Marugame (丸亀市, Marugame-shi) is a city located in Kagawa Prefecture, Japan. As of 1 October 2022[update], the city had an estimated population of 108,541 in 46101 households and a population density of 970 persons per km2.[1] The total area of the city is 111.79 square kilometres (43.16 sq mi).
Marugame
丸亀市 | |
|---|---|
 View of downtown Marugame City, from Marugame Castle | |
 Location of Marugame in Kagawa Prefecture | |
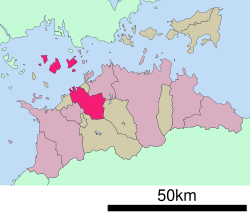 | |
| Coordinates: 34°17′N 133°48′E / 34.283°N 133.800°E | |
| Country | Japan |
| Region | Shikoku |
| Prefecture | Kagawa |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Kyoji Matsunaga (from April 2021) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 111.79 km2 (43.16 sq mi) |
| Population (October 1, 2022) | |
| • Total | 108,541 |
| • Density | 970/km2 (2,500/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+09:00 (JST) |
| City hall address | 2-3-1 Ōtemachi, Marugame-shi, Kagawa-ken 763-8501 |
| Website | Official website |
| Symbols | |
| Flower | Satsuki azalea |
| Tree | Myrica rubra |




Geography
editMarugame is located in north-center Kagawa Prefecture, on the island of Shikoku, facing the Seto Inland Sea to the north. The city covers the northeastern part of the Marugame Plain and part of the Shiwaku Islands. As with many other cities and towns in Kagawa Prefecture, there are many reservoirs. The Doki River flows from north to south through the center of the city, and to the south is Mount Tsutsumi, also known as Hatoko Fuji, one of the "Sanuki Seven Fujis". Mount Iino, nicknamed Sanuki Fuji and located on the border between Marugame and Sakaide, is another of the "Sanuki Seven Fujis".[2]
Neighbouring municipalities
editKagawa Prefecture
Climate
editMarugame has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen Cfa) characterized by warm summers and cool winters with light snowfall. The average annual temperature in Marugame is 15.7 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1439 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 26.6 °C, and lowest in January, at around 5.3 °C.[3]
Demographics
editPer Japanese census data,[4] the population of Marugame has recently plateaued after several decades of growth.
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 87,271 | — |
| 1960 | 81,523 | −6.6% |
| 1970 | 78,263 | −4.0% |
| 1980 | 94,849 | +21.2% |
| 1990 | 101,253 | +6.8% |
| 2000 | 108,356 | +7.0% |
| 2010 | 110,473 | +2.0% |
| 2020 | 109,513 | −0.9% |
History
editThe area of Marugame was part of ancient Sanuki Province and has been inhabited since ancient times, with many kofun burial mounds found within the city limits. From the Heian period onwards, it was noted as an entry point for pilgrims to the Kotohira-gū shrine. During the Edo Period, the area developed as the castle town for Marugame Domain, which was ruled for 210 years by the Kyōgoku clan. Following the Meiji restoration, the town of Marugame was established with the creation of the modern municipality system on February 15, 1890. It was elevated to city status on April 1, 1890, becoming the 53rd city in Japan. During the 1950s the southeast area of the city and some islands were amalgamated to form new parts of the city.
On March 22, 2005, the towns of Ayauta and Hanzan (both from Ayauta District) were merged into Marugame to create the current expanded city of Marugame.
Government
editMarugame has a mayor-council form of government with a directly elected mayor and a unicameral city council of 24 members. Marugame, together with Naoshima, contributes four members to the Kagawa Prefectural Assembly. In terms of national politics, the city is divided between the Kagawa 2nd district and the Kagawa 3rd district of the lower house of the Diet of Japan.
List of mayors of Marugame (from 1899 to present)
edit| Name | Office Entered | Office Left |
|---|---|---|
| Motoyoshi Toyoda (豊田元良) |
3 August 1899 | 8 January 1904 |
| Aina Hasegawa (長谷川和愛) |
18 June 1904 | 17 June 1910 |
| Kenkichi Fujiyoshi (藤好乾吉) |
8 June 1910 | 12 January 1915 |
| Kenichi Saito (斎藤研一) |
2 November 1915 | 1 June 1917 |
| Tokutaro Higuchi (樋口德太郎) |
15 September 1917 | 7 October 1920 |
| Kiyoshi Hisano (久野廉) |
3 June 1921 | 7 March 1923 |
| Iwao Osuka (大須賀巖) |
5 July 1923 | 4 July 1931 |
| Kikuma Takaki (高木季熊) |
17 November 1931 | 10 April 1934 |
| Seizaburo Ogaza (大柏淸三郎) |
25 July 1934 | 24 July 1942 |
| Toshisuke Irie (入江俊輔) |
25 July 1942 | 24 July 1946 |
| Katsuhide Mihara (三原勝英) |
26 April 1947 | 29 April 1963 |
| Shigetoshi Horiie (堀家重俊) |
30 April 1963 | 29 April 1991 |
| Keisuke Katayama (片山圭之) |
30 April 1991 | 29 April 2003 |
| Tetsuji Arai (新井哲二) |
30 April 2003 | 23 April 2013 |
| Masaharu Kaji (梶正治) |
24 April 2013 | present |
Economy
editMarugame has a mixed economy centered on agriculture (rice, vegetables, chicken, peaches) and manufacturing along a coastal belt of reclaimed land which contains a number of industrial parks, textile plants and shipyards. Traditionally, the city was noted for its production of uchiwa fans, claiming a 90% market share; however, due to mechanization and changes in fashion, only two workshops are left in the city. Due to its well-developed transportation network, industry is expanding, and the city is increasingly becoming a commuter town for neighboring Takamatsu.
In 2015, Imabari Shipbuilding announced the construction of a large dry dock capable of building world-class containerships in Marugame.[5]
Education
editMarugame has 18 public elementary schools and eight public middle schools operated by the city government, and four public high schools operated by the Kagawa Prefectural Board of Education. In addition, there are one private middle school, two private high schools and two correspondence high schools. The prefecture also operates one middle school and one high school.
Transportation
editRailways
editTakamatsu-Kotohira Electric Railroad - Kotohira Line
Highways
editSister cities
edit- Donostia / San Sebastián, Spain, since November 6, 1990[6]
- Pasig, Philippines[7]
- Willich, Germany, since July 6, 2023[8]
- Zhangjiagang, Jiangsu, China, friendship city since May 28, 1990[6]
Local attractions
edit- Kaitenyama Kofun, National Historic Site
- Marugame Castle, National Historic Site and one of only 12 Japanese castles with original wooden tenshu (keeps) remaining.
- Marugame Genichiro-Inokuma Museum of Contemporary Art (MIMOCA), situated just east of the railway station, houses the works of Genichiro Inokuma, as well as playing host to many visiting exhibitions.
- Reoma World, a recreational facility with many attractions, two restaurants, a spa and hotel in the theme park
- Shiwaku Kinbansho, National Historic Site
Events
edit- Marugame Half Marathon - Occurring in early February, the race attracts thousands of runners each year.[9] Held since 1947, the Asian record in the half marathon was set on the course by Kayoko Fukushi in 2006.[10]
Notable people from Marugame
edit- Yoshihiko Isozaki, politician
- Katsuyuki Motohiro, movie director
- Fumiko Saiga, judge on the International Criminal Court
- Toshio Yamauchi, politician
References
edit- ^ "Marugame city official statistics" (in Japanese). Japan.
- ^ "Mt. Iino (飯野山)". 14 May 2012.
- ^ Marugame climate data
- ^ Marugame population statistics
- ^ "Imabari to build giant dock in Japan". Nikkei Asia. Retrieved 2023-07-18.
- ^ a b "Marugame city homepage" (in Japanese). Japan.
- ^ "List of Sister City Affiliations with Japan (by country)". Clair Singapore. Archived from the original on October 23, 2016. Retrieved July 15, 2017.
- ^ "Freunde aus Japan begrüßt". www.stadt-willich.de (in German). Retrieved 2023-07-27.
- ^ Ota, Shigenobu (2009-02-02). Marugame Half Marathon. ARRS. Retrieved on 2010-02-07.
- ^ Nakamura, Ken (2006-02-05). Fukushi sets Asian Half-Marathon record in Marugame. IAAF. Retrieved on 2010-02-07.
External links
edit- Marugame City official website (in Japanese)
- Marugame City official website (in English)
- Marugame travel guide from Wikivoyage
- Geographic data related to Marugame, Kagawa at OpenStreetMap