Okinoerabujima (沖永良部島, Okinoerabu: いぃらぶ Yirabu, archaic Northern Ryukyuan: せりよさ Seriyosa), also known as Okinoerabu, is one of the Satsunan Islands, classed with the Amami archipelago between Kyūshū and Okinawa.[1]
 Aerial view of the island. (2013) | |
 | |
| Geography | |
| Location | East China Sea |
| Coordinates | 27°22′08″N 128°34′00″E / 27.36889°N 128.56667°E |
| Archipelago | Amami Islands |
| Area | 93.63 km2 (36.15 sq mi) |
| Length | 20 km (12 mi) |
| Width | 7 km (4.3 mi) |
| Coastline | 50 km (31 mi) |
| Highest elevation | 246 m (807 ft) |
| Highest point | Ōyama |
| Administration | |
Japan | |
| Prefectures | Kagoshima Prefecture |
| District | Ōshima District |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 13,767 (2012) |
| Pop. density | 150/km2 (390/sq mi) |
| Ethnic groups | Ryukyuan, Japanese |
The island, 93.63 km2 in area, has a population of approximately 14,000 persons. Administratively it is divided into the towns of Wadomari and China in Kagoshima Prefecture. Much of the island is within the borders of the Amami Guntō National Park.
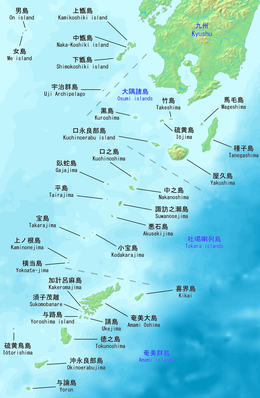
Geography
editOkinoerabujima is isolated from the other Amami islands, and is located in between Tokunoshima and Yoronjima, approximately 536 kilometres (289 nmi) south of the southern tip of Kyūshū and 60 kilometres (32 nmi) north of Okinawa.
The island is an elevated coralline island with a length of approximately 20 kilometres (12 mi) and width of 7 kilometres (4.3 mi), with Mount Ōyama at 246 metres (807 ft) above sea level at its highest peak.[2] In the eastern part of the island is an extensive limestone cave system, one of the largest in Asia.[3] The coast of the island is surrounded by a coral reef.
Climate
editOkinoerabujima has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification Cfa) with very warm summers and mild winters. Precipitation is significant throughout the year, but is somewhat lower in winter. The island is subject to frequent typhoons.
| Climate data for Tateyama, Okinoerabujima (1991−2020 normals, extremes 1969−present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 25.5 (77.9) |
27.4 (81.3) |
28.5 (83.3) |
29.8 (85.6) |
31.7 (89.1) |
33.9 (93.0) |
34.9 (94.8) |
34.4 (93.9) |
33.8 (92.8) |
31.8 (89.2) |
31.5 (88.7) |
27.1 (80.8) |
34.9 (94.8) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 18.8 (65.8) |
19.1 (66.4) |
20.8 (69.4) |
23.0 (73.4) |
25.7 (78.3) |
28.6 (83.5) |
31.3 (88.3) |
31.3 (88.3) |
30.2 (86.4) |
27.5 (81.5) |
24.2 (75.6) |
20.6 (69.1) |
25.1 (77.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 16.5 (61.7) |
16.6 (61.9) |
18.2 (64.8) |
20.5 (68.9) |
23.1 (73.6) |
25.9 (78.6) |
28.5 (83.3) |
28.6 (83.5) |
27.6 (81.7) |
25.1 (77.2) |
21.9 (71.4) |
18.4 (65.1) |
22.6 (72.6) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 14.2 (57.6) |
14.3 (57.7) |
15.8 (60.4) |
18.2 (64.8) |
21.0 (69.8) |
24.0 (75.2) |
26.4 (79.5) |
26.5 (79.7) |
25.5 (77.9) |
23.1 (73.6) |
19.9 (67.8) |
16.1 (61.0) |
20.4 (68.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 4.7 (40.5) |
6.1 (43.0) |
5.2 (41.4) |
10.2 (50.4) |
14.1 (57.4) |
17.5 (63.5) |
20.5 (68.9) |
22.0 (71.6) |
19.2 (66.6) |
16.2 (61.2) |
12.6 (54.7) |
7.8 (46.0) |
4.7 (40.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 91.5 (3.60) |
93.0 (3.66) |
141.7 (5.58) |
146.4 (5.76) |
196.9 (7.75) |
317.7 (12.51) |
144.7 (5.70) |
175.8 (6.92) |
176.9 (6.96) |
172.4 (6.79) |
107.8 (4.24) |
91.9 (3.62) |
1,856.7 (73.10) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 10.9 | 10.1 | 10.9 | 10.6 | 11.6 | 12.5 | 6.6 | 8.9 | 10.2 | 8.4 | 7.8 | 9.7 | 118.2 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 66 | 68 | 71 | 76 | 81 | 88 | 83 | 81 | 78 | 73 | 69 | 66 | 75 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 83.6 | 87.3 | 118.8 | 136.4 | 149.8 | 164.9 | 271.1 | 252.6 | 209.3 | 169.6 | 122.0 | 92.4 | 1,861.6 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency[4][5] | |||||||||||||
History
editIt is uncertain when Okinoerabujima was first settled. It was ruled by the Aji nobility who built numerous gusuku fortifications from the 8th century onwards. From 1266 it was part of Hokuzan, and from 1422 the Ryukyu Kingdom. The island was invaded by samurai from Satsuma Domain during the 1609 Invasion of Ryukyu and its incorporation into the official holdings of Satsuma was recognized by the Tokugawa shogunate in 1624. Satsuma rule was harsh, with the inhabitants of the island reduced to serfdom and forced to raise sugar cane to meet high taxation, which often resulted in famine. The island was subordinate to Tokunoshima from 1616 to 1690, when an independent daikansho was established. Throughout the Satsuma period, the island was used as a prison settlement, especially for political offenders, including many members of the Ryukyuan royal family. Saigō Takamori was exiled to Okinoerabujima from 1862 to 1864.
After the Meiji Restoration the island was incorporated into Ōsumi Province and later became part of Kagoshima Prefecture. Following World War II, along with the other Amami Islands, it was occupied by the United States until 1953, at which time it reverted to the control of Japan. In September 1977, a massive typhoon (Typhoon Babe (1977)) devastated the island, which experienced winds in excess of 210 km/h (130 mph) for two hours as the typhoon passed by.[6] Nearly two-thirds of the homes across the island were damaged or destroyed by the storm and 73 people were injured.[7] Most of the injuries across the island were caused by collapsing buildings.[8]
Fauna
editOkinoerabujima is home to several rare species of reptiles and insects endemic to the island itself, or more generally to the Ryukyu Islands. The island is one of fewer locations where swimming with whales (humpback whales) is legally approved.[9]
Economy
editWith moderate rainfall and a warm climate, the island is suitable for agriculture. Main crops include sweet potatoes, sugar cane and floriculture. Brown sugar refining and the production of distilled shōchū liquor is the major industry. The island is not a major tourist destination, unlike many in the Amami archipelago.
Transportation
editThe port of Wadomari, located in the town of the same name, has regular ferry services to Okinawa and Kagoshima. The smaller port of China, in the town of China, has ferries to Kagoshima and other of the Amami islands.
Okinoerabu Airport, in Wadomari, is located in east side of the island. Flights connect the island to Kagoshima, Tokunoshima, Amami (via Tokunoshima), and Okinawa (Naha).
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Teikoku's Complete Atlas of Japan, Teikoku-Shoin Co., Ltd., Tokyo, ISBN 4-8071-0004-1
- ^ Map of Okinoerabujima
- ^ Guide to Amami Islands - Okinoerabujima Archived 2011-03-21 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ 観測史上1~10位の値(年間を通じての値). JMA. Retrieved February 18, 2022.
- ^ 気象庁 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値). JMA. Retrieved February 18, 2022.
- ^ "Typhoon Rakes Japan". The Spokesman-Review. Tokyo, Japan. Associated Press. September 11, 1977. p. A5. Retrieved April 17, 2013.
- ^ United Press International (September 10, 1977). "Typhoon Babe Slashes Japan". Spokane Daily Chronicle. Tokyo, Japan. p. 2. Retrieved April 17, 2013.
- ^ "Typhoon Babe ravages Japan's island chain". The Day. Tokyo, Japan. Associated Press. September 10, 1977. p. 1. Retrieved April 17, 2013.
- ^ Kamibayashi T.. 2014. 沖永良部島の ホエールスイムとケイビング - Tourism activities in Okinoerabu Island:Swimming with whales and caving. みどりいし (25). pp.36-37. Retrieved on February 15, 2017
- Eldridge, Mark. The Return of the Amami Islands: The Reversion Movement and U.S.-Japan Relations. Levington Books (2004) ISBN 0739107100
- Hellyer. Robert. Defining Engagement: Japan and Global Contexts, 1640-1868. Harvard University Press (2009) ISBN 0674035771
- Turnbull, Stephen. The Most Daring Raid of the Samurai. Rosen Publishing Group (2011) ISBN 978-1-4488-1872-3
- Ravina, Mark. The Last Samurai: The Life and Battles of Saigo Takamori. Whiley (2011) ISBN 1118045564