The black-tailed dasyure (Murexia melanurus) is a species of marsupial in the family Dasyuridae.[2][3]
| Black-tailed dasyure[1] | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Infraclass: | Marsupialia |
| Order: | Dasyuromorphia |
| Family: | Dasyuridae |
| Subfamily: | Dasyurinae |
| Tribe: | Phascogalini |
| Genus: | Murexia |
| Species: | M. melanurus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Murexia melanurus (Thomas, 1899)
| |
| |
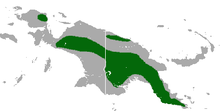
| black-tailed dasyure range | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Murexechinus melanurus (Van Dyck, 2002) | |
Range and habitat
editThe Black-tailed dasyure is native to New Guinea, where it ranges across the Central Cordillera of Western New Guinea, which is part of Indonesia, and of Papua New Guinea. It is also present in the Arfak Mountains of Western New Guinea and the Torricelli Mountains in northern Papua New Guinea. It is found from sea level to mid-montane areas up to 2,800 meters elevation.[2]
Its natural habitat is forest, including lowland rain forest and montane rain forest (mid-montane forest, beech forest, pandanus forest, and mossy forest).[2]
It is fairly abundant across its range, and its population is stable.
Breeding
editThe Black-tailed dasyure breeds throughout the year. Females have up to four young.[2]
References
edit- ^ Groves, C. P. (2005). Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 30–31. ISBN 0-801-88221-4. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ a b c d e f Leary, T.; Seri, L.; Wright, D.; Hamilton, S.; Helgen, K.; Singadan, R.; Menzies, J.; Allison, A.; James, R.; Dickman, C.; Lunde, D.; Aplin, K.; Woolley, P. (2016). "Murexia melanurus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T1591A21943184. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T1591A21943184.en. Retrieved 4 August 2021.
- ^ "Murexia melanurus". ASM Mammal Diversity Database. American Society of Mammalogists. Retrieved 24 July 2020.
External links
edit- Scientists discover new species with fatal attraction on Queensland's Gold Coast hinterland—Australian Broadcasting Corporation (Wednesday, 19 February 2014)
