Description of the Medieval Warm Period and Little Ice Age in IPCC reports
The description of the Medieval Warm Period and Little Ice Age in IPCC reports has changed since the first report in 1990 as scientific understanding of the temperature record of the past 1000 years has improved. The Medieval Warm Period (MWP) and Little Ice Age (LIA) are the best-known temperature fluctuations in the last millennium.
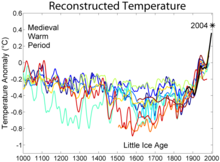
Critics of the "hockey stick graph" of all subsequent reports have claimed that the record of the MWP and LIA were suppressed in the IPCC Third Assessment Report although every report discussed the phenomena.
1990 report (FAR)
editWith the growth of interest in global warming in the 1980s came renewed interest in the past temperature record as well as the question of whether past times had been warmer or colder than "present". However, available records were then few. In Chapter 7 "Observed Climate Variations and Change", the Executive Summary on page 199 noted that palaeo-climatic evidence indicated surface temperature "fluctuations including the Holocene Optimum around 5,000-6,000 years ago, the shorter Medieval Warm Period around 1000 AD (which may not have been global) and the Little Ice Age which ended only in the middle to late nineteenth century. Details are often poorly known because palaeo-climatic data are frequently sparse."[1]
Section "7.2.7 Climate Of The Past 5,000,000 Years" of the report included, on page 202, "Figure 7.1: Schematic diagrams of global temperature variations since the Pleistocene on three time scales". The third diagram, figure 7.1 (c), used a schematic (non-quantitative) curve to represent temperature variations over the last 1000 years. The vertical temperature scale was labelled as "Temperature change (°C)" but no numerical labels were given; it could be taken to imply that temperature variations of the MWP and LIA were each of the order of 0.5 °C from the temperature around 1900. Text on the same page specifically stated recent climate changes were in a range of probably less than 2 °C. It noted that the "late tenth to early thirteenth centuries (about AD 950-1250) appear to have been exceptionally warm in western Europe, Iceland and Greenland", and this period "is known as the Medieval Climatic Optimum".[1]
The 1990 report noted that it was not clear 'whether all the fluctuations indicated were truly global. However, large regional changes in hydrological conditions have occurred, particularly in the tropics. Wetter conditions in the Sahara from 12 000 to 4,000 years BP enabled cultural groups to survive by hunting and fishing '(p 202). Figure 7.1 is about global temperature. A paper by Jones, Keith Briffa et al. noted that the schematic 7.1 (c) figure on p. 202 had no clear source, but can be traced to publications by Hubert Lamb representing the Central England temperature record; those publications have no explicit calibration against instrumental data, [and are] just Lamb’s qualitative judgement and interpretation of what he refers to as the ‘evidence’. [2]
Within the 1990 report, the LIA is taken to be global in extent but not the MWP. Climate over the last 1000 years is mentioned very briefly in the SPM of the 1990 report. The MWP is not mentioned at all, and the LIA described by "probably fluctuated by little more than 1°C. Some fluctuations lasted several centuries, including the LIA which ended in the [19th century] and which appears to have been global in extent". The MWP is mentioned in the executive summary to chapter 7, as "MWP around 1000 AD (which may not have been global)".
1992 supplement
editThe 1992 report (appendix C) used only two graphs of pre-instrumental temperatures, from (Wang and Wang 1991). They show air temperature based on documentary evidence in East and North China from 1350 to 1950. Fluctuations are of the order of 0.5-0.75 °C and indicate, variably, colder-than-present temperatures before the 20th century. The graph stops in 1350 and does not show a MWP. The only text reference to the MWP is qualified by in this region in boldface.
1995 report (SAR)
editBy 1995, research in the subject had advanced and hemispherical reconstructions of temperature were available, though only for the summer season (because tree rings are often most strongly influenced by summer temperatures). The 1995 IPCC report used a Northern Hemisphere summer temperature reconstruction (fig 3.20) from 1400 to 1979 by (Bradley and Jones 1993). This too shows no MWP (it only goes back to 1400) and colder temperatures otherwise before the 20th century, of the order of 0.5 °C colder. Fig 3.21 shows 8 ice core records from 1200 to present, which display a mixed pattern.
The MWP and LIA are introduced, in the text, as "two periods which have received special attention... These have been interpreted, at times, as periods of global warmth and coolness, respectively. Recent studies have re-evaluated the interval commonly known as the Medieval Warm Period to assess the magnitude and geographical extent of any prolonged warm interval between the 9th and 14th centuries (Hughes and Diaz, 1994). The available evidence is limited (geographically) and is equivocal." After discussing the evidence, it concluded "a clearer picture may emerge as more and better calibrated proxy records are produced. However, at this point, it is not yet possible to say whether, on a hemispheric scale, temperatures declined from the 11-12th to the 16-17th century. Nor, therefore, is it possible to conclude that global temperatures in the Medieval Warm Period were comparable to the warm decades of the late 20th century."
2001 report (TAR)
editThe 2001 report used Northern Hemisphere warm-season and annual reconstructions from 1000 AD to present by (Mann et al. 1999), (Jones et al. 1998) and (Briffa 2000).[3]
The IPCC TAR says of the MWP that the posited Medieval Warm Period appears to have been less distinct, more moderate in amplitude, and somewhat different in timing at the hemispheric scale than is typically inferred for the conventionally defined European epoch. The Northern Hemisphere mean temperature estimates of (Jones et al. 1998), (Mann et al. 1999), and (Crowley & Lowery 2000) show temperatures from the 11th to 14th centuries to be about 0.2°C warmer than those from the 15th to 19th centuries, but rather below mid-20th century temperatures.[4]
The TAR discusses Was there a "Little Ice Age" and a "Medieval Warm Period"? and says Thus current evidence does not support globally synchronous periods of anomalous cold or warmth over this timeframe, and the conventional terms of "Little Ice Age" and "Medieval Warm Period" appear to have limited utility in describing trends in hemispheric or global mean temperature changes in past centuries.[4]
2007 report (AR4)
editThe 2007 report used more recent temperature reconstructions including (Esper, Cook & Schweingruber 2002), (Bradley et al. 2003a), (Jones and Mann 2004), (D'Arrigo, Wilson & Jacoby 2006). The IPCC concluded the warmest period prior to the 20th century very likely occurred between 950 and 1100...The evidence currently available indicates that Northern Hemisphere mean temperatures during medieval times (950–1100) were indeed warm in a 2-kyr context and even warmer in relation to the less sparse but still limited evidence of widespread average cool conditions in the 17th century (Osborn & Briffa 2006). However, the evidence is not sufficient to support a conclusion that hemispheric mean temperatures were as warm, or the extent of warm regions as expansive, as those in the 20th century as a whole, during any period in medieval times (Jones et al., 2001; Bradley et al., 2003a,b; Osborn & Briffa 2006).[5]
2013 report (AR5)
editAR5 prefers the term "Medieval Climate Anomaly" (MCA) to "Medieval Warm Period". Chapter 5, section 5.3.5.1 discussed work since AR4 on the MCA and LIA. It notes that the timing and spatial structure of the MCA and LIA are complex, with different reconstructions exhibiting warm and cold conditions at different times for different regions and seasons. A combination of Northern Hemisphere temperature reconstructions shows mostly warm conditions from about 950 to about 1250 and colder conditions from about 1450 to about 1850, which are taken to represent the times of the MCA and LIA.
They express high confidence that the mean Northern Hemisphere temperature of the last 30 or 50 years exceed 30- or 50-year means of the past 800 years, and medium confidence that the last 30 years were likely the warmest 30-year period of the last 1400 years.[6]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ a b IPCC First Assessment Report Working Group 1 report, Chapter 7, Executive Summary p. 199, Climate Of The Past 5,000,000 Years p.202.
- ^ Jones, P.D.; Briffa, K.R.; Osborn, T.J.; et al. (February 2009), "High-resolution palaeoclimatology of the last millennium: a review of current status and future prospects" (PDF), The Holocene, 19 (1): 3–49, Bibcode:2009Holoc..19....3J, doi:10.1177/0959683608098952, S2CID 129606908, archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-10-21 Appendix A
- ^ IPCC TAR WG1 (2001), "Figure 2.21: Comparison of warm-season (Jones et al., 1998) and annual mean (Mann et al., 1998, 1999) multi-proxy-based and warm season tree-ring-based (Briffa, 2000) millennial Northern Hemisphere temperature reconstructions.", in Houghton, J.T.; Ding, Y.; Griggs, D.J.; Noguer, M.; van der Linden, P.J.; Dai, X.; Maskell, K.; Johnson, C.A. (eds.), Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis, Contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-80767-8
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ a b 2.3.3 Was there a "Little Ice Age" and a "Medieval Warm Period"?, 2001, archived from the original on 2006-05-29, in IPCC TAR WG1 2001
- ^ IPCC AR4 WG1 (2007), "Chapter 6 Paleoclimate" (PDF), in Solomon, S.; Qin, D.; Manning, M.; Chen, Z.; Marquis, M.; Avery, K.B.; Tignor, M.; Miller, H.L. (eds.), Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis, Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-88009-1
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Information from Paleoclimate Archives" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-12-06. Retrieved 2015-06-20.
- Jones, Phil D.; Briffa, K. R.; Barnett, T. P.; Tett, S. F. B. (May 1998), "High-resolution palaeoclimatic records for the last millennium: interpretation, integration and comparison with General Circulation Model control-run temperatures", The Holocene, 8 (4): 455–471, Bibcode:1998Holoc...8..455J, doi:10.1191/095968398667194956, S2CID 2227769.
- Briffa, Keith R. (1 January 2000), "Annual climate variability in the Holocene: interpreting the message of ancient trees", Quaternary Science Reviews, 19 (1–5): 87–105, Bibcode:2000QSRv...19...87B, doi:10.1016/S0277-3791(99)00056-6.
- Crowley, Thomas J.; Lowery, Thomas S. (February 2000), "How Warm Was the Medieval Warm Period?", Ambio: A Journal of the Human Environment, 29 (1): 51–54, doi:10.1579/0044-7447-29.1.51, S2CID 86527510.
- Esper, J.; Cook, E. R.; Schweingruber, F. H. (22 March 2002), "Low-Frequency Signals in Long Tree-Ring Chronologies for Reconstructing Past Temperature Variability", Science, 295 (5563): 2250–3, Bibcode:2002Sci...295.2250E, doi:10.1126/science.1066208, PMID 11910106, S2CID 22184321.
- D'Arrigo, Rosanne; Wilson, Rob; Jacoby, Gordon (7 February 2006), "On the long-term context for late twentieth century warming", Journal of Geophysical Research, 111 (D3): D03103, Bibcode:2006JGRD..111.3103D, CiteSeerX 10.1.1.405.7636, doi:10.1029/2005JD006352.
- Osborn, Timothy J.; Briffa, Keith R. (10 February 2006), "The Spatial Extent of 20th-Century Warmth in the Context of the Past 1200 Years", Science, 311 (5762): 841–4, Bibcode:2006Sci...311..841O, CiteSeerX 10.1.1.590.2928, doi:10.1126/science.1120514, PMID 16469924, S2CID 129718548.