This article needs more reliable medical references for verification or relies too heavily on primary sources. (January 2022) |  |
A joint dislocation, also called luxation, occurs when there is an abnormal separation in the joint, where two or more bones meet.[1] A partial dislocation is referred to as a subluxation. Dislocations are often caused by sudden trauma on the joint like an impact or fall. A joint dislocation can cause damage to the surrounding ligaments, tendons, muscles, and nerves.[2] Dislocations can occur in any major joint (shoulder, knees, etc.) or minor joint (toes, fingers, etc.). The most common joint dislocation is a shoulder dislocation.[1]
| Joint dislocation | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Latin: luxatio |
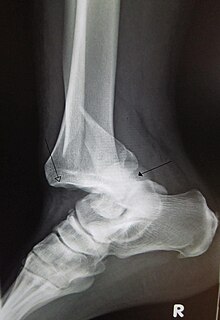 | |
| A traumatic dislocation of the tibiotarsal joint of the ankle with distal fibular fracture. Open arrow marks the tibia and the closed arrow marks the talus. | |
| Specialty | Orthopedic surgery |
Treatment for joint dislocation is usually by closed reduction, that is, skilled manipulation to return the bones to their normal position. Reduction should only be performed by trained medical professionals, because it can cause injury to soft tissue and/or the nerves and vascular structures around the dislocation.[3]
Symptoms and signs
editThe following symptoms are common with any type of dislocation.[1]
- Intense pain
- Joint instability
- Deformity of the joint area
- Reduced muscle strength
- Bruising or redness of joint area
- Difficulty moving joint
- Stiffness
Causes
editJoint dislocations are caused by trauma to the joint or when an individual falls on a specific joint.[4] Great and sudden force applied, by either a blow or fall, to the joint can cause the bones in the joint to be displaced or dislocated from normal position.[5] With each dislocation, the ligaments keeping the bones fixed in the correct position can be damaged or loosened, making it easier for the joint to be dislocated in the future.[6]
Some individuals are prone to dislocations due to congenital conditions, such as hypermobility syndrome and Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome. Hypermobility syndrome is genetically inherited disorder that is thought to affect the encoding of the connective tissue protein’s collagen in the ligament of joints.[7] The loosened or stretched ligaments in the joint provide little stability and allow for the joint to dislocate relatively easily.
Diagnosis
editSome times dislocation can also occur because of Rheumatoid arthritis, In Rheumatoid arthritis the production of synovial fluid decrease gradually causing pain, swollen joint, and stiffness. A forceful push causes friction and can dislocate the joint. Initial evaluation of a suspected joint dislocation should begin with a thorough patient history, including mechanism of injury, and physical examination. Special attention should be focused on the neurovascular exam both before and after reduction, as injury to these structures may occur during the injury or during the reduction process.[3] Subsequent imaging studies are frequently obtained to assist with diagnosis.
- Standard plain radiographs, usually a minimum of 2 views
- Generally, pre- and post-reduction X-rays are recommended. Initial X-ray can confirm the diagnosis as well as evaluate for any concomitant fractures. Post-reduction radiographs confirm successful reduction alignment and can exclude any other bony injuries that may have been caused during the reduction procedure.[8]
- In certain instances if initial X-rays are normal but injury is suspected, there is possible benefit of stress/weight-bearing views to further assess for disruption of ligamentous structures and/or need for surgical intervention. This may be utilized with AC joint separations.[9]
- Nomenclature: Joint dislocations are named based on the distal component in relation to the proximal one.[10]
- Ultrasound
- Ultrasound may be useful in an acute setting, particularly with suspected shoulder dislocations. Although it may not be as accurate in detecting any associated fractures, in one observational study ultrasonography identified 100% of shoulder dislocations, and was 100% sensitive in identifying successful reduction when compared to plain radiographs.[11] Ultrasound may also have utility in diagnosing AC joint dislocations.[12]
- In infants <6 months of age with suspected developmental dysplasia of the hip (congenital hip dislocation), ultrasound is the imaging study of choice as the proximal femoral epiphysis has not significantly ossified at this age.[13]
- Cross-sectional imaging (CT or MRI)
- Plain films are generally sufficient in making a joint dislocation diagnosis. However, cross-sectional imaging can subsequently be used to better define and evaluate abnormalities that may be missed or not clearly seen on plain X-rays. CT is useful in further analyzing any bony aberrations, and CT angiogram may be utilized if vascular injury is suspected.[14] In addition to improved visualization of bony abnormalities, MRI permits for a more detailed inspection of the joint-supporting structures in order to assess for ligamentous and other soft tissue injury.
Treatment
editA dislocated joint usually can be professionally reduced into its normal position only by a trained medical professional. Trying to reduce a joint without any training could substantially worsen the injury.[15]
X-rays are usually taken to confirm a diagnosis and detect any fractures which may also have occurred at the time of dislocation. A dislocation is easily seen on an X-ray.[16]
Once a diagnosis is confirmed, the joint is usually manipulated back into position. This can be a very painful process, therefore this is typically done either in the emergency department under sedation or in an operating room under a general anaesthetic.[17]
It is important the joint is reduced as soon as possible, as in the state of dislocation, the blood supply to the joint (or distal anatomy) may be compromised. This is especially true in the case of a dislocated ankle, due to the anatomy of the blood supply to the foot.[18]
Shoulder injuries can also be surgically stabilized, depending on the severity, using arthroscopic surgery.[16] The most common treatment method for a dislocation of the Glenohumeral Joint (GH Joint/Shoulder Joint) is exercise based management.[19] Another method of treatment is to place the injured arm in a sling or in another immobilizing device in order to keep the joint stable.[20] A 2012 Cochrane review, found no statistically significant difference in healing or long-term joint mobility between simple shoulder dislocations treated conservatively versus surgically.[21]
Some joints are more at risk of becoming dislocated again after an initial injury. This is due to the weakening of the muscles and ligaments which hold the joint in place. The shoulder is a prime example of this. Any shoulder dislocation should be followed up with thorough physiotherapy.[16]
On field reduction is crucial for joint dislocations. As they are extremely common in sports events, managing them correctly at the game at the time of injury, can reduce long term issues. They require prompt evaluation, diagnosis, reduction, and postreduction management before the person can be evaluated at a medical facility.[20]
After care
editAfter a dislocation, injured joints are usually held in place by a splint (for straight joints like fingers and toes) or a bandage (for complex joints like shoulders). Additionally, the joint muscles, tendons and ligaments must also be strengthened. This is usually done through a course of physiotherapy, which will also help reduce the chances of repeated dislocations of the same joint.[22]
For glenohumeral instability, the therapeutic program depends on specific characteristics of the instability pattern, severity, recurrence and direction with adaptations made based on the needs of the patient. In general, the therapeutic program should focus on restoration of strength, normalization of range of motion and optimization of flexibility and muscular performance. Throughout all stages of the rehabilitation program, it is important to take all related joints and structures into consideration.[23]
Epidemiology
edit- Each joint in the body can be dislocated, however, there are common sites where most dislocations occur. The following structures are the most common sites of joint dislocations:
- Dislocated shoulder
- Shoulder dislocations account for 45% of all dislocation visits to the emergency room.[24] Anterior shoulder dislocation, the most common type of shoulder dislocation (96-98% of the time) occurs when the arm is in external rotation and abduction (away from the body) produces a force that displaces the humeral head anteriorly and downwardly.[24] Vessel and nerve injuries during a shoulder dislocation is rare, but can cause many impairments and requires a longer recovery process.[24] There is a 39% average rate of recurrence of anterior shoulder dislocation, with age, sex, hyperlaxity and greater tuberosity fractures being the key risk factors.[25]
- Knee: Patellar dislocation
- Many different knee injuries can happen. Three percent of knee injuries are acute traumatic patellar dislocations.[26] Because dislocations make the knee unstable, 15% of patellas will re-dislocate.[27]
- Patellar dislocations often occur when the knee is in full extension and sustains a trauma from the lateral to medial side.[28]
- Elbow: Posterior dislocation, 90% of all elbow dislocations[29]
- Wrist: Lunate and Perilunate dislocation most common[30]
- Finger: Interphalangeal (IP) or metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joint dislocations[31]
- Hip: Posterior and anterior dislocation of hip
- Anterior dislocations are less common than posterior dislocations. 10% of all dislocations are anterior and this is broken down into superior and inferior types.[33] Superior dislocations account for 10% of all anterior dislocations, and inferior dislocations account for 90%.[33] 16-40 year old males are more likely to receive dislocations due to a car accident.[33] When an individual receives a hip dislocation, there is an incidence rate of 95% that they will receive an injury to another part of their body as well.[33] 46–84% of hip dislocations occur secondary to traffic accidents, the remaining percentage is due based on falls, industrial accidents or sporting injury.[25]
- Foot and Ankle:
- Lisfranc injury is a dislocation or fracture-dislocation injury at the tarsometatarsal joints
- Subtalar dislocation, or talocalcaneonavicular dislocation, is a simultaneous dislocation of the talar joints at the talocalcaneal and talonavicular levels.[34][35] Subtalar dislocations without associated fractures represent about 1% of all traumatic injuries of the foot and 1-2 % of all dislocations, and they are associated with high energy trauma. Early closed reduction is recommended, otherwise open reduction without further delay.[36]
- Total talar dislocation is very rare and has very high rates of complications.[37][38]
- Ankle Sprains primarily occur as a result of tearing the ATFL (anterior talofibular ligament) in the Talocrural Joint. The ATFL tears most easily when the foot is in plantarflexion and inversion.[39]
- Ankle dislocation without fracture is rare.[40]
Gallery
edit-
Dislocation of the left index finger
-
Radiograph of right fifth phalanx bone dislocation
-
Radiograph of left index finger dislocation
-
Depiction of reduction of a dislocated spine, ca. 1300
-
Dislocation of the carpo-metacarpal joint.
-
Radiograph of right fifth phalanx dislocation resulting from bicycle accident
-
Right fifth phalanx dislocation resulting from bicycle accident
-
Shoulder dislocation before (left) and after (right) being reduced
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ a b c Dislocations. Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital at Stanford. Retrieved 3 March 2013. [1] Archived 28 May 2013 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Smith, R. L., & Brunolli, J. J. (1990). Shoulder kinesthesia after anterior glenohumeral joint dislocation. Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy, 11(11), 507–513.
- ^ a b Skelley NW, McCormick JJ, Smith MV (May 2014). "In-game Management of Common Joint Dislocations". Sports Health. 6 (3): 246–255. doi:10.1177/1941738113499721. PMC 4000468. PMID 24790695.
- ^ Mayo Clinic: Finger Dislocation Joint Reduction
- ^ U.S. National Library of Medicine – Dislocation
- ^ Pubmed Health: Dislocation – Joint dislocation
- ^ Ruemper, A. & Watkins, K. (2012). Correlations between general joint hypermobility and joint hypermobility syndrome and injury in contemporary dance students. Journal of Dance Medicine & Science, 16(4): 161–166.
- ^ Chong M, Karataglis D, Learmonth D (September 2006). "Survey of the Management of Acute Traumatic First-Time Anterior Shoulder Dislocation Among Trauma Clinicians in the UK". Annals of the Royal College of Surgeons of England. 88 (5): 454–458. doi:10.1308/003588406X117115. ISSN 0035-8843. PMC 1964698. PMID 17002849.
- ^ Gaillard F. "Acromioclavicular injury | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org". radiopaedia.org. Retrieved 21 February 2018.
- ^ "Introduction to Trauma X-ray - Dislocation injury". www.radiologymasterclass.co.uk. Retrieved 15 February 2018.
- ^ Abbasi S, Molaie H, Hafezimoghadam P, Zare MA, Abbasi M, Rezai M, Farsi D (August 2013). "Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasonographic examination in the management of shoulder dislocation in the emergency department". Annals of Emergency Medicine. 62 (2): 170–175. doi:10.1016/j.annemergmed.2013.01.022. ISSN 1097-6760. PMID 23489654.
- ^ Heers G, Hedtmann A (2005). "Correlation of ultrasonographic findings to Tossy's and Rockwood's classification of acromioclavicular joint injuries". Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology. 31 (6): 725–732. doi:10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2005.03.002. PMID 15936487.
- ^ Gaillard F. "Developmental dysplasia of the hip | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org". radiopaedia.org. Retrieved 21 February 2018.
- ^ "UpToDate". www.uptodate.com. Retrieved 21 February 2018.
- ^ Bankart, A. (2004). The pathology and treatment of recurrent dislocation of the shoulder-joint. Acta Orthop Belg. 70: 515–519
- ^ a b c Dias, J., Steingold, R., Richardson, R., Tesfayohannes, B., Gregg, P. (1987). The conservative treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation. British Editorial Society of Bone and Joint Surgery. 69(5): 719–722.
- ^ Holdsworth, F. (1970). Fractures, dislocations, and fracture dislocations of the spine. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. 52 (8): 1534–1551.
- ^ Ganz, R., Gill, T., Gautier, E., Ganz, K., Krugel, N., Berlemann, U. (2001). Surgical dislocation of the adult hip. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. 83(8): 1119–1124.
- ^ Warby SA, Pizzari T, Ford JJ, Hahne AJ, Watson L (1 January 2014). "The effect of exercise-based management for multidirectional instability of the glenohumeral joint: a systematic review". Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery. 23 (1): 128–142. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2013.08.006. PMID 24331125.
- ^ a b Skelley NW, McCormick JJ, Smith MV (4 April 2017). "In-game Management of Common Joint Dislocations". Sports Health. 6 (3): 246–255. doi:10.1177/1941738113499721. ISSN 1941-7381. PMC 4000468. PMID 24790695.
- ^ Taylor F, Sims M, Theis JC, Herbison GP (18 April 2012). Cochrane Bone, Joint and Muscle Trauma Group (ed.). "Interventions for treating acute elbow dislocations in adults". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2012 (4): CD007908. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007908.pub2. PMC 6465046. PMID 22513954.
- ^ Itoi, E., Hatakeyama, Y., Kido, T., Sato, T., Minagawa, H., Wakabayashi, I., Kobayashi, M. (2003). Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery. 12(5): 413–415.
- ^ Cools AM, Borms D, Castelein B, Vanderstukken F, Johansson FR (1 February 2016). "Evidence-based rehabilitation of athletes with glenohumeral instability". Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy. 24 (2): 382–389. doi:10.1007/s00167-015-3940-x. ISSN 0942-2056. PMID 26704789. S2CID 21227767.
- ^ a b c Khiami F, Gérometta A, Loriaut P (2015). "Management of recent first-time anterior shoulder dislocations". Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research. 101 (1): S51–S57. doi:10.1016/j.otsr.2014.06.027. PMID 25596982.
- ^ a b Olds M, Ellis R, Donaldson K, Parmar P, Kersten P (1 July 2015). "Risk factors which predispose first-time traumatic anterior shoulder dislocations to recurrent instability in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Br J Sports Med. 49 (14): 913–922. doi:10.1136/bjsports-2014-094342. ISSN 0306-3674. PMC 4687692. PMID 25900943.
- ^ Hsiao M, Owens BD, Burks R, Sturdivant RX, Cameron KL (1 October 2010). "Incidence of Acute Traumatic Patellar Dislocation Among Active-Duty United States Military Service Members". The American Journal of Sports Medicine. 38 (10): 1997–2004. doi:10.1177/0363546510371423. ISSN 0363-5465. PMID 20616375. S2CID 19131206.
- ^ Fithian DC, Paxton EW, Stone ML, Silva P, Davis DK, Elias DA, White LM (1 July 2004). "Epidemiology and Natural History of Acute Patellar Dislocation". The American Journal of Sports Medicine. 32 (5): 1114–1121. doi:10.1177/0363546503260788. ISSN 0363-5465. PMID 15262631. S2CID 11899852.
- ^ Ramponi D (2016). "Patellar Dislocations and Reduction Procedure". Advanced Emergency Nursing Journal. 38 (2): 89–92. doi:10.1097/tme.0000000000000104. PMID 27139130. S2CID 42552493.
- ^ Elbow Dislocation
- ^ "Carpal dislocations". Archived from the original on 24 December 2014. Retrieved 5 March 2013.
- ^ Finger Dislocation Joint Reduction
- ^ a b c Golan E, Kang KK, Culbertson M, Choueka J (2016). "The Epidemiology of Finger Dislocations Presenting for Emergency Care Within the United States". HAND. 11 (2): 192–6. doi:10.1177/1558944715627232. PMC 4920528. PMID 27390562.
- ^ a b c d Clegg TE, Roberts CS, Greene JW, Prather BA (2010). "Hip dislocations—Epidemiology, treatment, and outcomes". Injury. 41 (4): 329–334. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2009.08.007. PMID 19796765.
- ^ Ruhlmann F, Poujardieu C, Vernois J, Gayet LE (2017). "Isolated Acute Traumatic Subtalar Dislocations: Review of 13 Cases at a Mean Follow-Up of 6 Years and Literature Review". The Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery (Review). 56 (1): 201–207. doi:10.1053/j.jfas.2016.01.044. PMID 26947001. S2CID 31290747.
- ^ García-Regal J, Centeno-Ruano AJ (2013). "[Talocalcaneonavicular dislocation without associated fractures]". Acta Ortopedica Mexicana (Review) (in Spanish). 27 (3): 201–4. PMID 24707608.
- ^ Prada-Cañizares A, Auñón-Martín I, Vilá Y Rico J, Pretell-Mazzini J (May 2016). "Subtalar dislocation: management and prognosis for an uncommon orthopaedic condition". International Orthopaedics (Review). 40 (5): 999–1007. doi:10.1007/s00264-015-2910-8. PMID 26208589. S2CID 6090499.
- ^ Michael A. Foy, Phillip S. Fagg (5 December 2011). Medicolegal Reporting in Orthopaedic Trauma E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 320–. ISBN 978-0-7020-4886-9.
- ^ For a graphic representation of displacements that may lead to a total talar dislocation see: Robert W. Bucholz (29 March 2012). Rockwood and Green's Fractures in Adults: Two Volumes Plus Integrated Content Website (Rockwood, Green, and Wilkins' Fractures). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 2061. ISBN 978-1-4511-6144-1.
- ^ Ringleb SI, Dhakal A, Anderson CD, Bawab S, Paranjape R (1 October 2011). "Effects of lateral ligament sectioning on the stability of the ankle and subtalar joint". Journal of Orthopaedic Research. 29 (10): 1459–1464. doi:10.1002/jor.21407. ISSN 1554-527X. PMID 21445995.
- ^ Wight L, Owen D, Goldbloom D, Knupp M (October 2017). "Pure Ankle Dislocation: A systematic review of the literature and estimation of incidence". Injury (Review). 48 (10): 2027–2034. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2017.08.011. PMID 28826653.
- ^ Earwaker J (1992). "Posttraumatic calcification of the annular ligament of the radius". Skeletal Radiol. 21 (3): 149–54. doi:10.1007/BF00242127. PMID 1604339. S2CID 43615869.
External links
edit