In polymer chemistry and materials science, dendronized polymers[1] (British English: dendronised polymers; from dendro- 'tree') are linear polymers to every repeat unit of which dendrons are attached. Dendrons are regularly-branched, tree-like fragments and for larger ones the polymer backbone is wrapped to give sausage-like, cylindrical molecular objects. Figure 1 shows a cartoon representation with the backbone in red and the dendrons like cake slices in green. It also provides a concrete chemical structure showing a polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) backbone, the methyl group (−CH3) of which is replaced by a dendron of the third generation (three consecutive branching points).
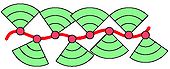 |
Figure 1. Cartoon representation (left) and a concrete example of a third generation dendronized polymer (right). The peripheral amine groups are modified by a substituent X which often is a protection group. Upon deprotection and modification substantial property changes can be achieved. The subscript n denotes the number of repeat units.
Structure and applications
editDendronized polymers can contain several thousands of dendrons in one macromolecule and have a stretched out, anisotropic structure. In this regard they differ from the more or less spherically shaped dendrimers, where a few dendrons are attached to a small, dot-like core resulting in an isotropic structure. Depending on dendron generation, the polymers differ in thickness as the atomic force microscopy image shows (Figure 2). Neutral and charged dendronized polymers are highly soluble in organic solvents and in water, respectively. This is due to their low tendency to entangle. Dendronized polymers have been synthesized with, e.g., polymethylmethacrylate, polystyrene, polyacetylene, polyphenylene, polythiophene, polyfluorene, poly(phenylene vinylene), poly(phenylene acetylene), polysiloxane, polyoxanorbornene, poly(ethylene imine) (PEI) backbones. Molar masses up to 200,000,000 g/mol have been obtained.[2] Dendronized polymers have been investigated for/as bulk structure control, responsivity to external stimuli, single molecule chemistry, templates for nanoparticle formation, catalysis, electro-optical devices, and bio-related applications. Particularly attractive is the use of water-soluble dendronized polymers for the immobilization of enzymes on solid surfaces (inside glass tubes or microfluidic devices) and for the preparation of dendronized polymer-enzyme conjugates.[3][4][5]
-
Figure 2. Atomic force microscopy height image of co-prepared dendronized polymers of generation one through four (PG1-PG4) reflecting the different thicknesses and apparent persistence lengths for each generation
-
Figure 3. Schematic representation of a molecular hybrid structure (conjugate) between a dendronized polymer and the two different enzymes HRP (horseradish peroxidase) and SOD (Cu,Zn-superoxide dismutase). PDB (SOD): 1SXA; PDB (HRP): 1ATJ; HRP sugar modification from Gray & Montgomery, Carbohydrate Research, 2006, 341, 198-209. Denpol structure: Bertran et al. RSC Adv., 2013, 3, 126-140.
Synthesis
editThe two main approaches into this class of polymers are the macromonomer route and the attach-to route. In the former, a monomer which already carries the dendron of final size is polymerized. In the latter the dendrons are constructed generation by generation directly on an already existing polymer. Figure 4 illustrates the difference for a simple case. The macromonomer route results in shorter chains for higher generations and the attach-to route is prone to lead to structure imperfections as an enormous number of chemical reactions have to be performed for each macromolecule.
History
editThe name “dendronized polymer” which meanwhile is internationally accepted was coined by Schlüter in 1998.[6] The first report on such a macromolecule which at that time was called “Rod-shaped Dendrimer” goes back to a patent by Tomalia in 1987[7] and was followed by Percec's first mentioning in the open literature of a polymer with “tapered side chains” in 1992.[8] In 1994 the potential of these polymers as cylindrical nanoobjects was recognized.[9] Many groups worldwide contributed to this field. They can be found in review articles.[10]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ "Weihai CY Dendrimer Technology Co., Ltd". www.whcyd.com. Archived from the original on 13 August 2013. Retrieved 14 January 2022.
- ^ B. Zhang, R. Wepf, K. Fischer, M. Schmidt, S. Besse, P. Lindner, B. T. King, R. Siegel, P. Schurtenberger, Y. Talmon, Y. Ding, M. Kröger, A. Halperin, A. D. Schlüter, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 737.
- ^ S. Fornera, T. Bauer, A. D. Schlüter, P. Walde, J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 502.
- ^ S. Fornera, P. Kuhn, D. Lombardi, A. D. Schlüter, P. S. Dittrich, P. Walde, ChemPlusChem 2012, 77, 98.
- ^ A. Grotzky, T. Nauser, H. Erdogan, A. D. Schlüter, P. Walde, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 11392.
- ^ A. D. Schlüter, Top. Curr. Chem. 1998, 197, 165.
- ^ D. A. Tomalia, P. M. Kirchoff, US Patent 4,694,064 1987.
- ^ V. Percec, J. Heck, M. Lee, G. Ungar, A. Alvarez-Castillo, J. Mater. Chem. 1992, 2, 1033.
- ^ R. Freudenberger, W. Claussen, A. D. Schlüter, H. Wallmeier, Polymer 1994, 35, 4496.
- ^ A. D. Schlüter, J. P. Rabe Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 864-883; A. Zhang, L. Shu, Z. Bo, A. D. Schlüter, Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2003, 204, 328-339; A. D. Schlüter, Top. Curr. Chem. 2005, 245, 151-191; H. Frauenrath Prog. Polym. Sci. 2005, 30, 325-384. B. M. Rosen, C. J. Wilson, D. A. Wilson, M. Peterca, M. R. Imam V. Percec, Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 6275-6540; Y. Chen, X. Xiong, Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 5049; J. I. Paez, M. Martinelli, V. Brunetti, M. C. Strumia, Polymers 2012, 4, 355.