This article needs additional citations for verification. (November 2016) |
Stays are ropes, wires, or rods on sailing vessels that run fore-and-aft along the centerline from the masts to the hull, deck, bowsprit, or to other masts which serve to stabilize the masts.[1]
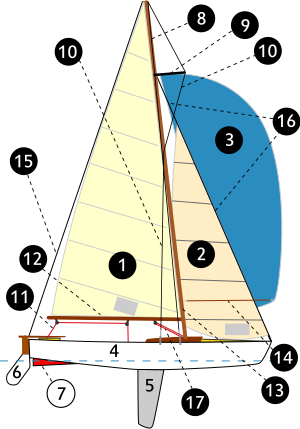
 2 – staysail
2 – staysail  3 – spinnaker
3 – spinnaker 
4 – hull
 5 – keel
5 – keel  6 – rudder
6 – rudder  7 – skeg
7 – skeg 
8 – mast
 9 – spreader
9 – spreader  10 – shroud
10 – shroud 
11 – sheet
 12 – boom
12 – boom  13 - mast
13 - mast 
14 – spinnaker pole
 15 – backstay
15 – backstay 
16 – forestay
 17 – boom vang
17 – boom vang 
A stay is part of the standing rigging and is used to support the weight of a mast.
It is a large strong rope, wire or rod extending from the upper end of each mast and running down towards the deck of the vessel in a midships fore-and-aft direction.
The shrouds serve a similar function but extend on each side of the mast and provide support in the athwartships direction. The object of both is to prevent the masts from falling down but the stays also prevent springing, when the ship is pitching deep.
Thus stays are fore and aft. Those led aft towards the vessel's stern are backstays while those that lead forward towards the bow are forestays.
"To stay" is also a verb: to bring the ship's head up to the wind (to point the bow upwind).[2] This is done in order to go about (to tack; tacking is sometimes also called staying the vessel[3]); the bow of the ship turns upwind, then continues turning until the wind comes over the other side. To miss stays is to fail in the attempt to go about;[4] if the vessel fails to go about, she is said to refuse stays.[3] In stays, or hove in stays, is the situation of a vessel when she is staying, or in the act of going about.[4] A vessel in bad trim, or lubberly-handled, is sure to be slack or loose in the stays: she may refuse stays fairly often. A suitable vessel well handled can usually be stayed swiftly, without losing noticeable way (without slowing down), and the sails will go over gently and without fuss or overshooting.[3][4]
Types of stays
edit- forestay or headstay
- reaches from the foremast-head towards the bowsprit end
- mainstay
- extends to the ship's stem. The mizzenstay stretches to a collar on the main-mast, immediately above the quarterdeck.
- fore-topmast stay
- goes to the end of the bowsprit, a little beyond the forestay, on which the fore-topmast staysail runs on hanks.
- main-topmast stay
- attaches to the hounds of the foremast, or comes on deck.
- mizzen-topmast stay
- goes to the hounds of the main-mast.
- top-gallant, royal, or any other masts
- have each a stay, named after their respective masts
- springstay
- is a kind of substitute nearly parallel to the principal stay, and intended to help the principal stay to support its mast
- triatic stay
- is a stay that runs between masts. On a ketch it runs between the main mast and the head of the mizzen mast and is used to stop the upper section of the mizzen mast being pulled backwards. On a steamer, an iron bar between the two knees secures the paddle-beams. (See funnel stays).
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Keegan, John (1989). The Price of Admiralty. New York: Viking. p. 280. ISBN 0-670-81416-4.
- ^ The Elements and Practice of Rigging And Seamanship. London. 1793.
- ^ a b c "WORKING TO WINDWARD". Text-Book of Seamanship. Originally published by "SMITH & MCDOUGAL, ELECTROTYPERS"; digital copy posted by the Historic Naval Ships Association. 1891.
{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help) - ^ a b c Smyth, William Henry; Belcher, Edward (1867). The sailor's word-book: An alphabetical digest of nautical terms, including some more especially military and scientific ... as well as archaisms of early voyagers, etc. London: Blackie and Son. pp. 652–653. Archived from the original on 2009-02-17.