Chloroprocaine, sold under the brand name Nesacaine among others is a local anesthetic given by injection.[2] It is used as the hydrochloride salt.[4] Chloroprocaine is a local anesthetic.[2][4]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Nesacaine, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com |
|
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | Intrathecal, eye drop |
| Drug class | Local anesthetic |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
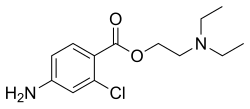
| Formula | C13H19ClN2O2 |
| Molar mass | 270.76 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Medical uses
editChloroprocaine (Nesacaine) is indicated for the production of local anesthesia by infiltration and peripheral nerve block;[2] and for the production of local anesthesia by infiltration, peripheral and central nerve block, including lumbar and caudal epidural blocks.[2]
Chloroprocaine (Clorotekal) is indicated for intrathecal injection in adults for the production of subarachnoid block (spinal anesthesia).[4]
Chloroprocaine is used for regional anesthesia including spinal anesthesia, caudal anesthesia and epidural anesthesia.[6][7]
It is also indicated for local anesthesia including brachial plexus block, cervical nerve block, occipital nerve block. mandibular nerve block or maxillary nerve block for dental anesthesia, ophthalmic anesthesia via infraorbital nerve block, ulnar nerve block, paravertebral block, intercostal nerve block, sciatic nerve block, stellate ganglion block, lumbar sympathetic block and interdigital block.[7]
It is also used for obstetric anesthesia including pudendal nerve block and paracervical block.[7]
Chloroprocaine (Iheezo) is indicated for ocular surface anesthesia.[3]
Subarachnoid block
editChloroprocaine was developed to meet the need for a short-acting spinal anaesthetic that is reliable and has a favourable safety profile to support the growing need for day-case surgery. Licensed in Europe for surgical procedures up to 40 minutes, chloroprocaine is an ester-type local anaesthetic with the shortest duration of action of all the established local anaesthetics. It has a significantly shorter duration of action than lidocaine and is significantly less toxic. Chloroprocaine has a motor block lasting for 40 minutes, a rapid onset time of 3–5 minutes (9.6 min ± 7.3 min at 40 mg dose; 7.9 min ± 6.0 min at 50 mg dose) and a time to ambulation of 90 minutes without complications, especially lacking transient neurologic symptomatology.
These data are based upon a retrospective review of 672 patients suitable for spinal anesthesia in surgical procedures less than 60 minutes' duration using 30–40 mg chloroprocaine. The results showed good surgical anesthesia, a fast onset time, and postoperative mobilization after 90 minutes without complications.[8]
The use of chloroprocaine in the subarachnoid space has been questioned.[9] In the early 1980s, several cases were reported of neurological deficits after inadvertent intrathecal injections intended for epidural delivery.[10] These doses were an order of magnitude higher than is currently used for intrathecal delivery.[11][12][13] It is also thought that these deficits were also related to the preservative sodium bisulfite,[14][15] although this is also controversial.[16][17]
Some studies have been published on the safe use of intrathecal chloroprocaine when appropriate dosage is used and with preservative-free preparations.[18][12]
It is approved for intrathecal use in the United States,[19], Europe,[20] and Canada.[1]
Obstetrics
editAmide-linked local anesthetic agents, such as lidocaine and bupivacaine, can become "trapped" in their ionized forms on the fetal side of the placenta, so their net transfer across the placenta is increased. An ester-linked local anesthetic agent, such as 2-chloroprocaine, is rapidly metabolized, and placental transfer is limited. Since the metabolism of 2-chloroprocaine by fetal plasma is slower than in maternal plasma, the potential for ion trapping exists. Fetal pH is slightly lower than maternal (7.32 to 7.38), thus most unionized drugs are "ion trapped" to a degree, even in a healthy fetus. Chloroprocaine (pKa 8.7) is the drug of choice for epidural analgesia and a decompensating fetus, because it does not participate in ion trapping. Placental transfer of 2-chloroprocaine is not influenced by fetal acidosis.[21]
The in vitro half-life of chloroprocaine is 21 seconds for maternal and 43 seconds for fetal blood. In patients who are homozygous atypical for plasma cholinesterase, chloroprocaine typically exists for two minutes in circulation.[22][23]
Synthesis
editThe hydrochloride salt of 4-amino-2-chlorobenzoyl chloride is made by the reaction of 2-chloro-4-aminobenzoic acid with thionyl chloride.[24] Synthesis of this drug is then accomplished by directly reacting the product of the last step with the hydrochloride salt of 2-diethylaminoethanol.
References
edit- ^ a b "Regulatory Decision Summary for Clorotekal". Drug and Health Products Portal. 22 August 2024. Retrieved 27 December 2024.
- ^ a b c d e "Nesacaine- chloroprocaine hydrochloride injection, solution; Nesacaine MPF- chloroprocaine hydrochloride injection, solution". DailyMed. 1 September 2022. Retrieved 21 January 2023.
- ^ a b "Iheezo- chloroprocaine hydrochloride ophthalmic gel gel". DailyMed. 27 September 2022. Retrieved 21 January 2023.
- ^ a b c d "Clorotekal- chloroprocaine hydrochloride injection, solution". DailyMed. 4 December 2020. Retrieved 27 December 2024.
- ^ https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/psusa/chloroprocaine-hydrochloride-list-nationally-authorised-medicinal-products-psusa00010078202203_en.pdf
- ^ Sintetica Limited (9 March 2017). "Ampres 10 mg/ml solution for injection". EMC. Archived from the original on 19 August 2019. Retrieved 2 December 2018.
- ^ a b c Physicians' Desk Reference. "chloroprocaine hydrochloride". USA: PDR.net. Archived from the original on 19 August 2019. Retrieved 2 December 2018.
- ^ Palas T (2009). "Ampres (chloroprocaine) Summary of Product Characteristics". Perimed. 3 (2): 31–34.
Cloroprocaina in chirurgia ambulatoriale: uno studio osservazionale
- ^ Drasner K (February 2005). "Chloroprocaine spinal anesthesia: back to the future?". Anesthesia & Analgesia. 100 (2): 549–52. doi:10.1213/01.ANE.0000143382.89888.C3. PMID 15673892.
- ^ Reisner LS, Hochman BN, Plumer MH (June 1980). "Persistent neurologic deficit and adhesive arachnoiditis following intrathecal 2-chloroprocaine injection". Anesthesia and Analgesia. 59 (6): 452–4. doi:10.1213/00000539-198006000-00014. PMID 7189987.
- ^ Förster JG, Kallio H, Rosenberg PH, Harilainen A, Sandelin J, Pitkänen MT (March 2011). "Chloroprocaine vs. articaine as spinal anaesthetics for day-case knee arthroscopy". Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica. 55 (3): 273–81. doi:10.1111/j.1399-6576.2010.02325.x. PMID 21039353. S2CID 205430566.
- ^ a b Förster JG, Rosenberg PH, Harilainen A, Sandelin J, Pitkänen MT (August 2013). "Chloroprocaine 40 mg produces shorter spinal block than articaine 40 mg in day-case knee arthroscopy patients". Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica. 57 (7): 911–9. doi:10.1111/aas.12107. PMID 23521140. S2CID 42930157.
- ^ Lacasse MA, Roy JD, Forget J, Vandenbroucke F, Seal RF, Beaulieu D, et al. (April 2011). "Comparison of bupivacaine and 2-chloroprocaine for spinal anesthesia for outpatient surgery: a double-blind randomized trial". Canadian Journal of Anaesthesia. 58 (4): 384–91. doi:10.1007/s12630-010-9450-x. PMID 21203878. S2CID 31870857.
- ^ Gissen AJ, Datta S, Lambert D (July 1984). "The chloroprocaine controversy: II. Is chloroprocaine neurotoxic?". Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine. 9 (3): 135–45. doi:10.1136/rapm-00115550-198409030-00004 (inactive 1 November 2024).
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of November 2024 (link) - ^ Wang BC, Li D, Hiller JM, Simon EJ, Budzilovich G, Hillman DE (December 1992). "Lumbar subarachnoid ethylenediaminetetraacetate induces hindlimb tetanic contractions in rats: prevention by CaCl2 pretreatment; observation of spinal nerve root degeneration". Anesthesia and Analgesia. 75 (6): 895–9. doi:10.1213/00000539-199212000-00006. PMID 1443708.
- ^ Taniguchi M, Bollen AW, Drasner K (January 2004). "Sodium bisulfite: scapegoat for chloroprocaine neurotoxicity?". Anesthesiology. 100 (1): 85–91. doi:10.1097/00000542-200401000-00016. PMID 14695728. S2CID 9604835.
- ^ Cabré F, Marín C, Cascante M, Canela EI (April 1990). "Occurrence and comparison of sulfite oxidase activity in mammalian tissues". Biochemical Medicine and Metabolic Biology. 43 (2): 159–62. doi:10.1016/0885-4505(90)90021-r. PMID 2346671.
- ^ Goldblum E, Atchabahian A (May 2013). "The use of 2-chloroprocaine for spinal anaesthesia". Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica. 57 (5): 545–52. doi:10.1111/aas.12071. PMID 23320599. S2CID 525005.
- ^ "Drug Approval Package: Clorotekal (chloroprocaine HCl) Injection". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 21 March 2018. Retrieved 27 December 2024.
- ^ "Rediscovered Local Holds Promise for Spinal Anesthesia". Anesthesiology News. McMahon Publishing. 5 June 2013. Archived from the original on 29 September 2022. Retrieved 20 September 2013.
- ^ Philipson EH, Kuhnert BR, Syracuse CD (February 1985). "Fetal acidosis, 2-chloroprocaine, and epidural anesthesia for cesarean section". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 151 (3): 322–4. doi:10.1016/0002-9378(85)90295-9. PMID 3970100.
- ^ Chestnut DH (2004). Obstetric Anesthesia: Principles and Practice (3rd ed.). Philadelphia: Elsevier Mosby. p. 333. ISBN 978-0-323-02357-3.
- ^ Hughes SC, Levinson G, Rosen MA, eds. (2002). Shnider and Levinson's Anesthesia for Obstetrics (4th ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 75. ISBN 978-0-683-30665-1.
- ^ Vardanyan RS, Hruby VJ (January 2006). "Local anesthetics". Synthesis of Essential Drugs. Amsterdam: Elsevier. pp. 9–18. doi:10.1016/b978-044452166-8/50002-9. ISBN 978-0-444-52166-8.