The Pee Dee River, also known as the Great Pee Dee River, is a river in the Carolinas of the United States. It originates in the Appalachian Mountains in North Carolina, where its upper course, above the mouth of the Uwharrie River, is known as the Yadkin River. The river empties into Winyah Bay, and then into the Atlantic Ocean near Georgetown.
| Pee Dee River | |
|---|---|
 Shad fishing in February,
Pee Dee River, Yauhannah, South Carolina | |
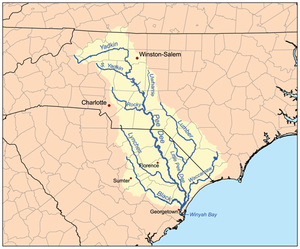 Pee Dee River watershed. | |
| Etymology | Pee Dee tribe |
| Location | |
| Country | United States |
| State | North Carolina, South Carolina |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Confluence of Uwharrie River and Yadkin River |
| • location | North Carolina |
| • coordinates | 35°22′51″N 80°3′29″W / 35.38083°N 80.05806°W[1] |
| • elevation | 272.3 ft (83.0 m) |
| Mouth | Winyah Bay |
• location | South Carolina |
• coordinates | 34°43′16″N 79°52′54″W / 34.72111°N 79.88167°W[1] |
• elevation | 0 ft (0 m) |
| Length | 232 mi (373 km)[2] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Winyah Bay |
| • average | 15000 cfs |
The northeastern counties of South Carolina compose the Pee Dee region of the state.
The exposed rock formations along its course are the source of a NIST reference standard.
It is an important source of electric power and public water supplies, as well as recreational use.
While the Pee Dee is free-flowing in South Carolina, upstream in North Carolina, several dams have been constructed on it. The opening and closing of these dams causes dramatic swings in the depth of the river in South Carolina. The sharing of water between the two states has sometimes been a matter of controversy, particularly during periods of drought.
Some commercial fishing is done during the winter shad run, and for shrimp in the lower reaches. The river is excellent for recreational fishing and boating.
There are numerous boat landings, yet most of the river is wild, with forests of tupelo, oak and gum along its shores. Herons and alligators can be seen along the way, and a lucky sighting of a bald eagle is possible.
Public and private organizations have restored and conserved sections of the Pee Dee River in South Carolina[3], along with the streams and wetlands around it, with ongoing efforts to restore and conserve even more sections of the river.[4]
The lower part of the river from Highway 378 to Winyah Bay has been designated a Scenic River.[5]
History
editThe river flows through the territory of the historic Pee Dee tribe, and is named after them. The Pee Dee were a part of the South Appalachian Mississippian culture. The first Europeans believed to have possibly navigated part of the river was a party sent by Lucas Vázquez de Ayllón in 1521.[6]
Snow's Island is a large island at the Pee Dee and Lynches rivers junction. It has been identified as the center of Johnsonville Impact Crater. The island was the headquarters of General Francis Marion for several months during the American Revolution. It proved a haven for him and his militia troops, as the British were unable to find the camp until it was abandoned.
The world's largest lumber company existed at the turn of the 20th century near the river's mouth at Georgetown. The virgin pine forests of the Pee Dee region were cutover, and the logs floated in rafts downriver to be sawn into lumber and exported to the northern United States and Europe.
Tributaries
editSome tributaries are the Lumber, the Little Pee Dee, Lynches, Black and Waccamaw rivers.
The river was an important trade route through the Low Country from colonial times. It is navigable from the Atlantic up to the Fall Line at Cheraw.
Today the river is not extensively used for navigation.
Rice
editThe lower part of the river flood plain was extensively developed for rice culture in colonial time; rice was the major export of the area from the port at Georgetown. Rice culture declined with the freedom of slave labor after the Civil War and with increased overseas competition. Two hurricanes at the beginning of the 20th century destroyed much of the rice canal infrastructure and effectively ended the remnants of rice culture.
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ a b U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Pee Dee River
- ^ "The National Map". U.S. Geological Survey. Retrieved February 14, 2011.
- ^ "Great Pee Dee Mitigation Bank". uniqueplacestosave.org. Retrieved December 11, 2024.
- ^ Baldwin, Skyler (November 1, 2024). "Grant to protect 62,000 acres in state's 'wood basket'". Charleston City Paper. Retrieved December 11, 2024.
- ^ "Designated Scenic Rivers". South Carolina Department of Natural Resources. Archived from the original on February 5, 2007.
- ^ Quattlebaum, Paul (1956). The Land Called Chicora (1st ed.). Gainesville, FL: University of Florida Press. p. 11.
External links
edit- Media related to Pee Dee River at Wikimedia Commons