Original file (1,065 × 640 pixels, file size: 139 KB, MIME type: image/png)
| This is a file from the Wikimedia Commons. Information from its description page there is shown below. Commons is a freely licensed media file repository. You can help. |
Contents
Summary
| DescriptionGlobal monthly temps closeup.png |
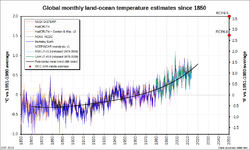
English: Global monthly land-ocean temperature estimates since 1970, from six different sources. |
| Source | Own work |
| Author | Glen Fergus |
Licensing
- You are free:
- to share – to copy, distribute and transmit the work
- to remix – to adapt the work
- Under the following conditions:
- attribution – You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
Summary
The graph shows global monthly near-surface air temperature anomaly estimates since 1970 from eight sources spanning three different estimation approaches. The plotted values are temperature anomalies — the difference between a month’s temperature from a given series and the mean for that month of the year for that series across a reference interval, here taken as 1951 – 1980. The overlaid trend is a 4th order polynomial fit to the mean of the plotted series.
Data sources
1. NASA GISTEMP global temperature series[1]
2. HadCRUT4 global temperature series[2]
3. HadCRUT + Cowtan & Way global temperature series (version 2)[3]
4. NOAA National Climate Data Center global temperature series[4]
5. Berkeley Earth land + ocean global temperature series[5]
6. NCEP / NCAR reanalysis (version 1) global average surface air temperatures[6][7]
Satellite MSU remote sensing cannot measure meteorological surface air temperature (typically defined as that at 2 m height). The best that can be obtained is a temperature estimate across the lower troposphere,[8] about the bottom 5000 m of atmosphere[8] That temperature is of course much colder than the surface temperature and varies somewhat differently with climatic influences. Nevertheless it is often compared with surface temperatures.[9] The satellite series do not extend across the reference interval adopted for the graph. Instead they are each rebased so that their mean across the 30 year interval 1979 – 2008 equals the mean of the five instrumental series across the same interval.
7. RSS temperature lower troposphere global temperature series (RSS TLT version 3.3)[10]
8. UAH temperature lower troposphere global temperature series (UAH TLT version 5.6)[11]
Future predictions
For comparison, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Fifth Assessment Report[12] central temperature estimates for 2050 for representative concentration pathways RCP6 (mid range) and RCP8.5 (high) are also shown.
Open source
The Microsoft Excel spreadsheet that produced this graph can be downloaded here: http://gergs.net/?attachment_id=1246.
References
- ↑ NASA GISS Surface Temperature Analysis. Goddard Institute for Space Studies.
- ↑ Met Office Hadley Centre observations datasets HadCRUT4. UK Met Office.
- ↑ Cowtan, K., & Way, R. G. (2013). Coverage bias in the HadCRUT4 temperature series and its impact on recent temperature trends. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society
- ↑ Global Surface Temperature Anomalies. National Climatic Data Center. Retrieved on 2010-06-16.
- ↑ Berkeley Earth Land + Ocean Data. Berkeley Earth.
- ↑ Kalnay et al.,The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project, Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 77, 437-470, 1996
- ↑ NCEP/NCAR Reanalysis Monthly Means and Other Derived Variables. Earth Systems Research Laboratory.
- ↑ a b Upper Air Temperature. Remote Sensing Systems..
- ↑ For example File:Satellite Temperatures.png
- ↑ MSU & AMSU Time Series Trend Browse Tool. Remote Sensing Systems.
- ↑ UAH MSU Data.
- ↑ Climate Change 2013, The Physical Science Basis. Retrieved on 2013-05-03.
Also see
Captions
Items portrayed in this file
depicts
some value
142,713 byte
640 pixel
1,065 pixel
image/png
7ba7647db99ebd8c6efe1a9d33f5922a50dba8eb
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 02:04, 28 April 2014 |  | 1,065 × 640 (139 KB) | Gergyl | Rev 7 |
| 23:24, 16 November 2013 |  | 1,064 × 639 (187 KB) | Gergyl | Rev 5 | |
| 08:15, 4 May 2011 |  | 1,066 × 619 (172 KB) | Glen Fergus | {{Information |Description ={{en|1=Global mean temperatures from various sources; since 1970}} |Source ={{own}} |Author =Glen Fergus |Date =2011-05-04 |Permission = |other_versions = }} |
File usage
The following page uses this file:
Metadata
This file contains additional information, probably added from the digital camera or scanner used to create or digitize it.
If the file has been modified from its original state, some details may not fully reflect the modified file.
| Horizontal resolution | 28.34 dpc |
|---|---|
| Vertical resolution | 28.34 dpc |