The Gudar is a river of central Ethiopia.[1] It is a left-bank tributary of the Abay or Blue Nile; tributaries of the Gudar include the Dabissa and the Taranta. The Gudar River has a drainage area about 7,011 square kilometers in size.[2] It was bounded by the historical Endagabatan province.[3]
| Gudar River Guder | |
|---|---|
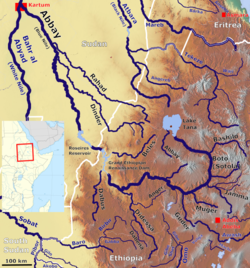 Map showing the Abbay (Blue Nile) basin, with the Gudar River (bottom right) | |
 | |
| Location | |
| Country | Ethiopia |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mouth | Blue Nile |
• coordinates | 9°51′49″N 37°40′16″E / 9.863615°N 37.671039°E |
• elevation | 932 m (3,058 ft) |
| Basin size | 7,011 km2 (2,707 sq mi) |
| Basin features | |
| Progression | Blue Nile → Nile → Mediterranean Sea |
| River system | Nile Basin |
In the 1600s, emperor Susenyos I and his troops traversed this river to meet Hadiya leader Sidi Mohammed at the Battle of Hadiya.[4]
A Greek resident built the first bridge over the Gudar in 1897.[5]
See also
editNotes
edit- ^ Abbay. Encyclopedia Aethiopica.
- ^ "Tana & Beles Integrated Water Resources Development: Project Appraisal Document (PAD), Vol.1", World Bank, 2 May 2008 (accessed 5 May 2009)
- ^ Endagabatan. Encyclopedia Aethiopica.
- ^ Lindahl, Bernhard. Local History of Ethiopia (PDF). Nordic Africa Institute. p. 9.
- ^ Richard Pankhurst, Economic History of Ethiopia (Addis Ababa: Haile Selassie University, 1968), p. 299