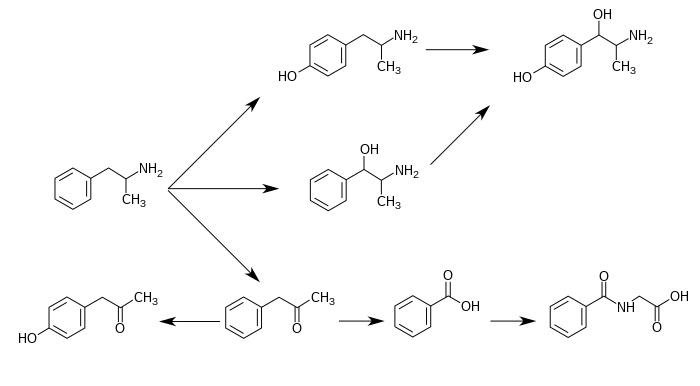
4-Hydroxyphenylacetone is the para-hydroxy analog of phenylacetone, an inactive metabolite of amphetamine in humans.[1][2] When it occurs as a metabolite of amphetamine, it is produced directly from the inactive metabolite phenylacetone.[1][3]

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)propan-2-one | |
| Other names
p-Hydroxyphenylacetone; para-Hydroxyphenylacetone
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.129.975 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H10O2 | |
| Molar mass | 150.177 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Metabolic pathways of amphetamine in humans[sources 1]
|
Notes
edit- ^ 4-Hydroxyamphetamine has been shown to be metabolized into 4-hydroxynorephedrine by dopamine beta-hydroxylase (DBH) in vitro and it is presumed to be metabolized similarly in vivo.[4][9] Evidence from studies that measured the effect of serum DBH concentrations on 4-hydroxyamphetamine metabolism in humans suggests that a different enzyme may mediate the conversion of 4-hydroxyamphetamine to 4-hydroxynorephedrine;[9][11] however, other evidence from animal studies suggests that this reaction is catalyzed by DBH in synaptic vesicles within noradrenergic neurons in the brain.[12][13]
Reference notes
editReferences
edit- ^ a b Santagati NA, Ferrara G, Marrazzo A, Ronsisvalle G (September 2002). "Simultaneous determination of amphetamine and one of its metabolites by HPLC with electrochemical detection". J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 30 (2): 247–55. doi:10.1016/S0731-7085(02)00330-8. PMID 12191709.
- ^ "4-Hydroxyphenylacetone". NCBI. PubChem Compound. Retrieved 25 October 2013.
- ^ a b "Adderall XR Prescribing Information" (PDF). United States Food and Drug Administration. Shire US Inc. December 2013. pp. 12–13. Retrieved 30 December 2013.
- ^ a b Glennon RA (2013). "Phenylisopropylamine stimulants: amphetamine-related agents". In Lemke TL, Williams DA, Roche VF, Zito W (eds.). Foye's principles of medicinal chemistry (7th ed.). Philadelphia, US: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 646–648. ISBN 9781609133450.
The simplest unsubstituted phenylisopropylamine, 1-phenyl-2-aminopropane, or amphetamine, serves as a common structural template for hallucinogens and psychostimulants. Amphetamine produces central stimulant, anorectic, and sympathomimetic actions, and it is the prototype member of this class (39). ... The phase 1 metabolism of amphetamine analogs is catalyzed by two systems: cytochrome P450 and flavin monooxygenase. ... Amphetamine can also undergo aromatic hydroxylation to p-hydroxyamphetamine. ... Subsequent oxidation at the benzylic position by DA β-hydroxylase affords p-hydroxynorephedrine. Alternatively, direct oxidation of amphetamine by DA β-hydroxylase can afford norephedrine.
- ^ Taylor KB (January 1974). "Dopamine-beta-hydroxylase. Stereochemical course of the reaction" (PDF). Journal of Biological Chemistry. 249 (2): 454–458. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)43051-2. PMID 4809526. Retrieved 6 November 2014.
Dopamine-β-hydroxylase catalyzed the removal of the pro-R hydrogen atom and the production of 1-norephedrine, (2S,1R)-2-amino-1-hydroxyl-1-phenylpropane, from d-amphetamine.
- ^ Krueger SK, Williams DE (June 2005). "Mammalian flavin-containing monooxygenases: structure/function, genetic polymorphisms and role in drug metabolism". Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 106 (3): 357–387. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2005.01.001. PMC 1828602. PMID 15922018.
Table 5: N-containing drugs and xenobiotics oxygenated by FMO - ^ Cashman JR, Xiong YN, Xu L, Janowsky A (March 1999). "N-oxygenation of amphetamine and methamphetamine by the human flavin-containing monooxygenase (form 3): role in bioactivation and detoxication". Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 288 (3): 1251–1260. PMID 10027866.
- ^ Santagati NA, Ferrara G, Marrazzo A, Ronsisvalle G (September 2002). "Simultaneous determination of amphetamine and one of its metabolites by HPLC with electrochemical detection". Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 30 (2): 247–255. doi:10.1016/S0731-7085(02)00330-8. PMID 12191709.
- ^ a b c Sjoerdsma A, von Studnitz W (April 1963). "Dopamine-beta-oxidase activity in man, using hydroxyamphetamine as substrate". British Journal of Pharmacology and Chemotherapy. 20 (2): 278–284. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb01467.x. PMC 1703637. PMID 13977820.
Hydroxyamphetamine was administered orally to five human subjects ... Since conversion of hydroxyamphetamine to hydroxynorephedrine occurs in vitro by the action of dopamine-β-oxidase, a simple method is suggested for measuring the activity of this enzyme and the effect of its inhibitors in man. ... The lack of effect of administration of neomycin to one patient indicates that the hydroxylation occurs in body tissues. ... a major portion of the β-hydroxylation of hydroxyamphetamine occurs in non-adrenal tissue. Unfortunately, at the present time one cannot be completely certain that the hydroxylation of hydroxyamphetamine in vivo is accomplished by the same enzyme which converts dopamine to noradrenaline.
- ^ Badenhorst CP, van der Sluis R, Erasmus E, van Dijk AA (September 2013). "Glycine conjugation: importance in metabolism, the role of glycine N-acyltransferase, and factors that influence interindividual variation". Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism & Toxicology. 9 (9): 1139–1153. doi:10.1517/17425255.2013.796929. PMID 23650932. S2CID 23738007.
Figure 1. Glycine conjugation of benzoic acid. The glycine conjugation pathway consists of two steps. First benzoate is ligated to CoASH to form the high-energy benzoyl-CoA thioester. This reaction is catalyzed by the HXM-A and HXM-B medium-chain acid:CoA ligases and requires energy in the form of ATP. ... The benzoyl-CoA is then conjugated to glycine by GLYAT to form hippuric acid, releasing CoASH. In addition to the factors listed in the boxes, the levels of ATP, CoASH, and glycine may influence the overall rate of the glycine conjugation pathway.
- ^ Horwitz D, Alexander RW, Lovenberg W, Keiser HR (May 1973). "Human serum dopamine-β-hydroxylase. Relationship to hypertension and sympathetic activity". Circulation Research. 32 (5): 594–599. doi:10.1161/01.RES.32.5.594. PMID 4713201. S2CID 28641000.
The biologic significance of the different levels of serum DβH activity was studied in two ways. First, in vivo ability to β-hydroxylate the synthetic substrate hydroxyamphetamine was compared in two subjects with low serum DβH activity and two subjects with average activity. ... In one study, hydroxyamphetamine (Paredrine), a synthetic substrate for DβH, was administered to subjects with either low or average levels of serum DβH activity. The percent of the drug hydroxylated to hydroxynorephedrine was comparable in all subjects (6.5-9.62) (Table 3).
- ^ Freeman JJ, Sulser F (December 1974). "Formation of p-hydroxynorephedrine in brain following intraventricular administration of p-hydroxyamphetamine". Neuropharmacology. 13 (12): 1187–1190. doi:10.1016/0028-3908(74)90069-0. PMID 4457764.
In species where aromatic hydroxylation of amphetamine is the major metabolic pathway, p-hydroxyamphetamine (POH) and p-hydroxynorephedrine (PHN) may contribute to the pharmacological profile of the parent drug. ... The location of the p-hydroxylation and β-hydroxylation reactions is important in species where aromatic hydroxylation of amphetamine is the predominant pathway of metabolism. Following systemic administration of amphetamine to rats, POH has been found in urine and in plasma.
The observed lack of a significant accumulation of PHN in brain following the intraventricular administration of (+)-amphetamine and the formation of appreciable amounts of PHN from (+)-POH in brain tissue in vivo supports the view that the aromatic hydroxylation of amphetamine following its systemic administration occurs predominantly in the periphery, and that POH is then transported through the blood-brain barrier, taken up by noradrenergic neurones in brain where (+)-POH is converted in the storage vesicles by dopamine β-hydroxylase to PHN. - ^ Matsuda LA, Hanson GR, Gibb JW (December 1989). "Neurochemical effects of amphetamine metabolites on central dopaminergic and serotonergic systems". Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 251 (3): 901–908. PMID 2600821.
The metabolism of p-OHA to p-OHNor is well documented and dopamine-β hydroxylase present in noradrenergic neurons could easily convert p-OHA to p-OHNor after intraventricular administration.
External links
edit- 4-hydroxyphenylacetone at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)