The Regional Agreement on Access to Information, Public Participation and Justice in Environmental Matters in Latin America and the Caribbean, better known as the Escazú Agreement (Spanish: Acuerdo de Escazú), is an international treaty signed by 25 Latin American and Caribbean nations concerning the rights of access to information about the environment, public participation in environmental decision-making, environmental justice, and a healthy and sustainable environment for current and future generations.[2] The agreement is open to 33 countries in Latin America and the Caribbean. Of the 25 signatories, it has been ratified by 17: Antigua and Barbuda, Argentina, Belize, Bolivia, Chile, Colombia, Dominica, Ecuador, Grenada, Guyana, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, and Uruguay.[1]
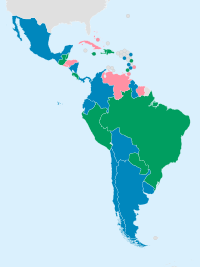 Ratified Signatories Non-signatories | |
| Drafted | 5 May 2015 – 4 March 2018 |
|---|---|
| Signed | 27 September 2018[1] |
| Location | Escazú, Costa Rica |
| Effective | 22 April 2021[1] |
| Signatories | 25[1] |
| Parties | 17[1] |
| Depositary | Secretary-General of the United Nations |
| Languages | English, French, Portuguese, Quechua, Spanish |


The agreement originated at the 2012 United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development and is the only binding treaty to be adopted as a result of the conference. With the UN's Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (ECLAC) acting as the technical secretariat for the process, it was drafted between 2015 and 2018 and adopted in Escazú, Costa Rica, on 4 March 2018.[3] The agreement was signed on 27 September 2018 and remained open for signature until 26 September 2020.[1] Eleven ratifications were required for the agreement to enter into force, which was achieved on 22 January 2021 with the accession of Mexico and Argentina.[4] The agreement entered into force on 22 April 2021.[5][1]
The Escazú Agreement is the first international treaty in Latin America and the Caribbean concerning the environment, and the first in the world to include provisions on the rights of environmental defenders.[2] The agreement strengthens the links between human rights and environmental protection by imposing requirements upon member states concerning the rights of environmental defenders. It aims to provide full public access to environmental information, environmental decision-making, and legal protection and recourse concerning environmental matters. It also recognizes the right of current and future generations to a healthy environment and sustainable development.[6][7]
Parties and signatories
edit| Member[1] | Date of signature | Date of ratification |
|---|---|---|
| Antigua and Barbuda | 27 September 2018 | 4 March 2020 |
| Argentina | 27 September 2018 | 22 January 2021 |
| Belize | 24 September 2020 | 7 March 2023 |
| Bolivia | 2 November 2018 | 26 September 2019 |
| Brazil | 27 September 2018 | |
| Chile | 18 March 2022 | 13 June 2022 |
| Colombia | 11 December 2019 | 25 September 2024 |
| Costa Rica | 27 September 2018 | |
| Dominica | 26 September 2020 | 22 April 2024 |
| Ecuador | 27 September 2018 | 21 May 2020 |
| Grenada | 26 September 2019 | 20 March 2023 |
| Guatemala | 27 September 2018 | |
| Guyana | 27 September 2018 | 18 April 2019 |
| Haiti | 27 September 2018 | |
| Jamaica | 26 September 2019 | |
| Mexico | 27 September 2018 | 22 January 2021 |
| Nicaragua | 27 September 2019 | 9 March 2020 |
| Panama | 27 September 2018 | 10 March 2020 |
| Paraguay | 28 September 2018 | |
| Peru | 27 September 2018 | |
| Dominican Republic | 27 September 2018 | |
| Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | 12 July 2019 | 26 September 2019 |
| Saint Kitts and Nevis | 26 September 2019 | 26 September 2019 |
| Saint Lucia | 27 September 2018 | 1 December 2020 |
| Uruguay | 27 September 2018 | 26 September 2019 |
Ratification delays
editSeveral commentators have expressed doubt that Brazil will ratify the treaty under Jair Bolsonaro, whose government has not been supportive of environmental or human rights mechanisms.[8][9] Colombia has finally ratified the agreement in July 2022. Colombia ranks among the top countries in the region for death of environmental defenders.[9]
Despite being one of the leading countries in the negotiation process for this agreement, Chile decided not to sign the Escazú Agreement in a last minute decision. Few months later, President Sebastián Piñera rejected the entire agreement, apparently due to objections made by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs regarding a potential request from Bolivia to get sovereign access to the Pacific Ocean and the pressure of business leaders.[10] After Piñera left office in March 2022, his successor Gabriel Boric decided to sign the Escazú Agreement, being the first bill presented by his government to the National Congress.[11] Chile ratified the agreement in June 2022.[12]
Costa Rica refused to ratify the agreement after Rodrigo Chaves Robles came to power.[13]
Youth Champion
editOn 2020, for the agreement's second anniversary, The Access Initiative (TAI), the United Nations Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (UN ECLAC) and the Government of Costa Rica selected 5 new youth champions, succeeding David R. Boyd, from amongst young activists around Latin America and the Caribbean:[14]
| Country | Names |
|---|---|
| Argentina | Nicole Becker |
| Chile | Sebastián Benfeld Garcés |
| Colombia | Laura Serna |
| Costa Rica | Kyara Cascante |
| Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | Nafesha Richardson |
References
edit- ^ a b c d e f g h "Regional Agreement on Access to Information, Public Participation and Justice in Environmental Matters in Latin America and the Caribbean". CEPAL. 9 April 2018. Archived from the original on 26 April 2021. Retrieved 20 April 2021.
- ^ a b "Regional Agreement on Access to Information, Public Participation and Justice in Environmental Matters in Latin America and the Caribbean" (PDF). CEPAL. 4 March 2018. Archived (PDF) from the original on 6 February 2021. Retrieved 20 April 2021.
- ^ "History of the Regional Agreement". Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean. 23 March 2018. Archived from the original on 2 June 2021. Retrieved 28 May 2021.
- ^ "STATEMENT: Escazú Agreement Moves A Big Step Closer to Making the World Safer for Environmental Defenders". World Resources Institute. 22 January 2021. Archived from the original on 22 April 2021. Retrieved 20 April 2021.
- ^ "Secretary-General's message marking the Entry into Force of the Escazú Agreement". United Nations Secretary-General. 22 April 2021. Archived from the original on 3 June 2021. Retrieved 28 May 2021.
- ^ "The Escazu Agreement". Environmental-rights.org. 2018. Archived from the original on 26 April 2021. Retrieved 20 April 2021.
- ^ "World's First Treaty Protecting Environmental Defenders Could Soon Be Enacted". Global Citizen. 24 August 2020. Archived from the original on 26 April 2021. Retrieved 20 April 2021.
- ^ "Brazil set to ignore Escazú agreement that protects environmental activists". Dialogo Chino. 2021-04-19. Archived from the original on 2021-04-29. Retrieved 2021-04-27.
- ^ a b Miguel, Teresa de (2021-04-26). "International agreement enters into force to end killings of environmental leaders in Latin America". EL PAÍS. Archived from the original on 2021-05-02. Retrieved 2021-04-27.
- ^ "Why Chile promoted the Escazú Agreement then rejected it". Dialogo Chino. 2020-11-26. Archived from the original on 2022-07-06. Retrieved 2022-06-21.
- ^ "Chile seeks accession to Escazú's regional environmental treaty". infobae (in European Spanish). 2022-03-18. Archived from the original on 2022-06-21. Retrieved 2022-06-21.
- ^ Comisión Económica para América Latina y el Caribe. "Acuerdo Regional sobre el Acceso a la Información, la Participación Pública y el Acceso a la Justicia en Asuntos Ambientales en América Latina y el Caribe". www.cepal.org (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 2022-06-19. Retrieved 2022-06-21.
- ^ Welle, Deutsche (2022-05-04). "¿Retrocede Costa Rica en su política ambiental?: Presidente electo no ratificará el Acuerdo de Escazú". AméricaEconomía | AméricaEconomía (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 2022-08-15. Retrieved 2022-08-11.
- ^ "STATEMENT: 5 Youth Champions of Escazú Announced". World Resources Institute. 4 March 2020. Archived from the original on 1 April 2022. Retrieved 21 April 2022.