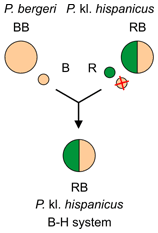
The Italian edible frog (Pelophylax kl. hispanicus) is a hybridogenic species in the true frog family Ranidae. These frogs are the offspring of P. bergeri and either P. ridibundus or the edible frog (P. kl. esculentus) which is itself of hybrid origin.
| Italian edible frog | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | Anura |
| Family: | Ranidae |
| Genus: | Pelophylax |
| Species: | |
| Binomial name | |
| Pelophylax kl. hispanicus (Bonaparte, 1839)
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
It is endemic to Italy; despite the specific name hispanicus (Latin for "the Spanish one"), it does not occur in Spain. Its natural habitats are rivers, intermittent rivers, swamps, freshwater lakes, intermittent freshwater lakes, freshwater marshes, and intermittent freshwater marshes. It is not considered threatened by the IUCN.
See also
editReferences
edit- Andreone, F. 2004. Pelophylax hispanicus. 2006 IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Downloaded on 23 July 2007.
- ^ Holsbeek, G.; Jooris, R. (2010). "Potential impact of genome exclusion by alien species in the hybridogenetic water frogs (Pelophylax esculentus complex)" (PDF). Biol Invasions. 12 (1). Springer Netherlands: 1–13. Bibcode:2010BiInv..12....1H. doi:10.1007/s10530-009-9427-2. ISSN 1387-3547. S2CID 23535815. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2019-07-13. Retrieved 2015-06-21.
