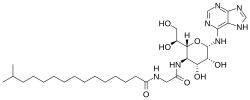
Spicamycin is an antibiotic with the molecular formula C30H51N7O7 which is produced by the bacterium Streptomyces alanosinicus.[1][2][3] Spicamycin also shows antitumor activity.[3]
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N-[2-[[2-(1,2-dihydroxyethyl)-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(7H-purin-6-ylamino)oxan-3-yl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]-14-methylpentadecanamide
| |
| Other names
Septacidin, NSC65104
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C30H51N7O7 | |
| Molar mass | 621.780 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
References
edit- ^ Burger, AM; Kaur, G; Hollingshead, M; Fischer, RT; Nagashima, K; Malspeis, L; Duncan, KL; Sausville, EA (March 1997). "Antiproliferative activity in vitro and in vivo of the spicamycin analogue KRN5500 with altered glycoprotein expression in vitro". Clinical Cancer Research. 3 (3): 455–63. PMID 9815705.
- ^ "Septacidin". Pubchem.ncbi.NLM.nih.gov.
- ^ a b Omura, Satoshi (6 December 2012). The Search for Bioactive Compounds from Microorganisms. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 107. ISBN 978-1-4612-4412-7.
Further reading
edit- Suzuki, Tamotsu; Suzuki, Sayaka T.; Yamada, Iwao; Koashi, Yoshiaki; Yamada, Kazue; Chida, Noritaka (1 May 2002). "Total Synthesis of Spicamycin". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 67 (9): 2874–2880. doi:10.1021/jo010925c. PMID 11975540.
- Suzuki, Tamotsu; Chida, Noritaka (February 2003). "The New and Efficient Synthesis of a Heptose Moiety of Spicamycin". Chemistry Letters. 32 (2): 190–191. doi:10.1246/cl.2003.190.