Beryllium oxide (BeO), also known as beryllia, is an inorganic compound with the formula BeO. This colourless solid is an electrical insulator with a higher thermal conductivity than any other non-metal except diamond, and exceeds that of most metals.[12] As an amorphous solid, beryllium oxide is white. Its high melting point leads to its use as a refractory material.[13] It occurs in nature as the mineral bromellite. Historically and in materials science, beryllium oxide was called glucina or glucinium oxide, owing to its sweet taste.
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Beryllium(II) monoxide | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Oxoberyllium | |
| Other names
Beryllia, Thermalox, Bromellite, Thermalox 995.[1]
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 3902801 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.758 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | beryllium+oxide |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1566 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| BeO | |
| Molar mass | 25.011 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless, vitreous crystals |
| Odor | Odourless |
| Density | 3.01 g/cm3[2] |
| Melting point | 2,578 °C (4,672 °F; 2,851 K)[2] |
| Band gap | 10.6 eV[3] |
| −11.9·10−6 cm3/mol[4] | |
| Thermal conductivity | 210 W/(m·K)[5] |
Refractive index (nD)
|
n11.7184, n2=1.733[6][7] |
| Structure[8] | |
| Hexagonal, zincite | |
| P63mc | |
| C6v | |
a = 2.6979 Å, c = 4.3772 Å
| |
Formula units (Z)
|
2 |
| Linear | |
| Thermochemistry[9] | |
Heat capacity (C)
|
25.6 J/(K·mol) |
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
13.77±0.04 J/(K·mol) |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−609.4±2.5 kJ/mol |
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG⦵)
|
−580.1 kJ/mol |
Enthalpy of fusion (ΔfH⦵fus)
|
86 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Very toxic, Group 1B carcinogen |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H301, H315, H317, H319, H330, H335, H350, H372 | |
| P201, P260, P280, P284, P301+P310, P305+P351+P338 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
15 mg/kg (mouse, oral)[11] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 0.002 mg/m3 C 0.005 mg/m3 (30 minutes), with a maximum peak of 0.025 mg/m3 (as Be)[10] |
REL (Recommended)
|
Ca C 0.0005 mg/m3 (as Be)[10] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
Ca [4 mg/m3 (as Be)][10] |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Beryllium telluride |
Other cations
|
|
| Supplementary data page | |
| Beryllium oxide (data page) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Preparation and chemical properties
editBeryllium oxide can be prepared by calcining (roasting) beryllium carbonate, dehydrating beryllium hydroxide, or igniting metallic beryllium:
- BeCO3 → BeO + CO2
- Be(OH)2 → BeO + H2O
- 2 Be + O2 → 2 BeO
Igniting beryllium in air gives a mixture of BeO and the nitride Be3N2.[12] Unlike the oxides formed by the other Group 2 elements (alkaline earth metals), beryllium oxide is amphoteric rather than basic.
Beryllium oxide formed at high temperatures (>800 °C) is inert, but dissolves easily in hot aqueous ammonium bifluoride (NH4HF2) or a solution of hot concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and ammonium sulfate ((NH4)2SO4).
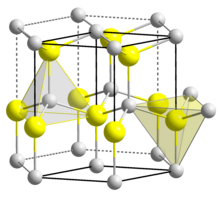
Structure
editBeO crystallizes in the hexagonal wurtzite structure, featuring tetrahedral Be2+ and O2− centres, like lonsdaleite and w-BN (with both of which it is isoelectronic). In contrast, the oxides of the larger group-2 metals, i.e., MgO, CaO, SrO, BaO, crystallize in the cubic rock salt motif with octahedral geometry about the dications and dianions.[12] At high temperature the structure transforms to a tetragonal form.[14]
In the vapour phase, beryllium oxide is present as discrete diatomic molecules. In the language of valence bond theory, these molecules can be described as adopting sp orbital hybridisation on both atoms, featuring one σ bond (between one sp orbital on each atom) and one π bond (between aligned p orbitals on each atom oriented perpendicular to the molecular axis). Molecular orbital theory provides a slightly different picture with no net σ bonding (because the 2s orbitals of the two atoms combine to form a filled sigma bonding orbital and a filled sigma* anti-bonding orbital) and two π bonds formed between both pairs of p orbitals oriented perpendicular to the molecular axis. The sigma orbital formed by the p orbitals aligned along the molecular axis is unfilled. The corresponding ground state is ...(2sσ)2(2sσ*)2(2pπ)4 (as in the isoelectronic C2 molecule), where both bonds can be considered as dative bonds from oxygen towards beryllium.[15]
Applications
editHigh-quality crystals may be grown hydrothermally, or otherwise by the Verneuil method. For the most part, beryllium oxide is produced as a white amorphous powder, sintered into larger shapes. Impurities, like carbon, can give rise to a variety of colours to the otherwise colourless host crystals.
Sintered beryllium oxide is a very stable ceramic.[16] Beryllium oxide is used in rocket engines[citation needed] and as a transparent protective over-coating on aluminised telescope mirrors. Metal-coated beryllium oxide (BeO) plates are used in the control systems of aircraft drive devices.[17]
Beryllium oxide is used in many high-performance semiconductor parts for applications such as radio equipment because it has good thermal conductivity while also being a good electrical insulator. It is used as a filler in some thermal interface materials such as thermal grease.[18] It is also employed in heat sinks and spreaders that cool electronic devices, such as CPUs, lasers, and power amplifiers.[19] Some power semiconductor devices have used beryllium oxide ceramic between the silicon chip and the metal mounting base of the package to achieve a lower value of thermal resistance than a similar construction of aluminium oxide. It is also used as a structural ceramic for high-performance microwave devices, vacuum tubes, cavity magnetrons [citation needed], and gas lasers. BeO has been proposed as a neutron moderator for naval marine high-temperature gas-cooled reactors (MGCR), as well as NASA's Kilopower nuclear reactor for space applications.[20]
Safety
editBeO is carcinogenic in powdered form[21] and may cause a chronic allergic-type lung disease berylliosis. Once fired into solid form, it is safe to handle if not subjected to machining that generates dust. Clean breakage releases little dust, but crushing or grinding actions can pose a risk.[22]
References
edit- ^ "beryllium oxide – Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 27 March 2005. Identification and Related records. Retrieved 8 November 2011.
- ^ a b Haynes, p. 4.51
- ^ Ryu, Y. R.; Lee, T. S.; Lubguban, J. A.; Corman, A. B.; White, H. W.; Leem, J. H.; Han, M. S.; Park, Y. S.; Youn, C. J.; Kim, W. J. (2006). "Wide-band gap oxide alloy: BeZnO". Applied Physics Letters. 88 (5): 052103. Bibcode:2006ApPhL..88e2103R. doi:10.1063/1.2168040.
- ^ Haynes, p. 4.126
- ^ Haynes, p. 12.222
- ^ Haynes, p. 10.248
- ^ Bromellite Mineral Data. webmineral
- ^ Haynes, p. 4.139
- ^ Haynes, pp. 5.1, 5.6, 6.155
- ^ a b c NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0054". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Beryllium oxide toxicity
- ^ a b c Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ Higgins, Raymond Aurelius (2006). Materials for Engineers and Technicians. Newnes. p. 301. ISBN 0-7506-6850-4.
- ^ Wells, A. F. (1984). Structural Inorganic Chemistry (5 ed.). Oxford Science Publications. ISBN 0-19-855370-6.
- ^ Fundamentals of Spectroscopy. Allied Publishers. p. 234. ISBN 978-81-7023-911-6. Retrieved 29 November 2011.
- ^ Petzow, Günter; Aldinger, Fritz; Jönsson, Sigurd; Welge, Peter; van Kampen, Vera; Mensing, Thomas; Brüning, Thomas (2005) "Beryllium and Beryllium Compounds" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a04_011.pub2
- ^ Trento, Chin (Dec 27, 2023). "What Are the Ceramic Materials With High Thermal Conductivity?". Stanford Advanced Materials. Retrieved Sep 3, 2024.
- ^ Greg Becker; Chris Lee; Zuchen Lin (2005). "Thermal conductivity in advanced chips — Emerging generation of thermal greases offers advantages". Advanced Packaging: 2–4. Archived from the original on June 21, 2000. Retrieved 2008-03-04.
- ^ "Beryllia (BeO)". Advanced Ceramic Materials. Retrieved Oct 18, 2024.
- ^ McClure, Patrick; Poston, David; Gibson, Marc; Bowman, Cheryl; Creasy, John (14 May 2014). "KiloPower Space Reactor Concept – Reactor Materials Study". Retrieved 21 November 2017.
- ^ "Hazardous Substance Fact Sheet" (PDF). New Jersey Department of Health and Senior Services. Retrieved August 17, 2018.
- ^ "Beryllium Oxide Safety". American Beryllia. Retrieved 2018-03-29.
Cited sources
edit- Haynes, William M., ed. (2016). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (97th ed.). CRC Press. ISBN 9781498754293.
