Ligurian Sea Cetacean Sanctuary
Originally called the International Ligurian Sea Cetacean Sanctuary (Ligurian Sea Sanctuary), what is now known as the Pelagos Sanctuary for Mediterranean Marine Mammals is a Marine Protected Area aimed at the protection of marine mammals (cetaceans). It covers an area of approximately 84,000 km2, comprising the waters between Toulon (French Riviera), Capo Falcone (western Sardinia), Capo Ferro (eastern Sardinia) and Fosso Chiarone (Tuscany).
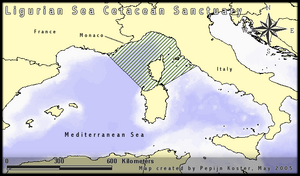
The sanctuary is located in the Ligurian basin of the Mediterranean Sea. In this area all the cetaceans occurring in the Mediterranean can be found at regular intervals. It is believed to be the main feeding ground for Fin Whales in the Mediterranean basin.
The sanctuary was established on 25 November 1999 and is the first (and currently the only) international / High Seas MPA in the world covering areas of the Mediterranean seas of France, Italy, and Monaco.
To underline the importance of the sanctuary, it has been added to the Specially Protected Areas of Mediterranean Importance (SPAMI) list of the 1999 Barcelona Convention.
Photo gallery
edit-
Stenella coeruleoalba Striped dolphin
-
Ziphius cavirostris Cuvier's beaked whale
-
Balaenoptera physalus Fin whale
External links
edit- Full text of the agreement on the creation of a Mediterranean Sanctuary for marine mammals
- Agreement on the Conservation of Cetaceans of the Black Sea Mediterranean Sea and Contiguous Atlantic Area
- WDCS Cetacean MPA's Case study: Pelagos Sanctuary for Mediterranean Marine Mammals
- Tullio Scovazzi, "The Mediterranean Marine Mammals Sanctuary" plus Appendix Agreement on the Creation of a Mediterranean Sanctuary for Marine Mammals (unofficial translation by F. Spadi), The International Journal of Marine and Coastal Law, Vol 16 (1), 2001[permanent dead link]
- "Notarbartolo di Sciara G., Agardy T., Hyrenbach D., Scovazzi T., Van Klaveren P. 2008. The Pelagos sanctuary for Mediterranean marine mammals. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 18:367-391." doi:10.1002/aqc.855
- RAC/SPA