The national flag of Japan is a rectangular white banner with a crimson-red circle at its center. The flag is officially called the Nisshōki (日章旗, 'flag of the sun') but is more commonly known in Japan as the Hinomaru (日の丸, 'ball of the sun'). It embodies the country's sobriquet: the Land of the Rising Sun.
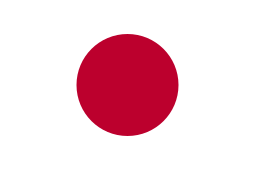 | |
| Nisshōki or Hinomaru | |
| Use | Civil and state flag, civil and state ensign |
|---|---|
| Proportion | 2:3 |
| Adopted | |
| Design | A crimson disc centered on a white field |
The Nisshōki flag is designated as the national flag in the Act on National Flag and Anthem, which was promulgated and became effective on 13 August 1999. Although no earlier legislation had specified a national flag, the sun-disc flag had already become the de facto national flag of Japan. Two proclamations issued in 1870 by the Daijō-kan, the governmental body of the early Meiji period, each had a provision for a design of the national flag. A sun-disc flag was adopted as the national flag for merchant ships under Proclamation No. 57 of Meiji 3 (issued on 27 January 1870),[1] and as the national flag used by the Navy under Proclamation No. 651 of Meiji 3 (issued on 3 October 1870).[2] Use of the Hinomaru was severely restricted during the early years of the Allied occupation of Japan after World War II; these restrictions were later relaxed.
The sun plays an important role in Japanese mythology and religion, as the Emperor is said to be the direct descendant of the Shinto sun goddess Amaterasu, and the legitimacy of the ruling house rested on this divine appointment. The name of the country as well as the design of the flag reflect this central importance of the sun. The ancient history Shoku Nihongi says that Emperor Monmu used a flag representing the sun in his court in 701, the first recorded use of a sun-motif flag in Japan.[3][4] The oldest existing flag is preserved in Unpō-ji temple, Kōshū, Yamanashi, which is older than the 16th century, and an ancient legend says that the flag was given to the temple by Emperor Go-Reizei in the 11th century.[5][6][7] During the Meiji Restoration, the sun disc and the Rising Sun Ensign of the Imperial Japanese Navy and Army became major symbols in the emerging Japanese Empire. Propaganda posters, textbooks, and films depicted the flag as a source of pride and patriotism. In Japanese homes, citizens were required to display the flag during national holidays, celebrations and other occasions as decreed by the government. Different tokens of devotion to Japan and its Emperor featuring the Hinomaru motif became popular among the public during the Second Sino-Japanese War and other conflicts. These tokens ranged from slogans written on the flag to clothing items and dishes that resembled the flag.
Public perception of the national flag varies. Historically, both Western and Japanese sources have described the flag as a powerful and enduring symbol to the Japanese. Since the end of World War II (the Pacific War), the use of the flag and the national anthem Kimigayo has been a contentious issue for Japan's public schools, and disputes about their use have led to protests and lawsuits. Several military banners of Japan are based on the Hinomaru, including the sunrayed naval ensign. The Hinomaru also serves as a template for other Japanese flags in public and private use.
History
editAncient to medieval
editThe exact origin of the Hinomaru is unknown,[8] but the rising sun has carried symbolic meaning since the early 7th century. Japan is often referred to as "the land of the rising sun".[9] The Japanese archipelago is east of the Asian mainland, and is thus where the sun "rises". In 607, an official correspondence that began with "from the Emperor of the rising sun" was sent to the Chinese Emperor Yang of Sui.[10]
The sun is closely related to the Imperial family, as legend states the imperial throne was descended from the sun goddess Amaterasu.[11][12] The religion, which is categorized as the ancient Ko-Shintō religion of the Japanese people, includes nature worship and animism, and the faith has been worshiping the sun, especially in agriculture and fishing. The Imperial God, Amaterasu-ōmikami, is the sun goddess. From the Yayoi period (300 BCE) to the Kofun period (250 CE) (Yamato period), the Naikō Kamonkyō, a large bronze mirror with patterns like a flower-petal, was used as a celebration of the shape of the shining sun and there is a theory that one of the Three Sacred Treasures, Yata no Kagami, is used like this mirror.[13]
During the Eastern expedition, Emperor Jimmu's brother Itsuse no Mikoto was killed in a battle against the local chieftain Nagasunehiko ("the long-legged man") in Naniwa (modern-day Osaka). Emperor Jimmu realized, as a descendant of the sun, that he did not want to fight towards the sun (to the east), but to fight from the sun (to the west). The Emperor's clan therefore went to the east side of Kii Peninsula to battle westward. They reached Kumano (or Ise) and went towards Yamato. They were victorious at the second battle with Nagasunehiko and conquered the Kinki region.[14][15]
The use of the sun-shaped flag was thought to have taken place since the emperor's direct imperial rule (親政) was established after the Isshi Incident in 645 (first year of the Taika).[16]
The Japanese history text Shoku Nihongi, completed in 797, has the first recorded use of the sun-motif flag by Emperor Monmu's Chōga (朝賀, 'new year's greetings ceremony') in 701 (the first year of the Taihō era).[3][4] For the decoration of the ceremony hall on New Year's Day the Nissho (日像, 'the flag with the golden sun') was raised.[3][4]
One prominent theory is influenced by the results of the Genpei War (1180–1185).[17] Until the Heian period, the Nishiki flag (錦の御旗, Nishiki no mihata), a symbol of the Imperial Court, had a golden sun circle and a silver moon circle on a red background.[17] At the end of the Heian era, the Taira clan called themselves a government army and used the red flag with a gold circle (赤地金丸) as per the Imperial Court.[17] The Genji (Minamoto clan) were in opposition so they used a white flag with a red circle (白地赤丸) when they fought the Genpei War (1180–1185).[17] When the Taira clan was defeated, the samurai government (幕府, bakufu) was formed by the Genji.[17] The warlords who came after such as Oda Nobunaga and Tokugawa Ieyasu realized they were successors of Genji, and so raised the Hinomaru flag in battle.[17]
In the 12th-century work The Tale of the Heike, it was written that different samurai carried drawings of the sun on their fans.[18] One legend related to the national flag is attributed to the Buddhist priest Nichiren. Supposedly, during a 13th-century Mongolian invasion of Japan, Nichiren gave a sun banner to the shōgun to carry into battle.[19]
During the Battle of Nagashino (28 June 1575), Oda Nobunaga and Tokugawa Ieyasu's allied forces fought Takeda Katsuyori.[17] Both Nobunaga and Ieyasu had their own flags with family crests, but they also held the Hinomaru.[17] On the other hand, the Takeda clan side also raised the Hinomaru.[17] Therefore, the Hinomaru was used as a national symbol.[17]
One of Japan's oldest flags is housed at the Unpo-ji temple in Kōshū city, Yamanashi Prefecture.[17] Legend states it was given by Emperor Go-Reizei to Minamoto no Yoshimitsu and has been treated as a family treasure by the Takeda clan for the past 1,000 years,[17][20] and is at least older than 16th century.
In the 16th century unification period, each daimyō had flags that were used primarily in battle. Most of the flags were long banners usually charged with the mon (family crest) of the daimyō lord. Members of the same family would have had different flags to carry into battle. The flags served as identification and were displayed by soldiers on their backs and horses. Generals also had their own flags, most of which differed from soldiers' flags due to their square shape.[21][page needed]
In 1854, during the Tokugawa shogunate, Japanese ships were ordered to hoist the Hinomaru to distinguish themselves from foreign ships.[18] Before then, different types of Hinomaru flags were used on vessels that were trading with the U.S. and Russia.[8] The Hinomaru was decreed the merchant flag of Japan in 1870 and was the legal national flag from 1870 to 1885, making it the first national flag Japan adopted.[22][23]
While the idea of national symbols was strange to the Japanese, the Meiji Government needed them to communicate with the outside world. This became especially important after the landing of U.S. Commodore Matthew Perry in Yokohama Bay.[24] Further Meiji Government implementations gave more identifications to Japan, including the anthem Kimigayo and the imperial seal.[25] In 1885, all previous laws not published in the Official Gazette of Japan were abolished.[26] Because of this ruling by the new cabinet of Japan, the Hinomaru was the de facto national flag since no law was in place after the Meiji Restoration.[27]
Early conflicts and the Pacific War
editThe use of the national flag grew as Japan sought to develop an empire, and the Hinomaru was present at celebrations after victories in the First Sino-Japanese and Russo-Japanese Wars. The flag was also used in war efforts throughout the country.[28] A Japanese propaganda film in 1934 portrayed foreign national flags as incomplete or defective with their designs, whilst portraying the Japanese flag as perfect in all forms.[29] In 1937, a group of girls from Hiroshima Prefecture showed solidarity with Japanese soldiers fighting in China during the Second Sino-Japanese War, by eating "flag meals" that consisted of an umeboshi in the middle of a bed of rice. The Hinomaru bento became the main symbol of Japan's war mobilization and solidarity with its soldiers until the 1940s.[30]
Japan's early victories in the Sino-Japanese War resulted in the Hinomaru again being used for celebrations. It was seen in the hands of every Japanese during parades.[28]
Textbooks during this period also had the Hinomaru printed with various slogans expressing devotion to the Emperor and the country. Patriotism was taught as a virtue to Japanese children. Expressions of patriotism, such as displaying the flag or worshiping the Emperor daily, were all part of being a "good Japanese".[31]
The flag was a tool of Japanese imperialism in the occupied Southeast Asian areas during the Second World War: people had to use the flag,[32] and schoolchildren sang Kimigayo in morning flag raising ceremonies.[33] Local flags were allowed for some areas such as the Philippines, Indonesia, and Manchukuo.[34][35][36] In Korea which was part of the Empire of Japan, the Hinomaru and other symbols were used to declare that the Koreans were subjects of the empire.[37]
During the Pacific War, Americans coined the derogatory term "meatballs" for the Hinomaru and Japanese military aircraft insignia.[38] To the Japanese, the Hinomaru was the "Rising Sun flag that would light the darkness of the entire world".[39] To Westerners, it was one of the Japanese military's most powerful symbols.[40]
U.S. occupation
editRight: The civil and naval ensign of occupied Japan. The Hinomaru simultaneously remained in de facto use.
The Hinomaru was the de facto flag of Japan throughout World War II and the occupation period.[27] During the occupation of Japan after World War II, permission from the Supreme Commander of the Allied Powers (SCAPJ) was needed to fly the Hinomaru.[41][42] Sources differ on the degree to which the use of the Hinomaru flag was restricted; some use the term "banned;"[43][44] however, while the original restrictions were severe, they did not amount to an outright ban.[27]
After World War II, an ensign was used by Japanese civil ships of the United States Naval Shipping Control Authority for Japanese Merchant Marines.[45] Modified from the "E" signal code, the ensign was used from September 1945 until the U.S. occupation of Japan ceased.[46] U.S. ships operating in Japanese waters used a modified "O" signal flag as their ensign.[47]
On 2 May 1947, General Douglas MacArthur lifted the restrictions on displaying the Hinomaru in the grounds of the National Diet Building, on the Imperial Palace, on the Prime Minister's residence, and on the Supreme Court building with the ratification of the new Constitution of Japan.[48][49] Those restrictions were further relaxed in 1948, when people were allowed to fly the flag on national holidays. In January 1949, the restrictions were abolished and anyone could fly the Hinomaru at any time without permission. As a result, schools and homes were encouraged to fly the Hinomaru until the early 1950s.[41]
Postwar to 1999
editSince World War II, Japan's flag has been criticized for its association with the country's militaristic past. Similar objections have also been raised to the current national anthem of Japan, Kimigayo.[20] The feelings about the Hinomaru and Kimigayo represented a general shift from a patriotic feeling about Dai Nippon (Great Japan) to the pacifist and anti-militarist Nihon. Because of this ideological shift, the flag was used less often in Japan directly after the war even though restrictions were lifted by the SCAPJ in 1949.[42][50]
As Japan began to re-establish itself diplomatically, the Hinomaru was used as a political weapon overseas. In a visit by Emperor Hirohito and Empress Kōjun to the Netherlands, the Hinomaru was burned by Dutch citizens who demanded that he either be sent home to Japan or tried for the deaths of Dutch prisoners of war during the Second World War.[51] Domestically, the flag was not even used in protests against a new Status of Forces Agreement being negotiated between the U.S. and Japan. The most common flag used by the trade unions and other protesters was the red flag of revolt.[52]
An issue with the Hinomaru and national anthem was raised once again when Tokyo hosted the 1964 Summer Olympic Games. Before the Olympic Games, the size of the sun disc of the national flag was changed partly because the sun disc was not considered striking when it was being flown with other national flags.[42] Tadamasa Fukiura, a color specialist, chose to set the sun disc at two-thirds of the flag's length. Fukiura also chose the flag colors for the 1964 games as well as for the 1998 Winter Olympics in Nagano.[53]
In 1989, the death of Emperor Hirohito once again raised moral issues about the national flag. Conservatives felt that if the flag could be used during the ceremonies without reopening old wounds, they might have a chance to propose that the Hinomaru become the national flag without being challenged about its meaning.[54] During an official six-day mourning period, flags were flown at half staff or draped in black bunting all across Japan.[55] Despite reports of protesters vandalizing the Hinomaru on the day of the Emperor's funeral,[56] schools' right to fly the Japanese flag at half-staff without reservations brought success to the conservatives.[54]
Since 1999
editThe Law Regarding the National Flag and National Anthem was passed in 1999, choosing both the Hinomaru and Kimigayo as Japan's national symbols. The passage of the law stemmed from the suicide of the principal of Sera High School in Sera, Hiroshima, Toshihiro Ishikawa, who could not resolve a dispute between his school board and his teachers over the use of the Hinomaru and Kimigayo.[57][58] The Act is one of the most controversial laws passed by the Diet since the 1992 "Law Concerning Cooperation for United Nations Peacekeeping Operations and Other Operations", also known as the "International Peace Cooperation Law".[59]
Prime Minister Keizō Obuchi of the Liberal Democratic Party (LDP) decided to draft legislation to make the Hinomaru and Kimigayo official symbols of Japan in 2000. His Chief Cabinet Secretary, Hiromu Nonaka, wanted the legislation to be completed by the 10th anniversary of Emperor Akihito's enthronement.[60] This is not the first time legislation was considered for establishing both symbols as official. In 1974, with the backdrop of the 1972 return of Okinawa to Japan and the 1973 oil crisis, Prime Minister Kakuei Tanaka hinted at a law being passed enshrining both symbols in the law of Japan.[61] In addition to instructing the schools to teach and play Kimigayo, Tanaka wanted students to raise the Hinomaru flag in a ceremony every morning, and to adopt a moral curriculum based on certain elements of the Imperial Rescript on Education pronounced by the Meiji Emperor in 1890.[62] Tanaka was unsuccessful in passing the law through the Diet that year.[63]
The main supporters of the bill were the LDP and the Komeito (CGP), while the opposition included the Social Democratic Party (SDPJ) and Communist Party (JCP), who cited the connotations both symbols had with the war era. The CPJ was further opposed for not allowing the issue to be decided by the public. Meanwhile, the Democratic Party of Japan (DPJ) could not develop party consensus on it. DPJ President and future prime minister Naoto Kan stated that the DPJ must support the bill because the party already recognized both symbols as the symbols of Japan.[64] Deputy Secretary General and future prime minister Yukio Hatoyama thought that this bill would cause further divisions among society and the public schools. Hatoyama voted for the bill while Kan voted against it.[60]
Before the vote, there were calls for the bills to be separated at the Diet. Waseda University professor Norihiro Kato stated that Kimigayo is a separate issue more complex than the Hinomaru flag.[65] Attempts to designate only the Hinomaru as the national flag by the DPJ and other parties during the vote of the bill were rejected by the Diet.[66] The House of Representatives passed the bill on 22 July 1999, by a 403 to 86 vote.[67] The legislation was sent to the House of Councilors on 28 July and was passed on 9 August. It was enacted into law on 13 August.[68]
On 8 August 2009, a photograph was taken at a DPJ rally for the House of Representatives election showing a banner that was hanging from a ceiling. The banner was made of two Hinomaru flags cut and sewn together to form the shape of the DPJ logo. This infuriated the LDP and Prime Minister Tarō Asō, saying this act was unforgivable. In response, DPJ President Yukio Hatoyama (who voted for the Law Regarding the National Flag and National Anthem)[60] said that the banner was not the Hinomaru and should not be regarded as such.[69]
Flag design
editPassed in 1870, the Prime Minister's Proclamation No. 57 had two provisions related to the national flag. The first provision specified who flew the flag and how it was flown; the second specified how the flag was made.[8] The ratio was seven units width and ten units length (7:10). The red disc, which represents the sun, was calculated to be three-fifths of the hoist width. The law decreed the disc to be in the center, but it was usually placed one-hundredth (1⁄100) towards the hoist.[70][71] (This makes the disc appear centered when the flag is flying; this technique is used in other flags, such as those of Bangladesh and Palau.) On 3 October of the same year, regulations about the design of the merchant ensign and other naval flags were passed.[72] For the merchant flag, the ratio was two units width and three units length (2:3). The size of the disc remained the same, but the sun disc was placed one-twentieth (1⁄20) towards the hoist.[73]
When the Law Regarding the National Flag and National Anthem passed, the dimensions of the flag were slightly altered.[74] The overall ratio of the flag was changed to two units width by three units length (2:3). The red disc was shifted towards the center, but the overall size of the disc stayed the same.[75] The background of the flag is white and the center is a red circle (紅色, beni iro), but the exact color shades were not defined in the 1999 law.[74] The only hint given about the red colour is that it is a "deep" shade.[76]
Issued by the Japan Defense Agency (now the Ministry of Defense) in 1973 (Shōwa 48), specifications list the red color of the flag as 5R 4/12 and the white as N9 in the Munsell color chart.[77] The document was changed on 21 March 2008 (Heisei 20) to match the flag's construction with current legislation and updated the Munsell colours. The document lists acrylic fiber and nylon as fibers that could be used in construction of flags used by the military. For acrylic, the red color is 5.7R 3.7/15.5 and white is N9.4; nylon has 6.2R 4/15.2 for red and N9.2 for white.[77] In a document issued by the Official Development Assistance (ODA), the red color for the Hinomaru and the ODA logo is listed as DIC 156 and CMYK 0-100-90-0.[78] During deliberations about the Law Regarding the National Flag and National Anthem, there was a suggestion to either use a bright red (赤色, aka iro) shade or use one from the color pool of the Japanese Industrial Standards.[79]
Colour chart
edit| Official colour (white) | Official colour (red) | Colour system | Source | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N9[80] | 5R 4/12[80] | Munsell | DSP Z 8701C[77] | 1973 |
| N/A | 156[81] | DIC | ODA Symbol Mark Guidelines[78] | 1995 |
Use and customs
editWhen the Hinomaru was first introduced, the government required citizens to greet the Emperor with the flag. There was some resentment among the Japanese over the flag,[why?] resulting in some protests. It took some time for the flag to gain acceptance among the people.[25]
Before World War II, all homes were required to display Hinomaru on national holidays.[27] Since the war, the display of the flag of Japan is mostly limited to buildings attached to national and local governments such as city halls; it is rarely seen at private homes or commercial buildings,[27] but some people and companies have advocated displaying the flag on holidays. Although the government of Japan encourages citizens and residents to fly the Hinomaru during national holidays, they are not legally required to do so.[82][83] Since the Emperor's 80th birthday on 23 December 2002, the Kyushu Railway Company has displayed the Hinomaru at 330 stations.[84]
Starting in 1995, the ODA has used the Hinomaru motif in their official logo. The design itself was not created by the government (the logo was chosen from 5,000 designs submitted by the public) but the government was trying to increase the visualization of the Hinomaru through their aid packages and development programs. According to the ODA, the use of the flag is the most effective way to symbolise aid provided by the Japanese people.[85]
Hinomaru Yosegaki
editDuring World War II, it was a popular custom for friends, classmates, and relatives of a deploying soldier to sign a Hinomaru and present it to him. The flag was also used as a good luck charm and a prayer to wish the soldier back safely from battle. One term for this kind of charm is Hinomaru Yosegaki (日の丸寄せ書き).[86] One tradition is that no writing should touch the sun disc.[87] After battles, these flags were often captured or later found on deceased Japanese soldiers. Some of these flags have become souvenirs,[87] and some have been returned to Japan and the descendants of the deceased.[88]
In modern times, the Hinomaru Yosegaki is still being used. The tradition of signing the Hinomaru as a good luck charm still continues, though in a limited fashion. The Hinomaru Yosegaki is shown at sporting events to give support to the Japanese national team.[89] The Yosegaki (寄せ書き, group effort flag) is used for campaigning soldiers,[90] athletes, retirees, transfer students in a community and for friends. The colored paper and flag has writing with a message. In modern Japan, it is given as a present to a person at a send-off party, for athletes, a farewell party for colleagues or transfer students, for graduation and retirement. After natural disasters such as the 2011 Tōhoku Earthquake and tsunami people write notes on a Hinomaru Yosegaki to show support.
Hachimaki
editThe hachimaki (鉢巻, 'helmet-scarf') is a white headband (bandana) with the red sun in the middle. Phrases are usually written on it. It is worn as a symbol of perseverance, effort, and/or courage by the wearer. These are worn on many occasions by for example sports spectators, women giving birth, students in cram school, office workers,[91] tradesmen taking pride in their work etc. During World War II, the phrases "Certain Victory" (必勝, Hisshō) or "Seven Lives" was written on the hachimaki and worn by kamikaze pilots. This denoted that the pilot was willing to die for his country.[92]
Hinomaru bentō
editBentō and makunouchi are types of Japanese lunch boxes, which can feature Hinomaru rice (日の丸ご飯, Hinomaru gohan). The Hinomaru bentō consists of gohan (steamed white rice) with a red umeboshi (dried plum) in the center which represents the sun and the flag of Japan. A Hinomaru lunch box (日の丸弁当, Hinomaru bentō) only has white rice and a red umeboshi in the center. The salty, vinegar-soaked umeboshi acts as a preservative for the rice. There are also Hinomaru rice bowls, which are less common.[93]
Culture and perception
editAccording to polls conducted by mainstream media, most Japanese people had perceived the flag of Japan as the national flag even before the passage of the Law Regarding the National Flag and National Anthem in 1999.[94] Despite this, controversies surrounding the use of the flag in school events or media still remain. For example, liberal newspapers such as the Asahi Shimbun and Mainichi Shimbun often feature articles critical of the flag of Japan, reflecting their readerships' political spectrum.[95] To other Japanese, the flag represents the time where democracy was suppressed when Japan was an empire.[96]
The display of the national flag at homes and businesses is also debated in Japanese society. Because of its association with uyoku dantai (right wing) activists, reactionary politics, or hooliganism, most homes and businesses do not fly the flag.[27] There is no requirement to fly the flag on any national holiday or special events. The town of Kanazawa, Ishikawa proposed plans in September 2012 to use government funds to buy flags with the purpose of encouraging citizens to fly the flag on national holidays.[97]
Negative perceptions of the national flag exist in former colonies of Japan as well as within Japan itself, such as in Okinawa Prefecture. In one notable example of this, on 26 October 1987, an Okinawan supermarket owner burned the flag before the start of the National Sports Festival of Japan.[98] The flag burner, Shōichi Chibana, burned the Hinomaru not only to show opposition to atrocities committed by the Japanese army and the continued presence of U.S. forces but also to prevent it from being displayed in public.[99] Other incidents in Okinawa included the flag being torn down during school ceremonies and students refusing to honor the flag as it was being raised to the sounds of Kimigayo.[28] In the capital city of Naha, Okinawa, the Hinomaru was raised for the first time since the return of Okinawa to Japan to celebrate the city's 80th anniversary in 2001.[100] In the People's Republic of China and Republic of Korea, both of which had been occupied by the Empire of Japan, the 1999 formal adoption of the Hinomaru was met with reactions of Japan moving towards the right and also a step towards re-militarization. The passage of the 1999 law also coincided with the debates about the status of the Yasukuni Shrine, U.S.-Japan military cooperation, and the creation of a missile defense program. In other nations that Japan occupied, the 1999 law was met with mixed reactions or glossed over. In Singapore, the older generation still harbors ill feelings toward the flag while the younger generation does not hold similar views. The Philippine government not only believed that Japan was not going to revert to militarism, but the goal of the 1999 law was to formally establish two symbols (the flag and anthem) in law and every state has a right to create national symbols.[101] Japan has no law criminalizing the burning of the Hinomaru, whereas foreign flags cannot be burned in Japan.[102][103]
Protocol
editAccording to protocol, the flag may fly from sunrise until sunset; businesses and schools are permitted to fly the flag from opening to closing. When flying the flags of Japan and another country at the same time in Japan, the Japanese flag takes the position of honor and the flag of the guest country flies to its right. Both flags must be at the same height and of equal size. When more than one foreign flag is displayed, Japan's flag is arranged in the alphabetical order prescribed by the United Nations.[104] When the flag becomes unsuitable to use, it is customarily burned in private. The Law Regarding the National Flag and Anthem does not specify on how the flag should be used, but different prefectures came up with their own regulations to use the Hinomaru and other prefectural flags.[105][106]
Mourning
editThe Hinomaru flag has at least two mourning styles. One is to display the flag at half-staff (半旗, han-ki), as is common in many countries. The offices of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs also hoist the flag at half-staff when a funeral is performed for a foreign nation's head of state.[107]
An alternative mourning style is to wrap the spherical finial with black cloth and place a black ribbon, known as a mourning flag (弔旗 [ja], chō-ki), above the flag. This style dates back to the death of Emperor Meiji on 30 July 1912, and the Cabinet issued an ordinance stipulating that the national flag should be raised in mourning when the Emperor dies.[108] The Cabinet has the authority to announce the half-staffing of the national flag.[109]
Public schools
editSince the end of World War II, the Ministry of Education has issued statements and regulations to promote the usage of both the Hinomaru and Kimigayo (national anthem) at schools under their jurisdiction. The first of these statements was released in 1950, stating that it was desirable, but not required, to use both symbols. This desire was later expanded to include both symbols on national holidays and during ceremonial events to encourage students on what national holidays are and to promote defense education.[42] In a 1989 reform of the education guidelines, the LDP-controlled government first demanded that the flag must be used in school ceremonies and that proper respect must be given to it and to Kimigayo.[110] Punishments for school officials who did not follow this order were also enacted with the 1989 reforms.[42]
The 1999 curriculum guideline issued by the Ministry of Education after the passage of the Law Regarding the National Flag and Anthem decrees that "on entrance and graduation ceremonies, schools must raise the flag of Japan and instruct students to sing the Kimigayo, given the significance of the flag and the song."[111] Additionally, the ministry's commentary on the 1999 curriculum guideline for elementary schools note that "given the advance of internationalization, along with fostering patriotism and awareness of being Japanese, it is important to nurture school children's respectful attitude toward the flag of Japan and Kimigayo as they grow up to be respected Japanese citizens in an internationalized society."[112] The ministry also stated that if Japanese students cannot respect their own symbols, then they will not be able to respect the symbols of other nations.[113]
Schools have been the center of controversy over both the anthem and the national flag.[43] The Tokyo Board of Education requires the use of both the anthem and flag at events under their jurisdiction. The order requires school teachers to respect both symbols or risk losing their jobs.[114] Some have protested that such rules violate the Constitution of Japan, but the Board has argued that since schools are government agencies, their employees have an obligation to teach their students how to be good Japanese citizens.[20] As a sign of protest, schools refused to display the Hinomaru at school graduations and some parents ripped down the flag.[43] Teachers have unsuccessfully brought criminal complaints against Tokyo Governor Shintarō Ishihara and senior officials for ordering teachers to honor the Hinomaru and Kimigayo.[115] After earlier opposition, the Japan Teachers Union accepts the use of both the flag and anthem; the smaller All Japan Teachers and Staffs Union still opposes both symbols and their use inside the school system.[116]
Related flags
editMilitary flags
editThe Japan Self-Defense Forces (JSDF) and the Japan Ground Self-Defense Force use the Rising Sun Flag with eight red rays extending outward, called Hachijō-Kyokujitsuki (八条旭日旗). A gold border is situated partially around the edge.[117]
A well-known variant of the sun disc design is the sun disc with 16 red rays in a Siemens star formation, which was also historically used by Japan's military, particularly the Imperial Japanese Army and the Imperial Japanese Navy. The ensign, known in Japanese as the Jyūrokujō-Kyokujitsuki (十六条旭日旗), was first adopted as the war flag on 15 May 1870, and was used until the end of World War II in 1945. It was re-adopted on 30 June 1954, and is now used as the war flag and naval ensign of the Japan Ground Self-Defense Force (JGSDF) and the Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force (JMSDF).[117] JSDF Chief of Staff Katsutoshi Kawano said the Rising Sun Flag is the Maritime Self-Defense Force sailors' "pride".[118] Due to its continued use by the Imperial Japanese Army, this flag carries the negative connotation similar to the Nazi flag in China and Korea.[119] These formerly colonised countries state that this flag is a symbol of Japanese imperialism during World War II, and was an ongoing conflict event for the 2020 Tokyo Olympics. The JMSDF also employs the use of a masthead pennant. First adopted in 1914 and readopted in 1965, the masthead pennant contains a simplified version of the naval ensign at the hoist end, with the rest of the pennant colored white. The ratio of the pennant is between 1:40 and 1:90.[120]
The Japan Air Self-Defense Force (JASDF), established independently in 1952, has only the plain sun disc as its emblem.[121] This is the only branch of service with an emblem that does not invoke the rayed Imperial Standard. However, the branch does have an ensign to fly on bases and during parades. The Japan Air Self-Defense Force flag was first adopted in 1955 after the JASDF was created in 1954. The flag is cobalt blue with a gold winged eagle on top of a combined star, the moon, the Hinomaru sun disc and clouds.[122][123] The latest version of the JASDF flag was re-adopted on 19 March 2001.[124]
Although not an official national flag, the Z signal flag played a major role in Japanese naval history. On 27 May 1905, Admiral Heihachirō Tōgō of the Mikasa was preparing to engage the Russian Baltic Fleet. Before the Battle of Tsushima began, Togo raised the Z flag on the Mikasa and engaged the Russian fleet, winning the battle for Japan. The raising of the flag said to the crew the following: "The fate of Imperial Japan hangs on this one battle; all hands will exert themselves and do their best." The Z flag was also raised on the aircraft carrier Akagi on the eve of Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, in December 1941.[125]
-
Post WWII flag of the Japan Air Self-Defense Force (JASDF)
-
Pre-WWII roundel (military aircraft insignia) of Navy and Army military aircraft
-
Post WWII roundel of the JASDF
Imperial flags
editBeginning in 1870, flags were created for the Japanese Emperor (then Emperor Meiji), the Empress, and other members of the imperial family.[126] At first, the Emperor's flag was ornate, with a sun resting in the center of an artistic pattern. He had flags that were used on land, at sea, and when he was in a carriage. The imperial family was also granted flags to be used at sea and while on land (one for use on foot and one carriage flag). The carriage flags were a monocolored chrysanthemum, with 16 petals, placed in the center of a monocolored background.[72] These flags were discarded in 1889 when the Emperor decided to use the chrysanthemum on a red background as his flag. With minor changes in the color shades and proportions, the flags adopted in 1889 are still in use by the imperial family.[127][128]
The current Emperor's flag is a 16-petal chrysanthemum (菊花紋, Kikkamon), colored in gold, centered on a red background with a 2:3 ratio. The Empress uses the same flag, except the shape is that of a swallow tail. The crown prince and the crown princess use the same flags, except with a smaller chrysanthemum and a white border in the middle of the flags.[129] The chrysanthemum has been associated with the Imperial throne since the rule of Emperor Go-Toba in the 12th century, but it did not become the exclusive symbol of the Imperial throne until 1868.[126]
Subnational flags
editEach of the 47 prefectures of Japan has its own flag which, like the national flag, consists of a symbol – called a mon – charged upon a monocolored field (except for Ehime Prefecture, where the background is bicolored).[130] There are several prefecture flags, such as Hiroshima's, that match their specifications to the national flag (2:3 ratio, mon placed in the center and is 3⁄5 the length of the flag).[131] Some of the mon display the name of the prefecture in Japanese characters; others are stylized depictions of the location or another special feature of the prefecture. An example of a prefectural flag is that of Nagano, where the orange katakana character na (ナ) appears in the center of a white disc. One interpretation of the mon is that the na symbol represents a mountain and the white disc, a lake. The orange color represents the sun while the white color represents the snow of the region.[132]
Municipalities can also adopt flags of their own. The designs of the city flags are similar to the prefectural flags: a mon on a monocolored background. An example is the flag of Amakusa in Kumamoto Prefecture: the city symbol is composed of the katakana character a (ア)✓and surrounded by waves.[133] This symbol is centered on a white flag, with a ratio of 2:3.[134] Both the city emblem and the flag were adopted in 2006.[134]
Derivatives
editIn addition to the flags used by the military, several other flag designs were inspired by the national flag. The former Japan Post flag consisted of the Hinomaru with a red horizontal bar placed in the center of the flag. There was also a thin white ring around the red sun. It was later replaced by a flag that consisted of the 〒 postal mark in red on a white background.[135]
Two recently-designed national flags resemble the Japanese flag. In 1971, Bangladesh gained independence from Pakistan, and it adopted a national flag that had a green background, charged with an off-centered red disc that contained a golden map of Bangladesh. The current flag, adopted in 1972, dropped the golden map and kept everything else. The Government of Bangladesh officially calls the red disc a circle;[136] the red color symbolizes the blood that was shed to create their country.[137] The island nation of Palau uses a flag of similar design, but the color scheme is completely different. While the Government of Palau does not cite the Japanese flag as an influence on their national flag, Japan did administer Palau from 1914 until 1944.[138] The flag of Palau is an off-centered golden-yellow full moon on a sky blue background.[139] The moon stands for peace and a young nation while the blue background represents Palau's transition to self-government from 1981 to 1994, when it achieved full independence.[140]
The Japanese naval ensign also influenced other flag designs. One such flag design is used by the Asahi Shimbun. At the bottom hoist of the flag, one quarter of the sun is displayed. The kanji character 朝 is displayed on the flag, colored white, covering most of the sun. The rays extend from the sun, occurring in a red and white alternating order, culminating in 13 total stripes.[141][142] The flag is commonly seen at the National High School Baseball Championship, as the Asahi Shimbun is a main sponsor of the tournament.[143] The rank flags and ensigns of the Imperial Japanese Navy also based their designs on the naval ensign.[144]
Gallery
edit-
Japanese flag at the Meiji Memorial
-
Japan Self-Defense Forces honor guards holding the national flag during Mike Pence's visit.
-
Flags of Japan and other G7 states flying in Toronto
-
A series of Japanese flags in a school entrance
-
Yokohama City (left) and the Hinomaru (center) flying on Yokohama Harbor
-
Firefighters in Tokyo holding the Japanese national flag during a ceremony
-
Large flags of Japan at the Tokyo Olympic Stadium during the final match of the East Asian Football Championship (14 February 2010)
-
Totenko-Rooster Crows with Hinomaru and lady, 1909
See also
edit- List of Japanese flags
- National symbols of Japan
- Nobori – Tall Japanese banner
- Sashimono – Small banners worn by soldiers in feudal Japan
- Uma-jirushi – Massive flags used on battlefields in feudal Japan
References
editFootnotes
editNotes
edit- ^ (in Japanese). Government of Japan – via Wikisource.
- ^ 法令全書 (in Japanese). National Diet. 27 October 1870. doi:10.11501/787950. Archived from the original on 28 March 2019. Retrieved 26 February 2019.
- ^ a b c "「国旗」の真実をどれだけ知っていますか". 23 December 2015. Archived from the original on 4 February 2016.
- ^ a b c "Shoku Nihongi". University of California, Berkeley (see original Japanese text). Archived from the original on 4 February 2021.
- ^ Yamanashi Tourism Organization. 日の丸の御旗 [archived 1 October 2011].(in Japanese)
- ^ Unpoji. 宝物殿の案内 [archived 4 November 2011].(in Japanese)
- ^ Little-Known Wars of Great and Lasting Impact: The Turning Points in Our History We Should Know More About. Fair Winds; 2009. ISBN 1-59233-375-3. p. 54. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b c Web Japan. Japanese Ministry of Foreign Affairs. National Flag and Anthem [PDF]; 2000 [archived 15 June 2010].
- ^ Edgington 2003, pp. 123–124
- ^ Dyer 1909, p. 24
- ^ Ashkenazi 2003, pp. 112–113
- ^ Hall 1996, p. 110
- ^ 森浩一著「日本神話の考古学」(朝日新聞出版 1993年7月)
- ^ 「日本古典文学大系 2 風土記」(岩波書店 1958年4月)の伊勢国風土記逸文に、神武天皇が伊勢国造の祖の天日別命に命じて伊勢国に攻め込ませ、国津神の伊勢津彦を追い出して伊勢を平定したとある。
- ^ 熊野からでは北に向かって戦う事になる。このため鈴木眞年のように、伊勢まで行って西から大和盆地に侵攻したとする説もある。
- ^ 泉欣七郎、千田健共編『日本なんでもはじめ』ナンバーワン、1985年、149頁、ISBN 4-931016-06-5
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l 国旗「日の丸」のルーツは「種子島家の船贈」 (PDF). Nishinomote City. 28 January 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 July 2021.
- ^ a b Itoh 2003, p. 205
- ^ Feldman 2004, pp. 151–155
- ^ a b c Hongo, Jun. Hinomaru, 'Kimigayo' express conflicts both past and future. The Japan Times. 17 July 2007 [archived 18 July 2012].
- ^ Turnbull 2001
- ^ Goodman, Neary 1996, pp. 77–78
- ^ National Diet Library. レファレンス事例詳細 [Reference Case Details]; 2 July 2009 [archived 20 July 2011]. Japanese.
- ^ Feiler 2004, p. 214
- ^ a b Ohnuki-Tierney 2002, pp. 68–69
- ^ Rohl 2005, p. 20
- ^ a b c d e f Befu 1992, pp. 32–33
- ^ a b c Befu 2001, pp. 92–95
- ^ Nornes 2003, p. 81
- ^ Cwiertka 2007, pp. 117–119
- ^ Partner 2004, pp. 55–56
- ^ Tipton 2002, p. 137
- ^ Newell 1982, p. 28
- ^ The Camera Overseas: The Japanese People Voted Against Frontier Friction. Life. 21 June 1937 [archived 13 August 2024]:75.
- ^ National Historical Institute. The Controversial Philippine National Flag [PDF]; 2008 [archived 1 June 2009].
- ^ Taylor 2004, p. 321
- ^ Goodman, Neary 1996, p. 102
- ^ Morita, D. (19 April 2007) "A Story of Treason", San Francisco: Nichi Bei Times.
- ^ Ebrey 2004, p. 443
- ^ Hauser, Ernest. Son of Heaven. Life. 10 June 1940 [archived 14 December 2011]:79.
- ^ a b Ministry of Education. 国旗,国歌の由来等 [Origin of the National Flag and Anthem]; 1 September 1999 [archived 10 January 2008]. Japanese.
- ^ a b c d e Goodman, Neary 1996, pp. 81–83
- ^ a b c Weisman, Steven R. For Japanese, Flag and Anthem Sometimes Divide. The New York Times. 29 April 1990 [archived 24 May 2013].
- ^ Hardarce, Helen; Adam L. Kern. New Directions in the Study of Meiji Japan. Brill; 1997. ISBN 90-04-10735-5. p. 653. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ 吉田 藤人. 邦人船員消滅 [Kunihito crew extinguished] [archived 9 December 2012]. Japanese.
- ^ University of Leicester. The Journal of Transport History. Manchester, United Kingdom: University of Leicester; 1987. p. 41. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Carr, Hulme 1956, p. 200
- ^ Yoshida, Shigeru. National Diet Library. Letter from Shigeru Yoshida to General MacArthur dated May 2, 1947; 2 May 1947 [archived 8 December 2008]. Japanese, English.
- ^ MacArthur, Douglas. National Archives of Japan. Letter from Douglas MacArthur to Prime Minister dated May 2, 1947; 2 May 1947 [archived 11 June 2011].
- ^ Meyer 2009, p. 266
- ^ Large 1992, p. 184
- ^ Yamazumi 1988, p. 76
- ^ Fukiura, Tadamasa (2009). ブラックマヨネーズ (TV). Japan: New Star Creation.
- ^ a b Borneman 2003, p. 112
- ^ Chira, Susan. Hirohito, 124th Emperor of Japan, Is Dead at 87. The New York Times. 7 January 1989 [archived 7 January 2010].
- ^ Kataoka 1991, p. 149
- ^ Aspinall 2001, p. 126
- ^ Vote in Japan Backs Flag and Ode as Symbols. The New York Times. 23 July 1999 [archived 1 June 2013].
- ^ Williams 2006, p. 91
- ^ a b c Itoh 2003, pp. 209–210
- ^ Goodman, Neary 1996, pp. 82–83
- ^ Education: Tanaka v. the Teachers. Time. 17 June 1974 [archived 23 June 2011].
- ^ Okano 1999, p. 237
- ^ Democratic Party of Japan. 国旗国歌法制化についての民主党の考え方 [The DPJ Asks For A Talk About the Flag and Anthem Law]; 21 July 1999 [archived 8 July 2013]. Japanese.
- ^ Contemporary Japanese Thought. Columbia University Press; 2005. ISBN 978-0-231-13620-4. p. 211. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Democratic Party of Japan. 国旗・国歌法案、衆院で可決 民主党は自主投票 [Flag and Anthem Law Passed by the House, DPJ Free Vote]; 22 July 1999 [archived 19 October 2013]. Japanese.
- ^ National Diet Library. 第145回国会 本会議 第47号; 22 July 1999 [archived 14 July 2012]. Japanese.
- ^ House of Representatives. 議案審議経過情報: 国旗及び国歌に関する法律案; 13 August 1999 [archived 23 March 2011]. Japanese.
- ^ 【日本の議論】日の丸裁断による民主党旗問題 国旗の侮辱行為への罰則は是か非か [(Japan) Discussion of penalties of acts of contempt against the Hinomaru by the DPJ]. Sankei Shimbun. 30 August 2009 [archived 2 September 2009]. Japanese. Sankei Digital.
- ^ 明治3年太政官布告第57号
- ^ Takenaka 2003, pp. 68–69
- ^ a b 明治3年太政官布告第651号
- ^ Takenaka 2003, p. 66
- ^ a b 国旗及び国歌に関する法律
- ^ Consulate-General of Japan in San Francisco. Basic / General Information on Japan; 1 January 2008 [archived 11 December 2012].
- ^ Cabinet Office, Government of Japan. National Flag & National Anthem; 2006 [archived 22 May 2009].
- ^ a b c Ministry of Defense. Defense Specification Z 8701C (DSPZ8701C) [PDF]; 27 November 1973 [archived 20 April 2012]. Japanese.
- ^ a b Office of Developmental Assistance. 日章旗のマーク、ODAシンボルマーク [National flag mark, ODA Symbol] [PDF]; 1 September 1995 [archived 28 September 2011]. Japanese.
- ^ National Diet Library. 第145回国会 国旗及び国歌に関する特別委員会 第4号 [145th Meeting of the Diet, Discussion about the bill Law Regarding the National Flag and National Anthem]; 2 August 1999 [archived 19 August 2011]. Japanese.
- ^ a b Hexadecimal obtained by placing the colors in Feelimage Analyzer Archived 25 January 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ DIC Corporation. DICカラーガイド情報検索 (ver 1.4) [DIC Color Guide Information Retrieval (version 1.4)]. Japanese.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Web Japan. Ministry of Foreign Affairs. 国旗と国歌 [National Flag and Anthem] [PDF] [archived 5 June 2011]. Japanese.
- ^ Yoshida, Shigeru. House of Councillors. 答弁書第九号; 27 April 1954 [archived 22 January 2010]. Japanese.
- ^ 47news. JR九州、日の丸を掲揚へ 有人330駅、祝日に [JR Kyushu 330 manned stations to hoist the national flag]; 26 November 2002 [archived 8 December 2008]. Japanese.
- ^ "Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan". Archived from the original on 26 January 2013. Retrieved 27 December 2012.
- ^ City of Himeji, Hyogo Prefecture. 開催中の平和資料館収蔵品展から「日の丸寄せ書き」について [Museum collections from the exhibition "Group flag efforts" being held for peace] [archived 13 August 2011]. Japanese.
- ^ a b Smith 1975, p. 171
- ^ McBain, Roger. Going back home. Courier & Press. 9 July 2005 [archived 21 July 2011].
- ^ Takenaka 2003, p. 101
- ^ 西宮市立郷土資料館の企画展示. Archived from the original on 19 June 2008. Retrieved 24 October 2019.
- ^ "Hachimaki – Japanese Headbands – DuncanSensei Japanese". DuncanSensei Japanese. 24 March 2015. Archived from the original on 6 March 2016. Retrieved 19 March 2016.
- ^ Cutler 2001, p. 271
- ^ Spacey, John (24 January 2014). "Japan's Patriotic Bento Box (Hinomaru)". Japan Talk. Archived from the original on 7 August 2017. Retrieved 24 October 2019.
- ^ Asahi Research. TV Asahi. 国旗・国歌法制化について [About the Law of the Flag and Anthem]; 18 July 1999 [archived 23 May 2008]. Japanese.
- ^ Hoso Bunka Foundation. テレビニュースの多様化により、異なる番組の固定視聴者間に生じる意見の差 [Diversity of television news, viewers differences of opinion arise between different programs] [PDF]; 2002 [archived 28 February 2008]. Japanese.
- ^ Khan 1998, p. 190
- ^ "Town eyes subsidy for residents to buy flag". The Japan Times. Archived from the original on 16 October 2012. Retrieved 27 December 2012.
- ^ Wundunn, Sheryl. Yomitan Journal: A Pacifist Landlord Makes War on Okinawa Bases. The New York Times. 11 November 1995 [archived 10 December 2008].
- ^ Smits, Gregory. Penn State University. Okinawa in Postwar Japanese Politics and the Economy; 2000 [archived 30 May 2013].
- ^ "Hinomaru flies at Naha for first time in 29 years". The Japan Times. [dead link]
- ^ Japan's Neo-Nationalism: The Role of the Hinomaru and Kimigayo Legislation. JPRI working paper. 2001–2007 [archived 28 April 2014];79:16.
- ^ Lauterpacht 2002, p. 599
- ^ Inoguchi, Jain 2000, p. 228
- ^ Ministry of Foreign Affairs. プロトコール [Protocol] [PDF]; 2009–2002 [archived 6 February 2011]. Japanese.
- ^ 国旗及び国歌の取扱いについて
- ^ 国旗及び県旗の取扱いについて
- ^ Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Page 1 「グローカル通信」平成21年5月号 プロトコール講座 [Protocol Question and Answer (May 2009)] [PDF]; 2009–2005 [archived 7 June 2011]. Japanese.
- ^ 大正元年閣令第一号
- ^ Office of the Cabinet. National Diet Library. 全国戦没者追悼式の実施に関する件; 14 May 1963 [archived 10 March 2005]. Japanese.
- ^ Trevor 2001, p. 78
- ^ Hiroshima Prefectural Board of Education Secretariat. 学習指導要領における国旗及び国歌の取扱い [Handling of the flag and anthem in the National Curriculum]; 11 September 2001 [archived 22 July 2011]. Japanese.
- ^ Ministry of Education. 小学校学習指導要領解説社会編,音楽編,特別活動編 [National Curriculum Guide: Elementary social notes, Chapter music Chapter Special Activities]; 1999 [archived 19 March 2006]. Japanese.
- ^ Aspinall 2001, p. 125
- ^ McCurry, Justin. A touchy subject. Guardian Unlimited. 5 June 2006 [archived 30 August 2013]. The Guardian.
- ^ The Japan Times. Ishihara's Hinomaru order called legit; 5 January 2006 [archived 27 December 2012].
- ^ Heenan 1998, p. 206
- ^ a b 自衛隊法施行令
- ^ "Japan to skip S. Korea fleet event over 'rising sun' flag". The Asahi Shimbun. 6 October 2018. Archived from the original on 6 October 2018. Retrieved 7 October 2018.
- ^ 国际, 在线. 赵薇欲代言抗日网游洗刷"军旗装事件"之辱(图) [Zhao Wei wishes to endorse the anti-Japanese gaming scrubbing]. Xinhua. 11 August 2006 [archived 7 July 2008]. Chinese.
- ^ 海上自衛隊旗章規則
- ^ 〇海上自衛隊の使用する航空機の分類等及び塗粧標準等に 関する達
- ^ 自衛隊の旗に関する訓令
- ^ 桜星の数はかつての陸上自衛隊と同様、階級ではなく部隊規模を示していた。
- ^ "Air Self Defense Force (Japan)". CRW Flags. Archived from the original on 15 March 2016. Retrieved 26 October 2019.
- ^ Carpenter 2004, p. 124
- ^ a b Fujitani 1996, pp. 48–49
- ^ Matoba 1901, pp. 180–181
- ^ Takahashi 1903, pp. 180–181
- ^ 皇室儀制令 [Imperial System] [archived 8 December 2008]. Japanese.
- ^ Government of Ehime Prefecture. 愛媛県のシンボル [Symbols of Ehime Prefecture]; 2009 [archived 9 January 2008]. Japanese.
- ^ 広島県県章および県旗の制定
- ^ Government of Nagano Prefecture. 長野県の県章 – 県旗 [Flag and Emblem of Nagano Prefecture]; 2006 [archived 18 September 2007]. Japanese.
- ^ 天草市章
- ^ a b 天草市旗
- ^ Communications Museum "Tei Park". 郵便のマーク [archived 2 January 2013]. Japanese.
- ^ Prime Minister's Office, People's Republic of Bangladesh. People's Republic of Bangladesh Flag Rules (1972) [PDF]; 2005–2007 [archived 14 July 2010].
- ^ Embassy of Bangladesh in the Netherlands. Facts and Figures [archived 24 July 2011].
- ^ Van Fossen, Anthony B.; Centre for the Study of Australia-Asia Relations, Faculty of Asian and International Studies, Griffith University. The International Political Economy of Pacific Islands Flags of Convenience. Australia-Asia. [archived 14 December 2011];66(69):53.
- ^ Republic of Palau National Government. Palau Flag; 18 July 2008 [archived 13 November 2009].
- ^ Smith 2001, p. 73
- ^ Saito 1987, p. 53
- ^ Tazagi 2004, p. 11
- ^ Mangan 2000, p. 213
- ^ Gordon 1915, pp. 217–218
Bibliography
edit- Ashkenazi, Michael. Handbook of Japanese Mythology. ABC-CLIO; 2003. ISBN 1-57607-467-6. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Aspinall, Robert W. Teachers' Unions and the Politics of Education in Japan. State University of New York Press; 2001. ISBN 0-7914-5050-3. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Befu, Harumi. Symbols of nationalism and Nihonjinron. In: Goodman, Roger and Kirsten Refsing. Ideology and Practice in Modern Japan. Routledge; 1992. ISBN 0-415-06102-4. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Befu, Harumi. Hegemony of Homogeneity: An Anthropological Analysis of Nihonjinron. Trans Pacific Press; 2001. ISBN 978-1-876843-05-2. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Borneman, John. Death of the Father: An Anthropology of the End in Political Authority. Berghahn Books; 2003–2011. ISBN 1-57181-111-7. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Carpenter, Ronald H. Rhetoric In Martial Deliberations And Decision Making: Cases And Consequences. University of South Carolina Press; 2004. ISBN 978-1-57003-555-5. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Carr, Harold Gresham; Frederick Edward Hulme. Flags of the world. London; New York: Warne; 1956. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Cutler, Thomas. The Battle of Leyte Gulf: 23–26 October 1944. Naval Institute Press; 2001. ISBN 1-55750-243-9.
- Cwiertka, Katarzyna Joanna. Modern Japanese Cuisine: Food, Power and National Identity. Reaktion Books; 2007. ISBN 1-86189-298-5. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Dyer, Henry. Japan in World Politics: A Study in International Dynamics. Blackie & Son Limited; 1909. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Edgington, David William. Japan at the Millennium: Joining Past and Future. UCB Press; 2003. ISBN 0-7748-0899-3. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Ebrey, Patricia Buckley; Anne Walthall; James Palais. East Asia: A Cultural, Social, and Political History. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing; 2004. ISBN 0-547-00534-2. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Feiler, Bruce. Learning to Bow: Inside the Heart of Japan. Harper Perennial; 2004. ISBN 0-06-057720-7. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Feldman, David. Do Elephants Jump?. HarperCollins; 2004. ISBN 0-06-053913-5.
- Fujitani, Takashi. Splendid Monarchy: Power and Pageantry in Modern Japan. University of California Press; 1996. ISBN 978-0-520-21371-5. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Goodman, Roger; Ian Neary. Case Studies on Human Rights in Japan. Routledge; 1996. ISBN 978-1-873410-35-6. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Gordon, William. Flags of the World, Past and Present. Frederick Warne & Co.; 1915. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Hall, James. Illustrated Dictionary of Symbols in Eastern and Western Art. Westview Press; 1996. ISBN 0-06-430982-7.
- Heenan, Patrick. The Japan Handbook. Routledge; 1998. ISBN 1-57958-055-6. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Inoguchi, Takashi; Purnendra Jain. Japanese Foreign Policy Today. Palgrave Macmillan Ltd; 2000. ISBN 0-312-22707-8. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Itoh, Mayumi. The Hatoyama Dynasty: Japanese Political Leadership Through the Generations. Palgrave Macmillan; 2003. ISBN 1-4039-6331-2.
- Kataoka, Tetsuya. Creating Single-Party Democracy: Japan's Postwar Political System. Hoover Institution Press; 1991. ISBN 0-8179-9111-5. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Khan, Yoshimitsu. Japanese Moral Education: Past and Present. Fairleigh Dickinson University Press; 1998. ISBN 0-8386-3693-4. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Large, Stephen. Emperor Hirohito and Showa Japan: A Political Biography. Routledge; 1992. ISBN 0-415-03203-2. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Lauterpacht, Elihu. In: C. J. Greenwood and A. G. Oppenheimer. International Law Reports. Cambridge University Press; 2002. ISBN 978-0-521-80775-3. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Mangan, J.A.; Finn, Gerry; Giulianotti, Richard and Majumdar, Boria. Football Culture Local Conflicts, Global Visions. Routledge; 2000. ISBN 978-0-7146-5041-8. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Matoba, Seinosuke. 陸軍と海軍 [Army and Navy]. 1901. (in Japanese). Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Meyer, Milton. Japan: A Concise History. Rowman & Littlefield Publishing Group; 2009. ISBN 0-7425-4117-7. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Newell, William. Japan in Asia: 1942–1945. Singapore University Press; 1982. ISBN 9971-69-014-4. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Nornes, Abe Mark. Japanese Documentary Film The Meiji Era through Hiroshima. University of Minnesota Press; 2003. ISBN 0-8166-4046-7. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Ohnuki-Tierney, Emiko. Kamikaze, Cherry Blossoms, and Nationalisms. University of Chicago Press; 2002. ISBN 978-0-226-62091-6.
- Okano, Kaori; Motonori Tsuchiya (1999), Education in Contemporary Japan, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-62686-6, archived from the original on 13 August 2024, retrieved 17 October 2020
- Partner, Simon. Toshié A Story of Village Life in Twentieth-Century Japan. University of California Press; 2004. ISBN 978-0-520-24097-1. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Röhl, Wilhelm. History of law in Japan since 1868, Part 5, Volume 12. Brill; 2005. ISBN 978-90-04-13164-4. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Saito, Shinya. 記者四十年 [Fourteen Years As A Reporter]. Asahi Shimbun Publishing; 1987. (in Japanese). ISBN 978-4-02-260421-7. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Smith, Whitney. Flags Through the Ages and Across the World. McGraw-Hill; 1975. ISBN 0-07-059093-1. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Smith, Whitney. Flag Lore Of All Nations. Millbrook Press; 2001. ISBN 0-7613-1753-8. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Takahashi, Yuuichi. 海軍問答 [Navy Dialogue]. 1903. (in Japanese). Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Takenaka, Yoshiharu. 知っておきたい国旗・旗の基礎知識 [Flag basics you should know]. Gifu Shimbun; 2003. (in Japanese). ISBN 4-87797-054-1.
- Taylor, Jean Gelman. Indonesia: Peoples and Histories. Yale University Press; 2004. ISBN 0-300-10518-5.
- Tazagi, Shirou. 梶山静六: 死に顔に笑みをたたえて [Seiroku Kajiyama: Praising the smile in the dying face]. Kodansha; 2004. (in Japanese). ISBN 4-06-212592-7. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Tipton, Elise. Modern Japan A Social and Political History. Routledge; 2002. ISBN 978-0-415-18538-7. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Trevor, Malcolm. Japan – Restless Competitor The Pursuit of Economic Nationalism. Routledge; 2001. ISBN 978-1-903350-02-7. Archived 13 August 2024 at the Wayback Machine
- Turnbull, Stephen; Howard Gerrard. Ashigaru 1467–1649. Osprey Publishing; 2001. ISBN 1-84176-149-4.
- Williams, David; Rikki Kersten (2006), The Left in the Shaping of Japanese Democracy, Routledge, ISBN 978-0-415-33435-8, archived from the original on 13 August 2024, retrieved 17 October 2020
- Yamazumi, Masami. 日の丸・君が代問題とは何か. Otsuki Shoten; 1988. (in Japanese). ISBN 4-272-41032-6.
Legislation
edit- Government of Japan. 明治3年太政官布告第57号 [Prime Minister's Proclamation No. 57]; 27 February 1870 [archived 23 May 2013]. (in Japanese).
- National Diet Library. 明治3年太政官布告第651号 [Prime Minister's Proclamation No. 651] [PDF]; 3 October 1870 [archived 20 October 2021]. (in Japanese).
- Government of Japan. 大正元年閣令第一号 (大喪中ノ国旗掲揚方) [Regulation 1 from 1912 (Raising Mourning Flag For the Emperor)]; 30 July 1912 [archived 18 August 2010]. (in Japanese).
- Government of Japan. 自衛隊法施行令 [Self-Defense Forces Law Enforcement Order]; 30 June 1954 [archived 7 April 2008]. (in Japanese).
- Ministry of Defense. 〇海上自衛隊の使用する航空機の分類等及び塗粧標準等に 関する達 [Standard Sizes, Markings and Paint Used On Aircraft] [PDF]; 24 December 1962 [archived 22 July 2011]. (in Japanese).
- Government of Hiroshima Prefecture. 広島県県章および県旗の制定 [Law About the Flag and Emblem of Hiroshima Prefecture]; 16 July 1968 [archived 19 July 2011]. (in Japanese).
- Government of Japan. 国旗及び国歌に関する法律 (法律第百二十七号) [Law Regarding the National Flag and National Anthem, Act No. 127]; 13 August 1999 [archived 21 May 2010]. (in Japanese).
- Police of the Hokkaido Prefecture. 国旗及び国歌の取扱いについて [Law Regarding Use of the National Flag and Anthem]; 18 November 1999 [archived 6 May 2008]. (in Japanese).
- Police of Kanagawa Prefecture. 国旗及び県旗の取扱いについて [Law Regarding the Use of the National and Prefectural Flag] [PDF]; 29 March 2003 [archived 4 October 2011]. (in Japanese).
- Government of Amakusa City. 天草市章 [Emblem of Amakusa]; 27 March 2003 [archived 30 September 2013]. (in Japanese).
- Government of Amakusa City. 天草市旗 [Flag of Amakusa]; 27 March 2003 [archived 28 September 2013]. (in Japanese).
- Ministry of Defense. 自衛隊の旗に関する訓令 [Flag Rules of the JASDF] [PDF]; 25 March 2008 [archived 22 July 2011]. (in Japanese).
- Ministry of Defense. 海上自衛隊旗章規則 [JMSDF Flag and Emblem Rules] [PDF]; 25 March 2008 [archived 22 July 2011]. (in Japanese).
External links
edit- Japan at Flags of the World
- Flag protocol (in Japanese)
- Website on the standards of the Imperial family (in Japanese)
- Hinomaru: The Meaning Behind the Flag of Japan