viable hepatocytes. They also play an important pathogenic role, contributing to nearly all of the liver injury associated with HBV infection.[19] Platelets have been shown to facilitate the accumulation of virus-specific cytotoxic T cells into the infected liver.[20] In some studies with mice, the injection with CXCR5+CD8+T cells show a significant decrease of HBsAg. Also, an increase of CXCL13 levels facilitated the recruitment of intrahepatic CXCR5+CD8+T cells and, these types of cells produced high levels of HBV-specific interferon (IFN)-γ and IL-21, which can help to improve the control of chronic HBV infection.[21]
Cytotoxic T cells have been implicated in the progression of arthritis. The main involvement of rheumatoid arthritis is its joint involvement. The synovial membrane is characterised by hyperplasia, increased vascularity and infiltration of inflammatory cells; mainly CD4+ T lymphocytes, which are the main organisers of cell-mediated immune responses. In different studies, rheumatoid arthritis is strongly linked to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II antigens. The only cells in the body that express MHC class II antigens are constitutive antigen-presenting cells. This strongly suggests that rheumatoid arthritis is caused by unidentified arthritogenic antigens. The antigen could be any exogenous antigen, such as viral proteins, or an endogenous protein.[22] Recently, a number of possible endogenous antigens have been identified, for example, human cartilage glycoprotein 39, heavy chain binding protein and citrullinated protein. Activated CD4+ T lymphocytes stimulate monocytes, macrophages and synovial fibroblasts to elaborate the cytokines interleukin-1, interleukin-6 and tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNFa), and to secrete metalloproteinases. The first three of which are key in driving inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. These activated lymphocytes also stimulate B cells to produce immunoglobulins, including rheumatoid factor.[23] Their pathogenic role is unknown, but may be due to complement activation through immune complex formation. Moreover, several animal studies suggest that cytotoxic T cells may have a predominantly proinflammatory effect in the disease. It is also studied that the production of cytokines by the CD8+ cells may accelerate the progresses of the arthritis disease.[24]
CD8+ T cells have been found to play a role in HIV infection. HIV over time has developed many strategies to evade the host cell immune system. For example, HIV has adopted very high mutation rates to allow them to escape recognition by CD8+ T cells.[25] They are also able to down-regulate expression of surface MHC Class I proteins of cells that they infect, in order to further evade destruction by CD8+ T cells.[25] If CD8+ T cells cannot find, recognize and bind to infected cells, the virus will not be destroyed and will continue to grow.
Furthermore, CD8+ T cells may be involved in Type 1 diabetes.[26] Studies in a diabetic mouse model showed that CD4+ cells are responsible for the massive infiltration of mononuclear leukocytes into pancreatic islets. However, CD8+ cells have been shown to play an effector role, responsible for the ultimate destruction of islet beta cells. However, in studies with NOD mice carrying a null mutation at the beta-2 microglobulin (B2M) locus and thus lacking major histocompatibility complex class I molecules and CD8+ T cells, it was found that they did not develop diabetes.[27]
CD8+ T cells may be necessary to resolve chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN).[28][29] Mice without CD8+ T cells show prolonged CIPN compared to normal mice and injection of educated CD8+ T cells resolve or prevent CIPN.
Cytotoxic T-lymphocytes have been implicated in the development of various diseases and disorders, for example in transplant rejection (cytotoxic T-lymphocytes attack the new organ after detecting it as foreign, due to HLA variation between donor and recipient);[30] in excessive cytokine production in severe SARS-CoV-2 infection (due to an exaggerated lymphocyte response, a large amount of pro-inflammatory cytokines are generated, damaging the subject);[31][32] inflammatory and degenerative diseases of the central nervous system, such as multiple sclerosis (T cells become sensitised to certain proteins, such as myelin, attacking healthy cells and recruiting more immune cells, aggravating the disease).[33]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Al-Shura AN (2020). "Lymphocytes". Advanced Hematology in Integrated Cardiovascular Chinese Medicine. Elsevier. pp. 41–46. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-817572-9.00007-0. ISBN 978-0-12-817572-9. S2CID 241913878.
Helper T cells/CD4+ •express CD4 glycoproteins on their cell surface, which activate in the presence of peptide antigens on the surface of invading pathogens; •respond immediately to protect the immune system; •secrete different cytokine proteins according to the immune response.
- ^ Venturi S, Venturi M (September 2009). "Iodine, thymus, and immunity". Nutrition. 25 (9): 977–979. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2009.06.002. PMID 19647627.
- ^ Kabelitz D, Wesch D (2003). "Features and functions of gamma delta T lymphocytes: focus on chemokines and their receptors". Critical Reviews in Immunology. 23 (5–6): 339–370. doi:10.1615/CritRevImmunol.v23.i56.10. PMID 15030305.
- ^ Deseke M, Prinz I (September 2020). "Ligand recognition by the γδ TCR and discrimination between homeostasis and stress conditions". Cellular & Molecular Immunology. 17 (9): 914–924. doi:10.1038/s41423-020-0503-y. PMC 7608190. PMID 32709926.
- ^ Tuengel J, Ranchal S, Maslova A, Aulakh G, Papadopoulou M, Drissler S, et al. (October 2021). "Characterization of Adaptive-like γδ T Cells in Ugandan Infants during Primary Cytomegalovirus Infection". Viruses. 13 (10): 1987. doi:10.3390/v13101987. PMC 8537190. PMID 34696417.
- ^ Rojas-Espinosa O (2017). Inmunología (de memoria) (Cuarta edición ed.). Ciudad de México: Médica Panamericana. ISBN 978-968-7988-28-3. OCLC 1022564980.
- ^ a b Hoyer S, Prommersberger S, Pfeiffer IA, Schuler-Thurner B, Schuler G, Dörrie J, Schaft N (December 2014). "Concurrent interaction of DCs with CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells improves secondary CTL expansion: It takes three to tango". European Journal of Immunology. 44 (12): 3543–3559. doi:10.1002/eji.201444477. PMID 25211552. S2CID 5655814.
- ^ Abbas AK, Lichtman AH, Pillai S (2018). Cellular and molecular immunology (Ninth ed.). Philadelphia, PA. ISBN 978-0-323-52323-3. OCLC 973917896.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Hivroz C, Chemin K, Tourret M, Bohineust A (2012). "Crosstalk between T lymphocytes and dendritic cells". Critical Reviews in Immunology. 32 (2): 139–155. doi:10.1615/CritRevImmunol.v32.i2.30. PMID 23216612.
- ^ Lanzavecchia A (June 1998). "Immunology. Licence to kill". Nature. 393 (6684): 413–414. Bibcode:1998Natur.393..413L. doi:10.1038/30845. PMID 9623994.
- ^ Bennett SR, Carbone FR, Karamalis F, Flavell RA, Miller JF, Heath WR (June 1998). "Help for cytotoxic-T-cell responses is mediated by CD40 signalling". Nature. 393 (6684): 478–480. Bibcode:1998Natur.393..478B. doi:10.1038/30996. PMID 9624004. S2CID 4325396.
- ^ Milstein O, Hagin D, Lask A, Reich-Zeliger S, Shezen E, Ophir E, et al. (January 2011). "CTLs respond with activation and granule secretion when serving as targets for T-cell recognition". Blood. 117 (3): 1042–1052. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-05-283770. PMC 3035066. PMID 21045195.
- ^ Chang HF, Bzeih H, Chitirala P, Ravichandran K, Sleiman M, Krause E, et al. (February 2017). "Preparing the lethal hit: interplay between exo- and endocytic pathways in cytotoxic T lymphocytes". Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. 74 (3): 399–408. doi:10.1007/s00018-016-2350-7. PMC 5241346. PMID 27585956.
- ^ Rudd-Schmidt JA, Hodel AW, Noori T, Lopez JA, Cho HJ, Verschoor S, et al. (November 2019). "Lipid order and charge protect killer T cells from accidental death". Nature Communications. 10 (1): 5396. Bibcode:2019NatCo..10.5396R. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-13385-x. PMC 6881447. PMID 31776337.
- ^ a b Bakshi RK, Cox MA, Zajac AJ (2014). "Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes". Encyclopedia of Medical Immunology. pp. 332–342. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-84828-0_36. ISBN 978-0-387-84827-3.
- ^ Tyagi, Tarun; et al. (2023). "Platelet-derived TLT-1 promotes tumor progression by suppressing CD8+ T cells". Journal of Experimental Medicine. 220 (1). doi:10.1084/jem.20212218. PMC 9814191. PMID 36305874.
- ^ a b Pearce EL, Mullen AC, Martins GA, Krawczyk CM, Hutchins AS, Zediak VP, et al. (November 2003). "Control of effector CD8+ T cell function by the transcription factor Eomesodermin". Science. 302 (5647): 1041–1043. Bibcode:2003Sci...302.1041P. doi:10.1126/science.1090148. PMID 14605368. S2CID 43479181.
- ^ Kemball CC, Alirezaei M, Whitton JL (September 2010). "Type B coxsackieviruses and their interactions with the innate and adaptive immune systems". Future Microbiology. 5 (9): 1329–1347. doi:10.2217/fmb.10.101. PMC 3045535. PMID 20860480.
- ^ Iannacone M, Sitia G, Guidotti LG (2006). "Pathogenetic and antiviral immune responses against hepatitis B virus". Future Virology. 1 (2): 189–96. doi:10.2217/17460794.1.2.189.
- ^ Iannacone M, Sitia G, Isogawa M, Marchese P, Castro MG, Lowenstein PR, et al. (November 2005). "Platelets mediate cytotoxic T lymphocyte-induced liver damage". Nature Medicine. 11 (11): 1167–1169. doi:10.1038/nm1317. PMC 2908083. PMID 16258538.
- ^ Li Y, Tang L, Guo L, Chen C, Gu S, Zhou Y, et al. (March 2020). "CXCL13-mediated recruitment of intrahepatic CXCR5+CD8+ T cells favors viral control in chronic HBV infection". Journal of Hepatology. 72 (3): 420–430. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2019.09.031. PMID 31610223. S2CID 204702318.
- ^ Chang MH, Nigrovic PA (March 2019). "Antibody-dependent and -independent mechanisms of inflammatory arthritis". JCI Insight. 4 (5): e125278. doi:10.1172/jci.insight.125278. PMC 6483516. PMID 30843881. S2CID 73512236.
- ^ Cope AP, Schulze-Koops H, Aringer M (September 2007). "The central role of T cells in rheumatoid arthritis". Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology. 25 (5 Suppl 46): S4-11. PMID 17977483.
- ^ Carvalheiro H, da Silva JA, Souto-Carneiro MM (January 2013). "Potential roles for CD8(+) T cells in rheumatoid arthritis". Autoimmunity Reviews. 12 (3): 401–409. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2012.07.011. PMID 22841983.
- ^ a b Gulzar N, Copeland KF (January 2004). "CD8+ T-cells: function and response to HIV infection". Current HIV Research. 2 (1): 23–37. doi:10.2174/1570162043485077. PMID 15053338.
- ^ Tsai S, Shameli A, Santamaria P (2008). "Chapter 4 CD8+ T Cells in Type 1 Diabetes". Immunopathogenesis of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Advances in Immunology. Vol. 100. pp. 79–124. doi:10.1016/S0065-2776(08)00804-3. ISBN 9780123743268. PMID 19111164.
- ^ Wang B, Gonzalez A, Benoist C, Mathis D (August 1996). "The role of CD8+ T cells in the initiation of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus". European Journal of Immunology. 26 (8): 1762–1769. doi:10.1002/eji.1830260815. PMID 8765018. S2CID 26229701.
- ^ Laumet G, Edralin JD, Dantzer R, Heijnen CJ, Kavelaars A (June 2019). "Cisplatin educates CD8+ T cells to prevent and resolve chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in mice". Pain. 160 (6): 1459–1468. doi:10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001512. PMC 6527475. PMID 30720585.
- ^ Krukowski K, Eijkelkamp N, Laumet G, Hack CE, Li Y, Dougherty PM, et al. (October 2016). "CD8+ T Cells and Endogenous IL-10 Are Required for Resolution of Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathic Pain". The Journal of Neuroscience. 36 (43): 11074–11083. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3708-15.2016. PMC 5098842. PMID 27798187.
- ^ Wiebe C, Nickerson PW (February 2020). "Human leukocyte antigen molecular mismatch to risk stratify kidney transplant recipients". Current Opinion in Organ Transplantation. 25 (1): 8–14. doi:10.1097/MOT.0000000000000714. PMID 31789952. S2CID 208537995.
- ^ Channappanavar R, Perlman S (July 2017). "Pathogenic human coronavirus infections: causes and consequences of cytokine storm and immunopathology". Seminars in Immunopathology. 39 (5): 529–539. doi:10.1007/s00281-017-0629-x. PMC 7079893. PMID 28466096.
- ^ Sarzi-Puttini P, Giorgi V, Sirotti S, Marotto D, Ardizzone S, Rizzardini G, et al. (March 2020). "COVID-19, cytokines and immunosuppression: what can we learn from severe acute respiratory syndrome?". Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology. 38 (2): 337–342. doi:10.55563/clinexprheumatol/xcdary. PMID 32202240. S2CID 214609305.
- ^ Neumann H, Medana IM, Bauer J, Lassmann H (June 2002). "Cytotoxic T lymphocytes in autoimmune and degenerative CNS diseases". Trends in Neurosciences. 25 (6): 313–319. doi:10.1016/S0166-2236(02)02154-9. PMID 12086750. S2CID 12593103.
External links
edit- Media related to Cytotoxic T cells at Wikimedia Commons
- T-cell Group – Cardiff University