Kozarska Dubica (Serbian Cyrillic: Козарска Дубица), formerly Bosanska Dubica (Serbian Cyrillic: Босанска Дубица) is a town and municipality in Republika Srpska, Bosnia and Herzegovina. As of 2013, it has a population of 21,542 inhabitants, while the town of Kozarska Dubica has a population of 11,566 inhabitants.
Kozarska Dubica
Козарска Дубица | |
|---|---|
Town and municipality | |
 Highlights of Kozarska Dubica | |
 Location of Kozarska Dubica within Republika Srpska | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 45°10′50″N 16°48′38″E / 45.18056°N 16.81056°E | |
| Country | |
| Entity | |
| Government | |
| • Municipal mayor | Igor Savković (SNSD) |
| • Municipality | 499.01 km2 (192.67 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 104 m (341 ft) |
| Population (2013 census) | |
| • Town | 11,566 |
| • Municipality | 21,542 |
| • Municipality density | 43/km2 (110/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Area code | 52 |
| Website | www |
Geography
editIt is situated in the eastern part of Bosanska Krajina region. The municipality of Hrvatska Dubica lies to the north, in Croatia. Kozarska Dubica is situated 26 kilometres (16 miles) from the Zagreb–Belgrade highway. The town and its suburbs border Croatia to the north, the town of Gradiška to the east, the town of Kostajnica to the west, and the town of Prijedor to the south. The land area of Kozarska Dubica is 499 square kilometres (193 sq mi).
Name
editThe town was originally known as "Bosanska Dubica" (Босанска Дубица in Serbian Cyrillic, literally "Bosnian Dubica") but was renamed "Kozarska Dubica" (Козарска Дубица in Serbian Cyrillic) by the authorities of Republika Srpska following the Bosnian War, which was part of a broad political resolution to remove all Bosnian prefixes.[1] This included towns like Gradiška (Bosanska Gradiška) and Novi Grad (Bosanski Novi).
History
editEarly history
editKozarska Dubica was built in 930.[citation needed] Dubica on the right bank of the Una it was first mentioned in 1258 as Castrum. It was the seat of the Dubica county of the Kingdom of Hungary. In 1538 Dubica came under Ottoman rule [2] Babonići-Vodički were in charge of the town until the 12th century. Dubica became an important fort during the Ottoman Empire due to its geographic positioning. It became a vital and important border crossing for many years. The last Austrian-Turkish war was the so-called Dubica War (1788–91) and was fought in this area. During the war in Dubica in the 1780s, the town, which was described at the time as having only a few houses and a mosque, was completely razed. The town fell under Ottoman occupation in 1538. Dubica encountered many different rulers during the Ottoman Empire and the later Austro-Hungarian Empire.
During World War II, the town was occupied by Axis troops and was included into the Pavelić's Independent State of Croatia (NDH). The fascist Ustashe regime committed the Genocide of the Serbs and the Holocaust. During the war, the NDH armed forces killed over 7,000 Serbs in the municipality of Bosanska Dubica, while the municipality lost more than half of its pre-war population.[3] The biggest massacre was committed by the Croatian Home Guard in January 1942, when the village Draksenić was burned and more than 1600 were people killed.[4]
During the 1970s, Bosanska Dubica experienced a great improvement in its economy. During the 1980s there was a boom in construction and renovation which was halted by the outbreak of yet another war.
The Serbian Orthodox Moštanica Monastery (Manastir Moštanica) appears on the coat of arms of Kozarska Dubica.
Bosnian War
editDuring the period July–September 1992 all three of the town's mosques were completely destroyed.[5] The main town's mosque Gradska Džamija (literally Town's Mosque), was rebuilt in 2003 and its Harem courtyard declared a national monument of Bosnia and Herzegovina.[5] The bridge between Bosanska Dubica and Hrvatska Dubica was destroyed on the Croatian side. During the war the city was under siege by the Croatian Army during a failed operation called Operacija Una 95. On September 18, 1995, the Croatian army made a descent across the Una River and took control of some parts of Bosanska Dubica. The next day, on September 19, Serb units from other parts of the front line forced the Croat army to retreat back over the river, with Serb planes from the Banja Luka airport attacked in the vicinity of the villages Živaja and Šaš in Croatia.[6] A total of 54 Serb civilians were killed by the regular Croatian army during a failed invasion from Croatia.
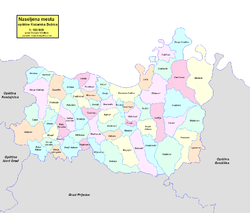
Settlements
editAside from the town of Kozarska Dubica, the municipality includes the following settlements:
- Aginci
- Babinac
- Bačvani
- Bijakovac
- Bjelajci
- Božići
- Brekinja
- Čelebinci
- Čitluk
- Čuklinac
- Demirovac
- Dizdarlije
- Donja Jutrogošta
- Donja Slabinja
- Donji Jelovac
- Draksenić
- Furde
- Gornja Gradina
- Gornjoselci
- Gradina Donja
- Gunjevci
- Hadžibajir
- Hajderovci
- Jasenje
- Johova
- Jošik
- Kadin Jelovac
- Klekovci
- Knežica
- Komlenac
- Košuća
- Koturovi
- Kriva Rijeka
- Maglajci
- Malo Dvorište
- Međeđa
- Međuvođe
- Mirkovac
- Mlječanica
- Mrazovci
- Murati
- Novoselci
- Odžinci
- Parnice
- Pobrđani
- Pucari
- Rakovica
- Sjeverovci
- Sključani
- Sreflije
- Strigova
- Suvaja
- Ševarlije
- Tuključani
- Ušivac
- Veliko Dvorište
- Verija
- Vlaškovci
- Vojskova i Vrioci
Demographics
editPopulation
edit| Population of settlements – Kozarska Dubica municipality | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Settlement | 1879. | 1885. | 1895. | 1910. | 1921. | 1931. | 1948. | 1953. | 1961. | 1971. | 1981. | 1991. | 2013. | |
| Total | 8,776 | 12,069 | 15,176 | 25,794 | 27,354 | 33.129 | 24,280 | 30,384 | 30,887 | 31,606 | 21,524 | |||
| 1 | Aginci | 407 | 275 | |||||||||||
| 2 | Božići | 414 | 219 | |||||||||||
| 3 | Brekinja | 316 | 223 | |||||||||||
| 4 | Čitluk | 425 | 218 | |||||||||||
| 5 | Demirovac | 467 | 359 | |||||||||||
| 6 | Donja Slabinja | 482 | 266 | |||||||||||
| 7 | Donji Jelovac | 466 | 254 | |||||||||||
| 8 | Draksenić | 725 | 565 | |||||||||||
| 9 | Jošik | 646 | 451 | |||||||||||
| 10 | Kadin Jelovac | 391 | 206 | |||||||||||
| 11 | Klekovci | 486 | 320 | |||||||||||
| 12 | Knežica | 626 | 394 | |||||||||||
| 13 | Kozarska Dubica | 4,452 | 4,720 | 6,259 | 9,185 | 11,170 | 13,680 | 11,566 | ||||||
| 14 | Malo Dvorište | 333 | 526 | |||||||||||
| 15 | Međeđa | 808 | 566 | |||||||||||
| 16 | Međuvođe | 529 | 317 | |||||||||||
| 17 | Mirkovac | 328 | 215 | |||||||||||
| 18 | Ševarlije | 350 | 228 | |||||||||||
| 19 | Sključani | 307 | 211 | |||||||||||
| 20 | Sreflije | 392 | 201 | |||||||||||
| 21 | Veliko Dvorište | 384 | 209 | |||||||||||
| 22 | Vrioci | 391 | 344 | |||||||||||
Ethnic composition
edit| Ethnic composition – Kozarska Dubica town | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013. | 1991. | 1981. | 1971. | 1961. | |||
| Total | 11,566 (100,0%) | 13,680 (100,0%) | 11,170 (100,0%) | 9,185 (100,0%) | 6,259 (100,0%) | ||
| Bosniaks | 6,084 (44,47%) | 4,812 (43,08%) | 4,927 (53,64%) | 1,138 (18,18%) | |||
| Serbs | 5,540 (40,50%) | 3,439 (30,79%) | 3,417 (37,20%) | 3,527 (56,35%) | |||
| Yugoslavs | 1,329 (9,715%) | 2,453 (21,96%) | 251 (2,733%) | 972 (15,53%) | |||
| Others | 439 (3,209%) | 76 (0,680%) | 62 (0,675%) | 16 (0,256%) | |||
| Croats | 288 (2,105%) | 316 (2,829%) | 481 (5,237%) | 558 (8,915%) | |||
| Albanians | 33 (0,295%) | 13 (0,142%) | 20 (0,320%) | ||||
| Montenegrins | 31 (0,278%) | 22 (0,240%) | 6 (0,096%) | ||||
| Roma | 6 (0,054%) | ||||||
| Macedonians | 3 (0,027%) | 4 (0,044%) | 15 (0,240%) | ||||
| Slovenes | 1 (0,009%) | 5 (0,054%) | 7 (0,112%) | ||||
| Hungarins | 3 (0,033%) | ||||||
| Ethnic composition – Kozarska Dubica municipality | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013. | 1991. | 1981. | 1971. | 1961. | |||
| Total | 21,524 (100,0%) | 31,606 (100,0%) | 30,867 (100,0%) | 30,384 (100,0%) | 24,280 (100,0%) | ||
| Serbs | 18,670 (86,74%) | 21,728 (68,75%) | 20,453 (66,26%) | 23,989 (78,95%) | 21,299 (87,72%) | ||
| Bosniaks | 2,168 (10,07%) | 6,440 (20,38%) | 5,052 (16,37%) | 5,114 (16,83%) | 1,165 (4,798%) | ||
| Others | 413 (1,919%) | 1,099 (3,477%) | 289 (0,936%) | 102 (0,336%) | 34 (0,140%) | ||
| Croats | 273 (1,268%) | 488 (1,544%) | 513 (1,662%) | 717 (2,360%) | 746 (3,072%) | ||
| Yugoslavs | 1,851 (5,856%) | 4 463 (14,46%) | 403 (1,326%) | 978 (4,028%) | |||
| Montenegrins | 38 (0,123%) | 28 (0,092%) | 7 (0,029%) | ||||
| Albanians | 34 (0,110%) | 13 (0,043%) | 22 (0,091%) | ||||
| Macedonians | 10 (0,032%) | 9 (0,030%) | 19 (0,078%) | ||||
| Slovenes | 6 (0,019%) | 6 (0,020%) | 7 (0,029%) | ||||
| Roma | 6 (0,019%) | ||||||
| Hungarins | 3 (0,010%) | 3 (0,010%) | 3 (0,012%) | ||||
Economy
editSituated in the valley of the rivers, the municipality of Kozarska Dubica has more than 316.09 square kilometres (122.04 sq mi) of arable land, to which agriculture is an important development factor. Agricultural production is focused on land cultivation, cattle breeding, raising of industrial crops, and recently the development of fruit and wine growing. The climate of Kozarska Dubica is conducive to the cultivation of different kinds of vegetables.
Most of the economy comes from the livestock. The largest milk production company is Mlijekoprodukt located near the town of Kozarska Dubica. It continues its tradition of growing fruits in the area. Kozarska Dubica also has an important construction company, IGP "UNA", which was established in 1962. Prior to the war there was a sugar factory operating as well.
- Economic preview
The following table gives a preview of total number of registered people employed in legal entities per their core activity (as of 2018):[7]
| Activity | Total |
|---|---|
| Agriculture, forestry and fishing | 121 |
| Mining and quarrying | 1 |
| Manufacturing | 1,477 |
| Electricity, gas, steam and air conditioning supply | 85 |
| Water supply; sewerage, waste management and remediation activities | 97 |
| Construction | 143 |
| Wholesale and retail trade, repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles | 862 |
| Transportation and storage | 103 |
| Accommodation and food services | 205 |
| Information and communication | 45 |
| Financial and insurance activities | 46 |
| Real estate activities | 9 |
| Professional, scientific and technical activities | 42 |
| Administrative and support service activities | 3 |
| Public administration and defense; compulsory social security | 218 |
| Education | 277 |
| Human health and social work activities | 221 |
| Arts, entertainment and recreation | 23 |
| Other service activities | 55 |
| Total | 4,033 |
Culture
editEvery year outside Bosnia and Herzegovina, the annual Bosansko Dubičko Veče is held. It is a celebration that brings together displaced Bosnians of all ethnicities from Kozarska Dubica. Celebrations in the United States are held in Chicago and St. Louis, Illinois. In Chicago it is always held on the Saturday before Memorial Day and hosted at the Rumija Cultural Center. Sydney, Australia, also holds the same celebration in order to gather people of Kozarska Dubica from different Australian and New Zealand areas. Work continues on creating a congress that would meet once every two years, in order to help young children born outside of Kozarska Dubica to retain the heritage and cultural traditions. These celebrations typically attract many Bosniaks; however, many Croats and Serbs also come to show their respect towards their heritage and the town of Kozarska Dubica, and to reunite with former neighbors.
-
Monastery Moštanica, probably founded in the 12th century
-
Serbian Orthodox church Sv. Petra i Pavla
-
17th-century wooden mosque
Tourism
editHunting is a traditional sport of the municipality of Kozarska Dubica. One hunting organization is called Jele (Deer) The area used for hunting is around 500 square kilometres (193 sq mi). Hunting is extravagant in Kozarska Dubica because of its two big mountains, Kozara and Prosara, with the hunting area filled with rich forests. Hunting ranges from deer to smaller animals such as wild ducks. Every April an international dog hunting competition occurs in Kozarska Dubica.
Spa Mlječanica is the center for physiatrics, rehabilitation, and health in Kozarska Dubica, located on the northwest slopes of Kozara. A modern, specialized institution for physical medicine and rehabilitation, it provides ideal conditions for a successful rest and recovery for its clients.
Fishing is a highly important industry in Kozarska Dubica. Because of its location right on the Una River, fishing has developed into a long time tradition, drawing people from different areas. Also, the Sava River is located not far from Kozarska Dubica at Jasenovac, where the Una enters the Sava.
Sports
editKozarska Dubica has an old tradition in sports that dates back to the early 20th century. In the 1930s, Kozarska Dubica established a football club named SK Una. Currently, FK Borac play in the second tier-First League of the Republika Srpska.
After World War II, Kozarska Dubica had an upsurge of different sport organizations. In 1962 the handball club Borac was established. On February 11, 1973, the basketball club BK Una was created. In 1982 the Karate Club Knešpolje was founded. Even today the different sports remain an important part of Kozarska Dubica. There are both male and female teams for handball. Also there are a couple of karate clubs and chess clubs.
Notes
edit- ^ Mitja Velikonja (2003). Religious Separation and Political Intolerance in Bosnia-Herzegovina. Texas A&M University Press. pp. 259. ISBN 978-1-60344-724-9.
- ^ HAMDIJA KREŠEVLJAKOVIĆ, 1953, STARI BOSANSKI GRADOVI (VIEUX BOURGS BOSNIAQUES) https://www.fmks.gov.ba/download/zzs/1953/1-1953.pdf #page=37
- ^ Cvetković, Dragan (2009). Bosna i Hercegovina: numeričko određenje ljudskih gubitaka u Drugom svetskom ratu. Belgrade. pp. 124–128. ISBN 9788686831019.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Barić, Nikola (2019). Historiae patriaeque cultor. Slavonski Brod. ISBN 978-953-8102-23-3.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ a b "Harem Gradske džamije u Bosanskoj Dubici, proglašava se nacionalnim spomenikom Bosne i Hercegovine". old.kons.gov.ba (in Bosnian). Komisija za očuvanje nacionalnih spomenika. Retrieved 31 December 2016.
- ^ Eduard Šoštarić (14 August 2006). "Otvorena istraga zbog akcije 'Una'" [Inquiry into the Operation Una commenced] (in Croatian). Nacional (weekly). Archived from the original on 6 April 2012. Retrieved 7 July 2012.
- ^ "Cities and Municipalities of Republika Srpska" (PDF). rzs.rs.ba. Republika Srspka Institute of Statistics. 25 December 2019. Retrieved 31 December 2019.
