The monsoon trough is a portion of the Intertropical Convergence Zone in the Western Pacific,[1][2] as depicted by a line on a weather map showing the locations of minimum sea level pressure,[1] and as such, is a convergence zone between the wind patterns of the southern and northern hemispheres.
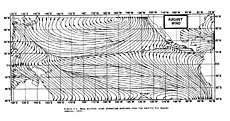
Westerly monsoon winds lie in its equatorward portion while easterly trade winds exist poleward of the trough.[3] Right along its axis, heavy rains can be found which usher in the peak of a location's respective rainy season. The monsoon trough plays a role in creating many of the world's rainforests.[4]
The term monsoon trough is most commonly used in monsoonal regions of the Western Pacific such as Asia and Australia. The migration of the ITCZ/monsoon trough into a landmass heralds the beginning of the annual rainy season during summer months. Depressions and tropical cyclones often form in the vicinity of the monsoon trough, with each capable of producing a year's worth of rainfall in a matter of days.
Movement and strength
editMonsoon troughing in the western Pacific reaches its zenith in latitude during the late summer when the wintertime surface ridge in the opposite hemisphere is the strongest. It can reach as far as the 40th parallel in East Asia during August and the 20th parallel in Australia during February. Its poleward progression is accelerated by the onset of the summer monsoon which is characterized by the development of lower air pressure over the warmest part of the various continents.[5][6][7] In the Southern Hemisphere, the monsoon trough associated with the Australian monsoon reaches its most southerly latitude in February,[8] oriented along a west-northwest/east-southeast axis. North-south-oriented mountain barriers, like the Rockies and the Andes, and large massifs, such as the Plateau of Tibet, also influence atmospheric flow. [9]
Effect of wind surges
editIncreases in the relative vorticity, or spin, with the monsoon trough are normally a product of increased wind convergence within the convergence zone of the monsoon trough. Wind surges can lead to this increase in convergence. A strengthening or equatorward movement in the subtropical ridge can cause a strengthening of a monsoon trough as a wind surge moves towards the location of the monsoon trough. As fronts move through the subtropics and tropics of one hemisphere during their winter, normally as shear lines when their temperature gradient becomes minimal, wind surges can cross the equator in oceanic regions and enhance a monsoon trough in the other hemisphere's summer.[10] A key way of detecting whether a wind surge has reached a monsoon trough is the formation of a burst of thunderstorms within the monsoon trough.[11]
Monsoon depressions
editIf a circulation forms within the monsoon trough, it is able to compete with the neighboring thermal low over the continent, and a wind surge will occur at its periphery. Such a circulation which is broad in nature within a monsoon trough is known as a monsoon depression. In the Northern Hemisphere, monsoon depressions are generally asymmetric, and tend to have their strongest winds on their eastern periphery.[11] Light and variable winds cover a large area near their center, while bands of showers and thunderstorms develop within their area of circulation.[12]
The presence of an upper level jet stream poleward and west of the system can enhance its development by leading to increased diverging air aloft over the monsoon depression, which leads to a corresponding drop in surface pressure.[13] Even though these systems can develop over land, the outer portions of monsoon depressions are similar to tropical cyclones.[14] In India, for example, 6 to 7 monsoon depressions move across the country yearly,[5] and their numbers within the Bay of Bengal increase during July and August of El Niño events.[15] Monsoon depressions are efficient rainfall producers, and can generate a year's worth of rainfall when they move through drier areas, such as the outback of Australia.[16]
Some tropical cyclones recognised by Regional Specialized Meteorological Centres would have characteristics of a monsoon depression throughout their lifetime. The Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) added monsoon depression as a category in 2015, and Cyclone Komen is the first system recognised as a fully monsoon depression by JTWC.[17]
Roles
editIn rainy season
editSince the monsoon trough is an area of convergence in the wind pattern, and an elongated area of low pressure at the surface, the trough focuses low level moisture and is defined by one or more elongated bands of thunderstorms when viewing satellite imagery. Its abrupt movement to the north between May and June is coincident with the beginning of the monsoon regime and rainy seasons across South and East Asia. This convergence zone has been linked to prolonged heavy rain events in the Yangtze river as well as northern China.[2] Its presence has also been linked to the peak of the rainy season in locations within Australia.[18]
In tropical cyclogenesis
editA monsoon trough is a significant genesis region for tropical cyclones. Vorticity-rich low level environments, with significant low level spin, lead to a better than average chance of tropical cyclone formation due to their inherent rotation. This is because a pre-existing near-surface disturbance with sufficient spin and convergence is one of the six requirements for tropical cyclogenesis.[19] There appears to be a 15- to 25-day cycle in thunderstorm activity associated with the monsoon trough, which is roughly half the wavelength of the Madden–Julian oscillation, or MJO.[20] This mirrors tropical cyclone genesis near these features, as genesis clusters in 2–3 weeks of activity followed by 2–3 weeks of inactivity. Tropical cyclones can form in outbreaks around these features under special circumstances, tending to follow the next cyclone to its poleward and west.[21]
Whenever the monsoon trough on the eastern side of the summertime Asian monsoon is in its normal orientation (oriented east-southeast to west-northwest), tropical cyclones along its periphery will move with a westward motion. If it reverses its orientation, orienting southwest to northeast, tropical cyclones will move more poleward. Tropical cyclone tracks with S-shapes tend to be associated with reverse-oriented monsoon troughs.[22] The South Pacific convergence zone and South Atlantic convergence zones are generally reverse oriented.[8] The failure of the monsoon trough, or the ITCZ, to move south of the equator in the eastern Pacific Ocean and Atlantic Ocean during the southern hemisphere summer, is considered one of the factors causing tropical cyclones to not normally form in those regions.[11] It has also been noted that when the monsoon trough lies near 20 degrees north latitude in the Pacific, the frequency of tropical cyclones is 2 to 3 times greater than when it lies closer to 10 degrees north.[2]
References
edit- ^ a b "Monsoon trough". Glossary of Meteorology. American Meteorological Society. Archived from the original on 17 June 2009. Retrieved 4 June 2009.
- ^ a b c Bin Wang. The Asian Monsoon. Retrieved 2008-05-03.
- ^ World Meteorological Organization. Severe Weather Information Centre. Retrieved 2008-05-03.
- ^ Hobgood (2008)Global Pattern of Surface Pressure and Wind. Archived 18 March 2009 at the Wayback Machine Ohio State University. Retrieved 2009-03-08.
- ^ a b National Centre for Medium Range Forecasting. Chapter-II Monsoon-2004: Onset, Advancement and Circulation Features. Archived 21 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved 2008-05-03.
- ^ Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Monsoon. Archived 23 February 2001 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved 2008-05-03.
- ^ Dr. Alex DeCaria. Lesson 4 – Seasonal-mean Wind Fields. Archived 22 August 2009 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved 2008-05-03.
- ^ a b U. S. Navy. 1.2 Pacific Ocean Surface Streamline Pattern. Retrieved 2006-11-26.
- ^ "Atmosphere - Effect of continents on air movement | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 13 May 2024.
- ^ Chih-Lyeu Chen. Effects of the Northeast Monsoon on the Equatorial Westerlies Over Indonesia.[dead link] Retrieved 2008-05-03.
- ^ a b c U. S. Navy. SECTION 3. DYNAMIC CONTRIBUTORS TO TROPICAL CYCLONE FORMATION. Retrieved 2006-11-26.
- ^ Chip Guard. Climate Variability on CNMI. Archived 22 June 2007 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved 2008-05-03.
- ^ Sixiong Zhao and Graham A. Mills. A Study of a Monsoon Depression Bringing Record Rainfall over Australia. Part II: Synoptic–Diagnostic Description.[permanent dead link] Retrieved 2008-05-03.
- ^ N.E. Davidson and G.J. Holland. A Diagnostic Analysis of Two Intense Monsoon Depressions over Australia.[permanent dead link] Retrieved 2008-05-03.
- ^ O. P. Singh, Tariq Masood Ali Khan, and Md. Sazedur Rahman. Impact of Southern Oscillation on the Frequency of Monsoon Depressions in the Bay of Bengal. Retrieved 2008-05-03.
- ^ Bureau of Meteorology. TWP-ICE Synoptic Overview, 1 February 2006. Retrieved 2008-05-03.
- ^ "North Indian Ocean Best Track Data". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Retrieved 25 May 2020.
- ^ Bureau of Meteorology. Climate of Giles. Archived 11 August 2008 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved 2008-05-03.
- ^ Christopher Landsea. Climate Variability of Tropical Cyclones: Past, Present and Future. Retrieved 2006-11-26.
- ^ Patrick A. Harr. Tropical Cyclone Formation/Structure/Motion Studies. Archived 29 November 2007 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved 2006-11-26.
- ^ Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Typhoon Polly. Archived 19 September 2006 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved 2006-11-26.
- ^ Mark A. Lander. Specific Tropical Cyclone Track Types and Unusual Tropical Cyclone Motions Associated with a Reverse-Oriented Monsoon Trough in the Western North Pacific. Retrieved 2006-11-26.