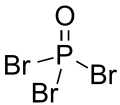
Phosphoryl bromide, also known as phosphorus oxybromide, is an inorganic compound with the formula POBr3.[3]
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Other names
Phosphorus oxybromide
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.252 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1939 2576 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| POBr3 | |||
| Molar mass | 286.685 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless crystals or thin plates with a faint orange tint | ||
| Odor | Pungent[1] | ||
| Density | 2.822 g/cm3[1] | ||
| Melting point | 56 °C (133 °F; 329 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 192 °C (378 °F; 465 K) | ||
| Reacts violently with water[1] | |||
| Solubility | Soluble in diethyl ether, benzene, chloroform, carbon disulfide, and concentrated sulfuric acid[1] | ||
| Structure[2] | |||
| Pnma, No. 62 | |||
a = 9.467 Å, b = 9.938 Å, c = 6.192 Å
| |||
Formula units (Z)
|
4 | ||
| Tetrahedral at the P atom | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
Corrosive to tissue | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
 
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H290, H314, H335 | |||
| P234, P260, P261, P264, P271, P280, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P312, P321, P363, P390, P403+P233, P404, P405, P501 | |||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
|||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Preparation
editPhosphoryl bromide is prepared by the reaction between phosphorus pentabromide and phosphorus pentoxide:[4][5]
- 3 PBr5 + P2O5 → 5 POBr3
It can also be prepared via the slow addition of liquid bromine to phosphorus tribromide at 0 °C, followed by the slow addition of water and vacuum distillation of the resulting slurry.[citation needed]
Structure and properties
editPhosphoryl bromide forms colorless crystals or thin plates with a faint orange tint.[6] Its crystals belong to the orthorhombic space group Pnma,[2][7] with intermolecular Br–O bridges creating infinite chains within the structure. The intermolecular bonding causes distortions from the C3v symmetry found in the free molecule.[2]
It is stored in sealed glass ampoules.
Uses
editPhosphoryl bromide finds use as a specialist brominating agent.
Safety
editPhosphoryl bromide reacts violently with water evolving heat, forming phosphoric acid and hydrobromic acid. Reacts with organic compounds to cause fire. Evolves highly toxic and corrosive gases when exposed to fire. When heated to decomposition, it emits highly toxic fumes like bromides, oxybromides and oxides of phosphorus. It is corrosive to metals and tissues.[6][1]
References
edit- ^ a b c d e https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Phosphorus-oxybromide
- ^ a b c Templeton, Lieselotte K.; Templeton, David H. (1971). "The crystal structure of POBr3: space group and refinement by least squares". Acta Crystallogr. B. 27 (8): 1678–1679. doi:10.1107/S0567740871004564. S2CID 97905269.
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. pp. 501–503. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ Hönigschmid, O.; Hirschbold‐Wittner, F. (1940). "Das Atomgewicht des Phosphors. Analyse des Phosphoroxybromids". Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie (in German). 243 (4): 355–360. doi:10.1002/zaac.19402430406. ISSN 1521-3749.
- ^ Booth, Harold S.; Seegmiller, C. G.; Baker, Philip S.; Wexler, Sol; Johnson, Roy D. (2007-01-05), Fernelius, W. Conard (ed.), "Phosphorus(V) Oxybromide: (Phosphoryl Tribromide)", Inorganic Syntheses, Hoboken, NJ, USA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., pp. 151–152, doi:10.1002/9780470132333.ch44, ISBN 978-0-470-13233-3, retrieved 2020-09-30
- ^ a b Perry, Dale L. (2011). Handbook of Inorganic Compounds (2nd ed.). Boca Raton: Taylor & Francis. p. 310. ISBN 978-1-4398-1461-1. OCLC 587104373.
- ^ Okuda, Tsutomu.; Hosokawa, Kazuto.; Yamada, Koji.; Furukawa, Yoshihiro.; Negita, Hisao. (1975). "Structural study of phosphoryl bromide by means of nuclear quadrupole resonance". Inorganic Chemistry. 14 (5): 1207–1209. doi:10.1021/ic50147a048. ISSN 0020-1669.