1963 Pacific hurricane season
The 1963 Pacific hurricane season was a below-average season, with 8 storms and 4 hurricanes forming. The season ran through the summer and fall of 1963.
| 1963 Pacific hurricane season | |
|---|---|
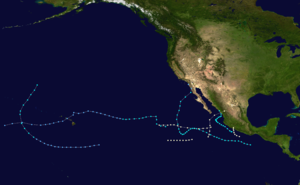 Season summary map | |
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | July 14, 1963 |
| Last system dissipated | October 14, 1963 |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | Mona |
| • Maximum winds | 85 mph (140 km/h) (1-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure | 961 mbar (hPa; 28.38 inHg) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 8 |
| Total storms | 8 |
| Hurricanes | 4 |
| Total fatalities | Unknown |
| Total damage | Unknown |
| Related articles | |
The strongest of these storms were Glenda and Mona, which both had 85 mph (135 km/h) winds. The first storm, Emily, made landfall near Manzanillo, Mexico as a Category 1 hurricane. The next hurricanes, Florence and Glenda, stayed far away from land. Jennifer-Katherine made landfall on Baja California as a tropical depression on September 18. Tropical Storm Irah affected Hawaii as a tropical depression. An unnamed tropical storm curved round Hawaii from 2–8 August. Lillian became post-tropical shortly before making landfall on September 29 with winds of 50 mph. Mona, the final storm of the season made landfall around about the same area as Lillian did with winds of 85 mph.
Systems
edit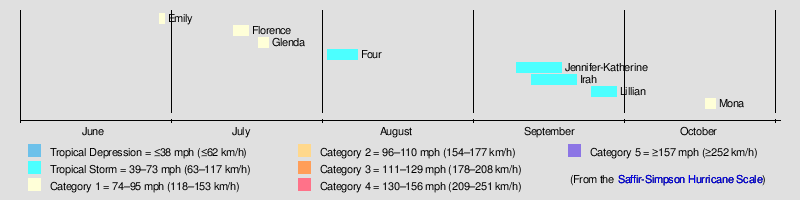
Hurricane Emily
edit| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | June 29 – June 30 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 mph (140 km/h) (1-min); 996[1] mbar (hPa) |
Hurricane Emily formed on June 29, while moving west. It then turned to the north and dissipated over the mountainous regions of Mexico.
Hurricane Florence
edit| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 14 – July 17 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 mph (140 km/h) (1-min); 992[1] mbar (hPa) |
Hurricane Florence followed a nearly-due west track, as it persisted to move away from land, and eventually weakened and dissipated without any effects on a landmass.
Hurricane Glenda
edit| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 19 – July 21 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 mph (140 km/h) (1-min); 997[1] mbar (hPa) |
Hurricane Glenda stayed at sea.
Tropical Storm Four
edit| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 2 – August 8 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min); |
Tropical Storm Four stayed over the ocean. Several vessels encountered gale-force winds in this storm from the 8th through the 10th as it proceeded northward across the shipping lanes. On August 12, the remnants of the cyclone dissipated near 50N 165W.
Tropical Storm Jennifer–Katherine
edit| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 9 – September 18 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min); 996[1] mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm Jennifer–Katherine moved through the Eastern Pacific in mid-September. It moved northward, and hit Baja California on September 18, bringing heavy rain to Southern California. A total of 6.5 inches (165 mm) fell in the mountains of southern California from the storm.[2] The storm had two names operationally because the NHC had assumed that Jennifer dissipated and that Katherine was a new storm, but reanalysis revealed that it was one storm.
Tropical Storm Irah
edit| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 12 – September 21 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min); 999[1] mbar (hPa) |
Irah peaked at a tropical storm and made a direct hit on Hawaii as a tropical depression.
Tropical Storm Lillian
edit| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 24 – September 29 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min); 991[1] mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Storm Lillian paralleled the Mexican coast. It was originally moving to the north-west, but turned to the west-northeast on September 28, before making landfall on Western Mexico as a tropical storm.
Hurricane Mona
edit| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 17 – October 19 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 mph (140 km/h) (1-min); 961[1] mbar (hPa) |
Hurricane Mona hit western Mexico on October 18.
Storm names
editThe following names were used for tropical storms that formed in the North Pacific Ocean east of 140°W during 1963. The names came from a series of four rotating lists. Names were used one after the other without regard to year, and when the bottom of one list was reached, the next named storm received the name at the top of the next list.[3]
|
|
|
Had any tropical storms formed in the North Pacific between 140°W and the International Date Line in 1963, their names would have been drawn from the Western Pacific typhoon naming list.[3]
See also
edit- 1963 Atlantic hurricane season
- 1963 Pacific typhoon season
- 1963 North Indian Ocean cyclone season
- Australian region cyclone seasons: 1962–63 1963–64
- South Pacific cyclone seasons: 1962–63 1963–64
- South-West Indian Ocean cyclone seasons: 1962–63 1963–64
References
edit- ^ a b c d e f g National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (1963). "The Climatological Data National Summary 1963". National Climatic Data Center. Retrieved August 13, 2014.
- ^ National Weather Service Forecast Office San Diego, California. Warnings for Tropical Storm Jennifer were issued from September 12 through 15 when a lack of observations led to an ending of observations. The final position was extrapolated at 18.8N 121.7W. Tropical Storm Katherine was identified on September 17 near 28.5N 117.0W and advisories were initiated. A History of Significant Local Weather Events. Archived February 29, 2008, at the Wayback Machine Retrieved on 2007-02-02.
- ^ a b Padgett, Gary (July 11, 2008). "Monthly Global Tropical Cyclone Summary: November 2007 First Installment". Australian Severe Weather. Retrieved February 10, 2010.