A progressive tax is a tax in which the tax rate increases as the taxable amount increases.[1][2][3][4] The term progressive refers to the way the tax rate progresses from low to high, with the result that a taxpayer's average tax rate is less than the person's marginal tax rate.[5][6] The term can be applied to individual taxes or to a tax system as a whole. Progressive taxes are imposed in an attempt to reduce the tax incidence of people with a lower ability to pay, as such taxes shift the incidence increasingly to those with a higher ability-to-pay. The opposite of a progressive tax is a regressive tax, such as a sales tax, where the poor pay a larger proportion[how?] of their income compared to the rich (eg spending on groceries and food staples varies little against income, so poor pay similar to rich even while latter has much higher income).[4]
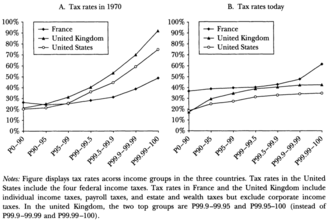
The term is frequently applied in reference to personal income taxes, in which people with lower income pay a lower percentage of that income in tax than do those with higher income. It can also apply to adjustments of the tax base by using tax exemptions, tax credits, or selective taxation that creates progressive distribution effects. For example, a wealth or property tax,[7] a sales tax on luxury goods, or the exemption of sales taxes on basic necessities, may be described as having progressive effects as it increases the tax burden of higher income families and reduces it on lower income families.[8][9][10]
Progressive taxation is often suggested as a way to mitigate the societal ills associated with higher income inequality,[11] as the tax structure reduces inequality;[12] economists disagree on the tax policy's economic and long-term effects.[13][14][15] One study suggests progressive taxation is positively associated with subjective well-being, while overall tax rates and government spending are not.[16]
Early examples
editIn the early days of the Roman Republic, public taxes consisted of assessments on owned wealth and property. For Roman citizens, the tax rate under normal circumstances was 1% of property value, and could sometimes climb as high as 3% in situations such as war. These taxes were levied against land, homes and other real estate, slaves, animals, personal items and monetary wealth. By 167 BC, Rome no longer needed to levy a tax against its citizens in the Italian peninsula, due to the riches acquired from conquered provinces. After considerable Roman expansion in the 1st century, Augustus Caesar introduced a wealth tax of about 1% and a flat poll tax on each adult; this made the tax system less progressive, as it no longer only taxed wealth.[17] In India under the Mughal Empire, the Dahsala system was introduced in A.D. 1580 under the reign of Akbar. This system was introduced by Akbar's finance minister, Raja Todar Mal, who was appointed in A.D. 1573 in Gujarat. The Dahsala system is a land-revenue system (system of taxation) which helped to make the collecting system be organised on the basis of land fertility.
Modern era
editThe first modern income tax was introduced in Great Britain by Prime Minister William Pitt the Younger in his budget of December 1798, to pay for weapons and equipment for the French Revolutionary War. Pitt's new graduated (progressive) income tax began at a levy of 2 old pence in the pound (1⁄120 or 0.83%) on annual incomes over £60 and increased up to a maximum of 2 shillings (10%) on incomes of over £200. Pitt hoped that the new income tax would raise £10 million, but actual receipts for 1799 totalled just over £6 million.[18]
Pitt's progressive income tax was levied from 1799 to 1802 when it was abolished by Henry Addington during the Peace of Amiens. Addington had taken over as prime minister in 1801, after Pitt's resignation over Catholic emancipation. The income tax was reintroduced by Addington in 1803 when hostilities recommenced, but it was again abolished in 1816, one year after the Battle of Waterloo.
The present form of income tax in the United Kingdom was reintroduced by Sir Robert Peel in the Income Tax Act 1842. Peel, as a Conservative, had opposed income tax in the 1841 general election, but a growing budget deficit required a new source of funds. The new income tax, based on Addington's model, was imposed on incomes above £150. Although this measure was initially intended to be temporary, it soon became a fixture of the British taxation system. A committee was formed in 1851 under Joseph Hume to investigate the matter but failed to reach a clear recommendation. Despite the vociferous objection, William Gladstone, Chancellor of the Exchequer from 1852, kept the progressive income tax, and extended it to cover the costs of the Crimean War. By the 1860s, the progressive tax had become a grudgingly accepted element of the English fiscal system.[19]
In the United States, the first progressive income tax was established by the Revenue Act of 1862. The act was signed into law by President Abraham Lincoln, and replaced the Revenue Act of 1861, which had imposed a flat income tax of 3% on annual incomes above $800. The Sixteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, adopted in 1913, permitted Congress to levy all income taxes without any apportionment requirement. By the mid-20th century, most countries had implemented some form of progressive income tax.[20]
Both Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels supported a progressive income tax.[21]
Negative Income Tax
editThe idea of Negative Income Tax (NIT) was stumbled upon and discussed by various thinkers and is most commonly attributed to Milton Friedman, who made it more prominent in his 1962 work ‘Capitalism and Freedom’. The theory places itself as an alternative to the contemporary progressive tax systems which are deemed too bureaucratic and inefficient, it’s emphasized for its lower administrative costs and unitary system of providing welfare and support without discrediting the beneficiaries. It also eliminates unnecessary processes and institutions by directly providing to the substandard.[22]
NIT is a system where the flow of the tax payment is inverted for salaries falling a specified threshold; Individuals surpassing the given level have to contribute money to the state, while those below are recipients of said funds. Theoretical framework of this idea could be referred back to William Petty, Vilferdo Pareto, and Paul Samuelson among others.
The adjustability of subsidies given to the poor households by the system eliminates the welfare trap issue faced by other proposals (i.e. means-test). The ‘wage subsidy’ is best demonstrated by the gap between ones salary, base pay, and real income post-subsidy. Once the minimal criteria defined by the according government is met, the recipient becomes the payer.
Milton provides five other advantages to NIT. It allows households and families to sustain themselves directly from their income without having to rely on other programs or plans. Secondly, it provides cash to the recipient, which is perceived as the most superior means of support. Thirdly, Milton claims that negative income tax could replace all other supporting programs and work as the universal program on its own. Fourthly, lower administration costs associated with NIT compared to other systems. Lastly, it should not, in theory, interfere with market mechanisms unlike other government interventionist laws (i.e. minimum wage).[23]
A survey conducted in 1995 established that the majority of American economists advocated for the addition of a negative income tax into the welfare system.[24] The United States federal government took a key interest on the matter and between 1968 and 1982 sponsored four experiments across various states to see the effects of NIT on labor supply, income, and substitution effects. As part of the result, most participants reduced their labor supply, especially the youth by as much as four weeks. These responses may seem imminent from a generous system like NIT.[25]
NIT saw extensive use under President Nixon's Family Assistance Plan in 1969. It was also implemented in 1975 for the working poor through the earned income tax credit.[26] The system is still in power today, but differs from the original theories of Milton and his supporters.
Measuring progressivity
editIndices such as the Suits index,[7] Gini coefficient, Kakwani index, Theil index, Atkinson index, and Hoover index have been created to measure the progressivity of taxation, using measures derived from income distribution and wealth distribution.[27]
Marginal and effective tax rates
editThe rate of tax can be expressed in two different ways; the marginal rate expressed as the rate on each additional unit of income or expenditure (or last dollar spent) and the effective (average) rate expressed as the total tax paid divided by total income or expenditure. In most progressive tax systems, both rates will rise as the amount subject to taxation rises, though there may be ranges where the marginal rate will be constant. Usually, the average tax rate of a taxpayer will be lower than the marginal tax rate. In a system with refundable tax credits, or income-tested welfare benefits, it is possible for marginal rates to fall as income rises, at lower levels of income.[citation needed]
Inflation and tax brackets
editTax laws might not be accurately indexed to inflation. For example, some tax laws may ignore inflation completely. In a progressive tax system, failure to index the brackets to inflation will eventually result in effective tax increases (if inflation is sustained), as inflation in wages will increase individual income and move individuals into higher tax brackets with higher percentage rates. This phenomenon is known as bracket creep and can cause fiscal drag.[citation needed]
Economic effects
editThere is debate between politicians and economists over the role of tax policy in mitigating or exacerbating wealth inequality[citation needed] and the effects on economic growth.[citation needed]
Income equality
editProgressive taxation has a direct effect on decreasing income inequality.[12] This is especially true if taxation is used to fund progressive government spending such as transfer payments and social safety nets.[11] However, the effect may be muted if the higher rates cause increased tax evasion.[12][28] When income inequality is low, aggregate demand will be relatively high, because more people who want ordinary consumer goods and services will be able to afford them, while the labor force will not be as relatively monopolized by the wealthy.[29][30] High levels of income inequality can have negative effects on long-term economic growth, employment, and class conflict.[31][32] Progressive taxation is often suggested as a way to mitigate the societal ills associated with higher income inequality.[11] The difference between the Gini index for an income distribution before taxation and the Gini index after taxation is an indicator for the effects of such taxation.[33]
The economists Thomas Piketty and Emmanuel Saez wrote that decreased progressiveness in US tax policy in the post World War II era has increased income inequality by enabling the wealthy greater access to capital.[13]
According to economist Robert H. Frank, tax cuts for the wealthy are largely spent on positional goods such as larger houses and more expensive cars. Frank argues that these funds could instead pay for things like improving public education and conducting medical research,[34] and suggests progressive taxation as an instrument for attacking positional externalities.[35]
Economic growth
editA report published by the OECD in 2008 presented empirical research showing a weak negative relationship between the progressivity of personal income taxes and economic growth.[14] Describing the research, William McBride, a staff writer with the conservative Tax Foundation, stated that progressivity of income taxes can undermine investment, risk-taking, entrepreneurship, and productivity because high-income earners tend to do much of the saving, investing, risk-taking, and high-productivity labor.[36][37] In contrast, according to the IMF, some advanced economies could increase progressivity in taxation for tackling inequality, without hampering growth, as long as progressivity is not excessive. The IMF also states that the average top income tax rate for OECD member countries fell from 62 percent in 1981 to 35 percent in 2015, and that in addition, tax systems are less progressive than indicated by the statutory rates, because wealthy individuals have more access to tax relief.[38]
Educational attainment
editEconomist Gary Becker has described educational attainment as the root of economic mobility.[39] Progressive tax rates, while raising taxes on high income, have the goal and corresponding effect of reducing the burden on low income, improving income equality. Educational attainment is often conditional on cost and family income, which for the poor, reduces their opportunity for educational attainment.[40][41] Increases in income for the poor and economic equality reduces the inequality of educational attainment.[42][43] Tax policy can also include progressive features that provide tax incentives for education, such as tax credits and tax exemptions for scholarships and grants.[44][45]
A potentially adverse effect of progressive tax schedules is that they may reduce the incentives for educational attainment.[15][41][46] By reducing the after-tax income of highly educated workers, progressive taxes can reduce the incentives for citizens to attain education, thereby lowering the overall level of human capital in an economy.[15][41][46] However, this effect can be mitigated by an education subsidy funded by the progressive tax.[47] Theoretically, public support for government spending on higher education increases when taxation is progressive, especially when income distribution is unequal.[48]
Opposition and criticism
editHayek's argumentation
editFriedrich Hayek viewed the implementation of progressive tax systems as incompatible with the principles of an open and liberal society. He argued that the imposition of higher taxes on higher incomes creates a bias against economic wealth and negatively impacts the incentives of the working age. His thought stems from philosophical and moral theories. Hayek believed that fiscal problems are partly to its foundations in moral philosophy practiced by society. Progressive tax prohibits the incentives of free market competition, whilst the wealth is subordinated to the democratic vote of a majority. This results in illegitimate transfers of political power.
Hayek believed the sweeping rise of progressive tax has risen from deceptive justifications which in reality didn't bring fruit. He claims the historical and methodological conditions gave way to the imposition of the system. The system was established from ludicrous premises and failed to attain its redistributive goals. The progressive tax failed to benefit the poor, instead the benefit fell to the middle class who comprised the majority of voters, a majority which may push for tax changes.[49]
Hayek advocated for a flat (or proportional) tax rate. Estonia was one of the first countries in Europe to adapt such a tax system.[50]
Nozick's argumentation
editRobert Nozick in his famous work 'Anarchy, State and Utopia' made the widely known statement: "Taxation of earnings from labor is on a par with forced labor".[51] He acknowledged the difference between the previous forms of slavery, but holds the belief that it is just as immoral regardless. Nozick believed that the government should have limited role in most sectors, including the economy. He advocates for what's known as the 'minimal state', hence the government should not enforce 'redistribution' as it would minimize the rewards given by the free market forces. Whatever revenue is generated by taxes is to be spent on basic maintenance (i.e. road repairs).[52]
Loopholes
editThe current United States tax code has been criticized by many who believe that the nation's wealthiest are not paying their share. This is because the current tax system charges the individual based on wages and not investment income, an area where the upper-class make most of their money. Prominent investor Warren Buffett has been a strong voice in support of taxing the rich proportional to investment income as well as wages. Buffett famously pointed out that if you analyzed every employee in his office including himself, he is quoted saying, "I'll probably be the lowest paying taxpayer in the office."[53] This support ultimately led to the proposal of "The Buffett Rule" by President Barack Obama which proposed a 30% minimum tax on people making more than $1 million a year.[54] The aim of the Buffett Rule was to ensure that investment income would constitute as a taxable income instead of simply wages. Ultimately, the rule was rejected by congress in March 2012. President Joe Biden attempted to do what President Obama could not and introduced the "Paying a Fair Share Act" which followed the Buffett's Rule philosophy. As of August 2023, the bill has not picked up steam in congress. Those that take advantage of these tax codes in the United States include some of the most wealthy and prominent. It is said that "Bezos reportedly paid no federal income taxes at all in 2007 and 2011, while Musk paid none in 2018."[55]
Psychological factors
editA 2011 study psychologists Shigehiro Oishi, Ulrich Schimmack, and Ed Diener, using data from 54 countries, found that progressive taxation was positively associated with the subjective well-being, while overall tax rates and government spending were not. The authors added, "We found that the association between more-progressive taxation and higher levels of subjective well-being was mediated by citizens' satisfaction with public goods, such as education and public transportation."[16] Tax law professor Thomas D. Griffith, summarizing research on human happiness, has argued that because inequality in a society significantly reduces happiness, a progressive tax structure which redistributes income would increase welfare and happiness in a society.[56] Since progressive taxation reduces the income of high earners and is often used as a method to fund government social programs for low income earners, calls for increasing tax progressivity have sometimes been labeled as envy or class warfare,[clarification needed][35][57][58] while others may describe such actions as fair or a form of social justice.[58][59]
Even with studies that conclude that a progressive tax can be positively associated with the increased well-being of certain individuals, experts point out that many wealthy democracies are often hesitant to enforce progressive taxes. A study conducted by Yale political scientist Kenneth Scheve and David Stasavage of New York University published in the Comparative Political Studies journal helps explains why that is. Their research findings concluded that voters hold the belief that all citizens should be treated equally with regards to taxation regardless of the income that they bring in. The authors point to this reasoning as one of the main reasons certain countries refuse to raise taxes on the wealthier despite rising inequality. Kenneth Scheve is quoted saying, “Progressive taxation is a powerful policy tool for responding to rising inequality, but we found that wealthy democracies don’t resort to it very often.” The study results result from studies conducted in the United Kingdom, United States, and Germany. Contrary to a progressive tax, some voters argue that a fair tax system should take into account whether individuals earned their wealth through hard work compared to others. This perspective emphasizes equal-treatment fairness norms, which suggest that all citizens should be treated equally in areas such as voting rights and legal protections. Accordingly, these voters believe that everyone should pay the same tax rate, mirroring the concept of equal treatment. While progressive tax policies may address income inequality in certain countries, there is a significant segment of the population that opposes them based on this notion of political equality. This opposition may hinder the formation of a consensus to address inequality by raising taxes on higher incomes and wealth.[60]
Computation
editThere are two common ways of computing a progressive tax, corresponding to point–slope form and slope–intercept form of the equation for the applicable bracket. These compute the tax either as the tax on the bottom amount of the bracket plus the tax on the marginal amount within the bracket; or the tax on the entire amount (at the marginal rate), minus the amount that this overstates tax on the bottom end of the bracket.
For example, suppose there are tax brackets of 10%, 20%, and 30%, where the 10% rate applies to income from $1 to 10,000; the 20% rate applies to income from $10,001 to 20,000; and the 30% rate applies to all income above $20,000. In that case the tax on $20,000 of income (computed by adding up tax in each bracket) is . The tax on $25,000 of income could then be computed two ways. Using point–slope form (tax on bottom amount plus tax on marginal amount) yields: Geometrically, the line for tax on the top bracket passes through the point and has a slope of 0.3 (30%).
Alternatively, 30% tax on $20,000 yields , which overstates tax on the bottom end of the top bracket by , so using slope–intercept form yields: Geometrically, the line for tax on the top bracket intercepts the y-axis at −$3,000 – it passes through the point – and has a slope of 0.3 (30%).
In the United States, the first form was used through 2003, for example (for the 2003 15% Single bracket):[61]
- If the amount on Form 1040, line 40 [Taxable Income], is: Over— 7,000
- But not over— 28,400
- Enter on Form 1040, line 41 [Tax] $700.00 + 15%
- of the amount over— 7,000
From 2004, this changed to the second form, for example (for the 2004 28% Single bracket):[62]
- Taxable income. If line 42 is— At least $100,000 but not over $146,750
- (a) Enter the amount from line 42
- (b) Multiplication amount × 28% (.28)
- (c) Multiply (a) by (b)
- (d) Subtraction amount $5,373.00
- Tax. Subtract (d) from (c). Enter the result here and on Form 1040, line 43
Examples
editMost systems around the world contain progressive aspects. When taxable income falls within a particular tax bracket, the individual pays the listed percentage of tax on each dollar that falls within that monetary range. For example, a person in the U.S. who earned $10,000 US of taxable income (income after adjustments, deductions, and exemptions) would be liable for 10% of each dollar earned from the 1st dollar to the 7,550th dollar, and then for 15% of each dollar earned from the 7,551st dollar to the 10,000th dollar, for a total of $1,122.50.
In the United States, there are seven income tax brackets ranging from 10% to 39.6% above an untaxed level of income based on the personal exemption and usually various other tax exemptions, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit and home mortgage payments. The federal tax rates for individual taxpayers in the United States for the tax year 2021 are as follows: 10% from $0 to $9,950; 12% from $9,950 to $40,525; 22% from $40,525 to $86,375; 24% from $86,375 to $164,925; 32% from $164,925 to $209,425; 35% from $209,425 to $523,600; and 37% from $523,600 and over.[64] The US federal tax system also includes deductions for state and local taxes for lower income households which mitigates what are sometimes regressive taxes, particularly property taxes. Higher income households are subject to the alternative minimum tax that limits deductions and sets a flat tax rate of 26% to 28% with the higher rate commencing at $175,000 in income. There are also deduction phaseouts starting at $112,500 for single filers. The net effect is increased progressivity that completely limits deductions for state and local taxes and certain other credits for individuals earning more than $306,300.[65] In order to counteract regressive state and local taxes, many US states implement progressive income taxes.[66] 32 states and the District of Columbia have graduated-rate income taxes.[67] The brackets differ across states.
There has been a hefty decline in progressivity of the United States federal tax system since the 1960s. The two periods with the largest tax progressivity reductions occurred under the Reagan administration in the 1980s and the Bush administration in the 2000s.[68] The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 implemented by President Trump greatly affected the United States tax system. The act took steps to dramatically lower taxes for high-income households, open deduction loopholes for businesses, and cut the federal corporate tax rate down to 21 percent.[69] It maintained the structure of seven tax brackets for personal income but lowered five of the seven by one percent or more.[70] For example, after the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 was implemented, in 2017, a married couple with a total income of $250,000 after deductions would have faced a tax rate of 33%. However, by 2023 and 2024, their highest tax rate would have decreased to 24%. This change would have resulted in a notable disparity in their take-home pay compared to previous years.[71]
Albania transitioned from a flat tax to a progressive tax in 2014.[72] Kraja, Lirëza and Morelli[72] have concluded that while a progressive tax framework may be more effective in achieving policy objectives like reducing income inequality and boosting government tax revenue, policymakers must carefully weigh its impact on investment and entrepreneurship and implement strong tax administration and enforcement measures to combat tax evasion within a progressive tax framework.
Belgium has the following personal income tax rates (for the income year 2021): 25% from EUR€0 to €13,540; 40% from €13,540 to €23,900; 45% from €23,900 to €41,360; and 50% from €41,360 and any amount over.[73]
Canada has the following federal tax rates on income (for the year 2021): 15% from C$0 to $49,020; 20.5% from $49,020 to $98,040; 26% from $98,040 to $151,978; 29% from $151,978 to $216,511; and 33% on income over $216,511.[74]
Denmark has the following state tax rates regarding personal income: 12.11% for the bottom tax base; 15% for the top tax base, or income exceeding DKK 544,800. Additional taxes, such as the municipal tax (which has a country average of 24.971%), the labour market tax, and the church tax, are also applied to individual's income.[75]
Germany has the following personal income tax rates for a single taxpayer (for the 2020 tax year): 0% up to EUR€9,744; 14-42% from €9,744 to €57,918; 42% from €57,918 to €274,612; and 45% for €274,612 and any amount over.[76]
Indonesia has implemented progressive vehicular taxes at the municipal level in Cimahi and Palembang,[77][78] which had a significant impact of the progressive tax system on the local income of the municipality.
Norway has the following personal income tax rates (for the year 2020): 1.9% from NOK180,800 to NOK254,500; 4.2% from NOK254,500 to NOK639,750; 13.2% from NOK639,750 to NOK999,550; and 16.2% from NOK999,550 and above.[79]
Sweden has the following state income tax brackets for natural persons: 0% on income up to SEK 413,200; 20% from SEK 413,200 to SEK 591,600; and 25% from SEK 591,600 and any amount over.[80]
The United Kingdom has the following income tax rates: 0% from £0 to £12,570; 20% from £12,571 to £50,270; 40% from £50,271 to £150,000; and 45% from £150,000 and over.[81] In Scotland, however, there are more tax brackets than in other UK countries. Scotland has the following additional income tax brackets: 19% from £12,571 to £14,667; 20% from £14,667 to £25,296; 21% from £25,297 to £43,662; 41% from £43,663 to £150,000; and 46% for any amount over £150,000.[82]
New Zealand has the following income tax brackets: 10.5% up to NZ$14,000; 17.5% from NZ$14,001 to NZ$48,000; 30% from NZ$48,001 to NZ$70,000; 33% from NZ$70,001 to NZ$180,000; 39% for any amount over NZ$180,000; and 45% when the employee does not complete a declaration form.[83] All values are in New Zealand dollars and exclude the earner levy.
Australia has the following progressive income tax rates (for the 2012–2013 financial year): 0% effective up to A$18,200; 19% from A$18,201 to A$37,000; 32.5% from A$37,001 to A$80,000; 37% from A$80,001 to A$180,000; and 45% for any amount over A$180,000.[84]
Italy also follows a progressive tax blueprint. As of October 2020, the progressive tax rates in Italy are outlined as follows. Income between 0 and €15,000 – 23%, €15,000 – €28,000 – 25%, €28,000 – €50,000 – 35%, €50,000 and over – 43%.[85]
See also
edit- Compound empowerment
- Democratic socialism – Socialism emphasising democracy
- Economic progressivism – Political and economic philosophy
- Equity in taxation – Economic concept of fairness
- Income tax – Tax based on taxable income
- Optimal tax – Field of study
- Redistribution of income and wealth – Political philosophy
- Robin Hood effect – Economic occurrence
- Social democracy – Political ideology within the socialist movement
- Suits index – Measure of tax progressiveness
- Taxable income elasticity – Representation of the relationship between taxation and government revenue
- Tax bracket – Division at which a tax rate changes
- Tax evasion – Financial crime
- Tax incidence – Measure of the economic effect of a tax
- X tax – A form of consumption tax
Contrasting models:
- Proportional tax – Fixed fraction of source
- Regressive tax – Higher tax ratio on poorer sources
References
edit- ^ "progressive". Merriam–Webster. "(4b): increasing in rate as the base increases"
- ^ "progressive". American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language (4th ed.). Archived from the original on 9 February 2009.
(6). Increasing in rate as the taxable amount increases
- ^ "progressive tax". WordNet. Princeton University. Retrieved 17 February 2023.
progressive tax, graduated tax (any tax in which the rate increases as the amount subject to taxation increases)
- ^ a b Sommerfeld, Ray M.; Madeo, Silvia A.; Anderson, Kenneth E.; Jackson, Betty R. (1992). Concepts of Taxation. Fort Worth, Texas: Dryden Press.
- ^ Hyman, David M. (1990). Public Finance: A Contemporary Application of Theory to Policy (3rd ed.). Chicago, Illinois: Dryden Press.
- ^ James, Simon (1998). A Dictionary of Taxation. Northampton, Massachusetts: Edgar Elgar.
- ^ a b Suits, Daniel B. (September 1977). "Measurement of Tax Progressivity". American Economic Review. 67 (4): 747–752. JSTOR 1813408.
- ^ "Internal Revenue Service". Archived from the original on 16 August 2007. Retrieved 27 March 2009.
The luxury tax is a progressive tax – it takes more from the wealthy than from the poor.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ "Luxury tax". Britannica Online Encyclopedia. Archived from the original on 7 July 2012.
Excise levy on goods or services considered to be luxuries rather than necessities. Modern examples are taxes on jewelry and perfume. Luxury taxes may be levied with the intent of taxing the rich ...
- ^ Schaefer, Jeffrey M. (September 1969). "Clothing Exemptions and Sales Tax Regressivity". The American Economic Review. 59 (4). Part 1, pp. 596–599. JSTOR 1813222.
- ^ a b c Pickett, Kate; Wilkinson, Richard (26 April 2011). The Spirit Level: Why Greater Equality Makes Societies Stronger. Bloomsbury. ISBN 978-1-60819-341-7.
- ^ a b c Moyes, P. (1988). "A note on minimally progressive taxation and absolute income inequality". Social Choice and Welfare. 5 (2–3): 227–234. doi:10.1007/BF00735763.
- ^ a b Piketty, Thomas; Saez, Emmanuel (2003). "Income Inequality in the United States, 1913–1998" (PDF). Quarterly Journal of Economics. CXVIII (1st ed.).
- ^ a b Arnold, Jens (14 October 2008). "Do Tax Structures Affect Aggregate Economic Growth? Empirical Evidence From A Panel of OECD Countries". OECD. Archived from the original on 16 October 2013. Retrieved 2 January 2014.
- ^ a b c Becker, Gary S.; Murphy, Kevin M. (May 2007). "The Upside of Income Inequality". American Enterprise Institute. Archived from the original on January 2, 2014. Retrieved January 8, 2014.
- ^ a b Oishi, Shigehiro; Schimmack, Ulrich; Diener, Ed (2012). "Progressive Taxation and the Subjective Well-Being of Nations". Psychological Science. 23 (1): 86–92. doi:10.1177/0956797611420882. PMID 22157676. S2CID 8211113.
- ^ Roman Taxes. Unrv.com. Retrieved on 2014-04-12.
- ^ "A tax to beat Napoleon". HM Revenue & Customs. Archived from the original on 29 July 2013. Retrieved 18 February 2023.
- ^ Bank, Steven A. (2011). Anglo-American Corporate Taxation: Tracing the Common Roots of Divergent Approaches. Cambridge University Press. pp. 28–29. ISBN 978-1-139-50259-7.
- ^ James, Kathryn (2011). "Exploring the Origins and Global Rise of VAT". Journal of Economics. 35 (4): 15–22. SSRN 2291281.
- ^ Ireland, David (8 July 2019). "What Marxist Tax Policies Actually Look Like". Historical Materialism. 27 (2): 188–221. doi:10.1163/1569206X-00001543. ISSN 1465-4466.
- ^ "Negative income tax, explained | MIT Sloan". mitsloan.mit.edu. 24 April 2024. Retrieved 26 April 2024.
- ^ Moffitt, Robert A (1 August 2003). "The Negative Income Tax and the Evolution of U.S. Welfare Policy". Journal of Economic Perspectives. 17 (3): 119–140. doi:10.1257/089533003769204380. ISSN 0895-3309.
- ^ Alston, Richard M.; Kearl, J.R.; Vaughan, Michael B. (May 1992). ""Is There a Consensus Among Economists in the 1990's?"" (PDF). The American Economic Review. 82 (2). American Economic Association: 203–209.
- ^ Robins, Philip K. (1985). "A Comparison of the Labor Supply Findings from the Four Negative Income Tax Experiments". The Journal of Human Resources. 20 (4): 567–582. doi:10.2307/145685. ISSN 0022-166X.
- ^ Hamilton, Jonathan H. (1 April 2010). "Optimal tax theory: the journey from the negative income tax to the earned income tax credit". Southern Economic Journal. 76 (4): 860–878.
- ^ Philip B. Coulter: Measuring Inequality, 1989, ISBN 0-8133-7726-9 (This book describes about 50 different inequality measures.)
- ^ Duncan, Denvil, Klara Sabirianova Peter (October 2012). "Unequal Inequalities: Do Progressive Taxes Reduce Income Inequality?" (PDF). Institute for the Study of Labor.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ The Economics of Welfare] Arthur Cecil Pigou
- ^ Andrew Berg and Jonathan D. Ostry, 2011, "Inequality and Unsustainable Growth: Two Sides of the Same Coin?" IMF Staff Discussion Note SDN/11/08, International Monetary Fund
- ^ Alesina, Alberto; Dani Rodrick (May 1994). "Distributive Politics and Economic Growth" (PDF). Quarterly Journal of Economics. 109 (2): 465–90. doi:10.2307/2118470. JSTOR 2118470.
- ^ Castells-Quintana, David; Vicente Royuela (2012). "Unemployment and long-run economic growth: The role of income inequality and urbanisation" (PDF). Investigaciones Regionales. 12 (24): 153–173. hdl:10017/27066. Retrieved 17 October 2013.
- ^ Shlomo Yitzhaki (1998). "More than a Dozen Alternative Ways of Spelling Gini" (PDF). Economic Inequality. 8: 13–30.
- ^ Frank, Robert H. "Positional Externalities Cause Large and Preventable Welfare Losses" (PDF). American Economic Association. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 7, 2015. Retrieved March 17, 2014.
- ^ a b Frank, Robert H. (June 2003). "Are Positional Externalities Different from Other Externalities?" (PDF). Brookings Institution. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 December 2012. Retrieved 17 March 2014.
- ^ McBride, William (18 December 2012). "What Is the Evidence on Taxes and Growth?". Tax Foundation. Archived from the original on 27 December 2012. Retrieved 2 January 2014.
- ^ McBride, William (20 February 2013). "Comments on Who Pays? A Distributional Analysis of the Tax Systems in All 50 States". Tax Foundation. Archived from the original on 24 February 2013. Retrieved 2 January 2014.
- ^ "Fiscal policy can make the difference". International Monetary Fund IMF. 11 October 2017. Retrieved 12 October 2017.
- ^ Becker, Gary S. (15 October 2013). "Becker Explores the Roots of Upward Mobility". The University of Chicago. Archived from the original on 2 February 2016. Retrieved 24 January 2014.
- ^ Campbell, Mary; Haveman, R.; Sandefur, G.; Wolfe, B. (2005). "11 Economic inequality and educational attainment across a generation". Focus. 23 (3): 11–15.
we found that family income and wealth have positive and statistically significant links to attainment: children who grow up in families with higher income and greater wealth receive more schooling.
- ^ a b c Mueller, Richard (May 2008). Access and Persistence of Students from Low - Income Backgrounds in Canadian Post - Secondary Education: A Review of the Literature. MESA Project. Educational Policy Institute. doi:10.2139/ssrn.2256110. S2CID 152353956. SSRN 2256110.
students from low income backgrounds are more sensitive to changes in tuition and aid packages than their colleagues from higher income families, as are students attending community colleges compared to universities.
- ^ Campbell, Mary; Haveman, R.; Sandefur, G.; Wolfe, B. (2005). "11 Economic inequality and educational attainment across a generation" (PDF). Focus. 23 (3): 11–15.
[Implications of increased economic inequality:] Average achievement goes up slightly, but so does the variability of achievement. Average years of schooling increase by less than 1 percent. Inequality, in contrast, increases substantially, by over 8 percent when all four measures of inequality are considered together. Moreover, a higher proportion of students do not complete high school or 11th grade.
- ^ Checchi, Daniele (May 2001). "Education, Inequality and Income Inequality". Distributional Analysis Research Programme. 52. Suntory and Toyota International Centres for Economics and Related Disciplines, LSE.
income inequality effectively reduces school enrollment, mainly at secondary level.
- ^ "Growth in Means-Tested Programs and Tax Credits for Low-Income Households". Congressional Budget Office. 11 February 2013. Retrieved 28 January 2014.
- ^ Rachel Johnson; James Nunns; Jeffrey Rohaly; Eric Toder; Roberton Williams (July 2011). "Why Some Tax Units Pay No Income Tax" (PDF). Tax Policy Center. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 August 2011. Retrieved 28 January 2014.
- ^ a b Heckman, J., L. Lochner and C. Tabner, Tax Policy and Human Capital Formation, American Economic Review, 88, 293–297. Accessed: 31 July 2012.
- ^ Krueger, Dirk; Ludwig, Alexander (May 2013). "Optimal Progressive Labor Income Taxation and Education Subsidies When Education Decisions and Intergenerational Transfers Are Endogenous". American Economic Review. 103 (3): 496–501. doi:10.1257/aer.103.3.496. S2CID 17244958.
- ^ Ansell, Ben (2010). From the Ballot to the Blackboard: The Redistributive Political Economy of Education. Cambridge University Press. p. 175.
Under conditions of high income inequality and tax progressivity, there will be even greater support for higher education spending even if most people do not receive it
- ^ Estrada, Fernando (2010). "The power to tax: a lecture of Hayek". mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de. pp. 4–6. Retrieved 28 April 2024.
- ^ Roudik, Peter (December 2006). "Estonia: Taxation System and Implementation of Flat Income Tax" (PDF). The Law Library of Congress.
- ^ Nozick, Robert (19 January 2014), "23. Anarchy, State and Utopia", 23. Anarchy, State and Utopia, Princeton University Press, p. 169, doi:10.1515/9781400848393-024/html?lang=en, ISBN 978-1-4008-4839-3, retrieved 28 April 2024
- ^ Sampson, Geoffrey (1978). "Liberalism and Nozick's `Minimal State'". Mind. 87 (345): 93. ISSN 0026-4423.
- ^ Isidore, Chris (4 March 2013). "Buffett says he's still paying lower tax rate than his secretary". CNNMoney. Retrieved 24 March 2024.
- ^ "Buffett Rule: What It Means, Criticism, FAQs". Investopedia. Retrieved 24 March 2024.
- ^ Writer, Aila Slisco (8 June 2021). "Warren Buffett Defends Paying the Least Among America's Richest". Newsweek. Retrieved 24 March 2024.
- ^ Griffith, Thomas D. (2004). "Progressive Taxation And Happiness". Boston College Law Review. 45 (5): 1363.
- ^ Powell, Jim (17 October 2012). "Class Warfare: The Mortal Enemy Of Economic Growth And Jobs". Forbes. Retrieved 3 February 2014.
- ^ a b Kim, Susanna (19 September 2011). "Warren Buffett Rule: Class Warfare or Tax Fairness?". ABC News. Retrieved 3 February 2014.
- ^ Cummings, Mike (19 July 2022). "Beliefs about political equality prevent consensus on progressive taxes". YaleNews. Retrieved 24 March 2024.
- ^ Form 1040 Instructions (2003), 2003 Tax Rate Schedules, p. 74
- ^ Form 1040 Instructions (2004), 2004 Tax Computation Worksheet—Line 43, p. 72
- ^ "The Distribution of Household Income and Federal Taxes, 2010". US Congressional Budget Office. 4 December 2013. Retrieved 6 January 2014.
- ^ "IRS provides tax inflation adjustments for tax year 2021". Internal Revenue Service. 26 October 2020. Retrieved 22 April 2021.
- ^ 26 USC 55. Also see IRS Form 6251 (individuals) and Form 4626 (corporations).
- ^ Institute on Taxation and Economic Policy. (2018). Who pays? A distributional analysis of the tax systems in all 50 states. https://itep.org/whopays/
- ^ Loughead, Katherine. "State Individual Income Tax Rates and Brackets". Tax Foundation. Retrieved 22 April 2021.
- ^ Piketty, Thomas; Saez, Emmanuel (1 January 2007). "How Progressive is the U.S. Federal Tax System? A Historical and International Perspective". Journal of Economic Perspectives. 21 (1): 3–24. doi:10.1257/jep.21.1.3. ISSN 0895-3309. S2CID 5160267.
- ^ Hendricks, Galen (28 October 2020). "6 Ways the Trump Administration Is Rigging an Already Unfair Tax Code". Center for American Progress. Retrieved 22 April 2021.
- ^ Amadeo, Kimberly. "How Trump's Tax Reform Plan Affects You". The Balance. Retrieved 22 April 2021.
- ^ "Trump Tax Brackets: Did My Tax Rate Change? - SmartAsset | SmartAsset". smartasset.com. Retrieved 24 March 2024.
- ^ a b Kraja, Gentiana; Lirëza, Linert; Morselli, Alessandro (May 2023). "Comparative Study on Flat Tax and Progressive Tax in Albania". Journal of Educational and Social Research. 13 (3): 354. doi:10.3694/jesr-2023-0083.
- ^ "Belgium - Individual - Taxes on personal income". taxsummaries.pwc.com. Retrieved 22 April 2021.
- ^ "Canadian income tax rates for individuals - current and previous years". aem. 30 December 2020. Retrieved 22 April 2021.
- ^ "Denmark - Individual - Taxes on personal income". taxsummaries.pwc.com. Retrieved 22 April 2021.
- ^ "Germany - Individual - Taxes on personal income". taxsummaries.pwc.com. Retrieved 22 April 2021.
- ^ Maharani, Deswita; Mudzaka, Mochamad Kohar (April 2023). "The Effect of Progressive Tax on Regional Income (Study at One of The Centers of Income Management in Cimahi City)". Jurnal Ekonomi, Bisnis & Entrepreneurship. 17 (1). Indonesia: 95–102. doi:10.55208/jebe.v17i1.330.
- ^ Barokah1, Bela; Tripermata2, Lukita; Putri, Andini Utari (May 2023). "The Effect of Progressive Tax Implementation, Tax Sanctions and Tax Knowledge on the Level of Motor Vehicle Taxpayer Compliance in Palembang City: Case Study on WPOP Joint Office Samsat City of Palembang I". International Journal of Community Service & Engagement. 4 (2). doi:10.47747/ijcse.v4i2.1160.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Norway - Income Tax - KPMG Global". KPMG. 2 March 2021. Retrieved 22 April 2021.
- ^ skatteverket.se, Skatteverket. "Belopp och procent inkomstår 2013 - privat". www.skatteverket.se (in Swedish). Retrieved 22 April 2021.
- ^ "Income Tax rates and Personal Allowances". GOV.UK. Retrieved 22 April 2021.
- ^ "Income Tax in Scotland". GOV.UK. Retrieved 22 April 2021.
- ^ "Tax rates for individuals". ird.govt.nz. Inland Revenue Department (New Zealand). Retrieved 9 November 2022.
- ^ "Individual income tax rates". ato.gov.au. Australian Taxation Office. Archived from the original on 29 June 2011. Retrieved 15 May 2013.
- ^ "Italian Taxes & Tax Advantages For Expats Explained". Expatra. 23 October 2023. Retrieved 28 March 2024.
External links
edit- The Progressive Income Tax: Theoretical Foundations
- Slemrod, Joel B. (2002). "Progressive Taxes". In David R. Henderson (ed.). Concise Encyclopedia of Economics (1st ed.). Library of Economics and Liberty. OCLC 317650570, 50016270, 163149563