Lenexa /lɪˈnɛksə/ is a city in Johnson County, Kansas, United States,[1] and part of the Kansas City metropolitan area. As of the 2020 census, the population of the city was 57,434.[3][4] making it the 9th most populated city in Kansas.[5][6] It is bordered by the cities of Shawnee to the north, Overland Park to the east, De Soto to the west and Olathe to the south.
Lenexa, Kansas | |
|---|---|
 Lenexa City Center (2017) | |
 Location within Johnson County and Kansas | |
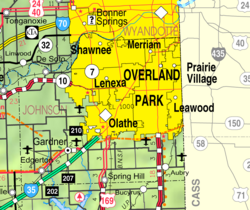 | |
| Coordinates: 38°57′58″N 94°44′02″W / 38.96611°N 94.73389°W[1] | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Kansas |
| County | Johnson |
| Incorporated | 1907 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Julie Sayers |
| • City Manager | Beccy Yocham |
| Area | |
• Total | 34.39 sq mi (89.08 km2) |
| • Land | 34.07 sq mi (88.24 km2) |
| • Water | 0.32 sq mi (0.83 km2) 1.02% |
| Elevation | 873 ft (266 m) |
| Population | |
• Total | 57,434 |
| • Density | 1,700/sq mi (640/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC-6 (CST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-5 (CDT) |
| ZIP codes | 66200-66299 |
| Area code | 913 |
| FIPS code | 20-39350 |
| GNIS ID | 485612[1] |
| Website | lenexa.com |
History
editThis section needs additional citations for verification. (September 2013) |
Twelve years before the town of Lenexa was platted, James Butler Hickok staked a claim on 160 acres (65 ha) at what is now the corner of 83rd and Clare Road.[7] Filed in 1857, the claim was not far from the Kansas River, and was 20 miles (32 km) southwest of Westport, Missouri, and the start of the Santa Fe Trail. The trail meandered through this area on its way to Santa Fe, New Mexico.
On March 22, 1858, Hickok was elected one of the first four constables of nearby Monticello Township. Later, Hickok became a scout for the Free-State Army, a sharpshooter and eventually, one of the most famous folk heroes of the American West, Wild Bill Hickok.
At about the same time as Hickok filed his claim, a census of the Shawnee Indians living in the area was being taken, and one of the residents listed was Na-Nex-Se Blackhoof. She was the widow of Chief Blackhoof, the second signer of the 1854 treaty that ceded 1,600,000 acres (650,000 ha) of the Kansas Shawnee Indian reservation to the United States government.
In 1865, the Kansas and Neosho Valley Railroad was organized to take advantage of favorable new land laws. It later changed its name to Missouri River, Ft. Scott and Gulf Railroad, and in 1869 purchased a right-of-way from C.A. Bradshaw in the area that is now Lenexa, with the stipulation that a depot be built on the property.
Bradshaw also sold 10.5 acres (4.2 ha) to Octave Chanute, a railroad civil engineer, who platted the town in 1869. Legend states that the first town name proposed was "Bradshaw", but Bradshaw modestly refused and the name "Lenexa", a derivation of the name Na-Nex-Se,[citation needed] the name of Shawnee Chief Thomas Blackhoof's wife, was adopted.
Geography
editLenexa is located at 38°57′53″N 94°45′34″W / 38.96472°N 94.75944°W (38.964689, -94.759535).[1] According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 34.45 square miles (89.23 km2), of which, 34.10 square miles (88.32 km2) is land and 0.35 square miles (0.91 km2) is water.[8]
Demographics
edit| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1910 | 583 | — | |
| 1920 | 472 | −19.0% | |
| 1930 | 452 | −4.2% | |
| 1940 | 502 | 11.1% | |
| 1950 | 803 | 60.0% | |
| 1960 | 2,497 | 211.0% | |
| 1970 | 5,242 | 109.9% | |
| 1980 | 18,639 | 255.6% | |
| 1990 | 34,034 | 82.6% | |
| 2000 | 40,238 | 18.2% | |
| 2010 | 48,190 | 19.8% | |
| 2020 | 57,434 | 19.2% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census[9] 2010-2020[4] | |||
2020 census
editThe 2020 United States census counted 57,434 people, 23,934 households, and 15,432 families in Lenexa.[10][11] The population density was 1,685.7 per square mile (650.8/km2). There were 25,308 housing units at an average density of 742.8 per square mile (286.8/km2).[11][12] The racial makeup was 78.05% (44,827) white or European American (75.9% non-Hispanic white), 6.41% (3,681) black or African-American, 0.4% (232) Native American or Alaska Native, 4.15% (2,381) Asian, 0.07% (38) Pacific Islander or Native Hawaiian, 2.87% (1,650) from other races, and 8.05% (4,625) from two or more races.[13] Hispanic or Latino of any race was 8.34% (4,790) of the population.[14]
Of the 23,934 households, 27.7% had children under the age of 18; 51.8% were married couples living together; 24.3% had a female householder with no spouse or partner present. 28.1% of households consisted of individuals and 9.2% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older.[11] The average household size was 2.4 and the average family size was 2.9.[15] The percent of those with a bachelor's degree or higher was estimated to be 39.7% of the population.[16]
21.7% of the population was under the age of 18, 8.2% from 18 to 24, 28.4% from 25 to 44, 24.8% from 45 to 64, and 17.0% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 38.4 years. For every 100 females, there were 104.6 males.[11] For every 100 females ages 18 and older, there were 106.5 males.[11]
The 2016-2020 5-year American Community Survey estimates show that the median household income was $90,487 (with a margin of error of +/- $3,777) and the median family income was $110,925 (+/- $4,040).[17] Males had a median income of $59,365 (+/- $4,837) versus $42,653 (+/- $1,613) for females. The median income for those above 16 years old was $49,977 (+/- $2,070).[18] Approximately, 2.8% of families and 5.0% of the population were below the poverty line, including 5.7% of those under the age of 18 and 3.1% of those ages 65 or over.[19][20]
The ancestry of Lenexa in 2020 was 25.5% German, 13.3% Irish, 13.2% English, 3.9% Italian, 2.3% French, 2.1% Scottish, 2.0% Polish, 2.0% Norwegian, and 1.9% Subsaharan African.[3]
2010 census
editAs of the census[21] of 2010, there were 48,190 people, 19,288 households, and 13,065 families living in the city. The population density was 1,413.2 inhabitants per square mile (545.6/km2). There were 20,832 housing units at an average density of 610.9 per square mile (235.9/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 84.4% White, 5.8% African American, 0.4% Native American, 3.8% Asian, 0.1% Pacific Islander, 3.0% from other races, and 2.5% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 7.3% of the population.
There were 19,288 households, of which 33.7% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 55.3% were married couples living together, 9.0% had a female householder with no husband present, 3.4% had a male householder with no wife present, and 32.3% were non-families. 25.2% of all households were made up of individuals, and 7.3% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.48 and the average family size was 3.00.
The median age in the city was 36.6 years. 24.7% of residents were under the age of 18; 8.3% were between the ages of 18 and 24; 28.2% were from 25 to 44; 28.5% were from 45 to 64; and 10.3% were 65 years of age or older. The gender makeup of the city was 48.7% male and 51.3% female.
2000 census
editAs of the U.S. Census in 2000, there were 40,238 people, 15,574 households, and 10,559 families living in the city. The population density was 1,173.8 inhabitants per square mile (453.2/km2). There were 16,378 housing units at an average density of 477.8 per square mile (184.5/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 89.50% White, 6.50% Black or African American, 0.38% Native American, 3.63% Asian, 0.03% Pacific Islander, 1.60% from other races, and 1.61% two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 3.97% of the population. 24.8% were of German, 12.4% English, 12.1% Irish and 7.2% American ancestry.[22]
There were 15,574 households, out of which 35.1% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 57.4% were married couples living together, 7.6% had a female householder with no husband present, and 32.2% were non-families. 24.3% of all households were made up of individuals, and 5.8% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.54 and the average family size was 3.08.
In the city, the population was spread out, with 25.7% under the age of 18, 9.5% from 18 to 24, 32.0% from 25 to 44, 24.2% from 45 to 64, and 8.6% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 35 years. For every 100 females, there were 95.8 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 93.1 males.
Economy
editLenexa is the birthplace of Garmin and the regional headquarters of Kiewit Construction.[23][24]
Largest employers
editAccording to the city's 2015 Comprehensive Annual Financial Report,[25] the largest employers in the city are:
| # | Employer | # of Employees |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | United Parcel Service | 2,087 |
| 2 | Quest Diagnostics/Lab One | 1,954 |
| 3 | Kiewit Power Engineers Company | 1,292 |
| 4 | JC Penney Logistics Center | 1,200 |
| 5 | Alliance Data Systems | 730 |
| 6 | Gear for Sports | 600 |
| 7 | Lakeview Village | 586 |
| 8 | Lexmark | 570 |
| 9 | Clinical Reference Lab | 567 |
| 10 | PRA International | 560 |
Government
editLenexa is the home of a Records Center managed by the National Archives and Records Administration. The facility stores federal records from agencies in Iowa, Kansas, Missouri, and Nebraska including Department of Veterans Affairs and the Internal Revenue Service.[26] The facility is also known informally as "The Caves" and is known to store items from the trauma room at Parkland Memorial Hospital in Dallas, Texas, where John F. Kennedy was pronounced dead following his assassination.[27] As of November 2023, the current mayor of Lenexa is Julie Sayers and the current City Manager is Beccy Yocham.[28][29]
Education
editLenexa does not have a public school district of its own. Instead, Lenexa students go to either Shawnee Mission School District, Olathe School District, or De Soto School District schools. It is also home to a handful of private schools. Lenexa's first private high school, St. James Academy, opened in 2005. The Johnson County Library has a branch in the Lenexa City Center. Wichita based Friends University also has a branch in Lenexa. The International Assembly for Collegiate Business Education is based in Lenexa; its competitive peer, the Accreditation Council for Business Schools and Programs, is based in neighboring Overland Park.
Culture
editEvents
editEach June the city hosts "The Great Lenexa Barbecue Battle", which is also the Kansas State Championship. Lenexa was known as the "Spinach Capital of the World"[30] in the 1930s and celebrates with the Spinach Festival every September.
Religion
editLenexa is home to the St. George Serbian Orthodox Church, a parish founded in Kansas City in 1906 and moved to Lenexa in 2006. The parish constructed a new Byzantine style church and cultural center. The church hosts a SerbFest every year in the summer and a Food Festival and Bazaar in the fall.
The Church of the Nazarene, an evangelical Protestant denomination which was headquartered for many years in Kansas City, moved its international headquarters to Lenexa in 2008.
Healthcare
editOn April 13, 2023, construction began for AdventHealths new hospital AdventHealth Lenexa.[31]
Transportation
editJohnson County Transit provides local bus service in and around the city.
Notable people
editPeople who were born in or have lived in Lenexa include these:
- Warren Ault (1887–1989), historian[32]
- Cam F. Awesome (born 1988), boxer[33]
- Baron Corbin (born 1984), WWE Wrestler[34]
- Madison Desch (born 1997), gymnast[35]
- Drake Dunsmore (born 1988), football tight end[36]
- Wild Bill Hickok (1837–1876), gunfighter. He staked a claim on 160 acres (0.65 km2) at what is now the corner of 83rd and Clare Road.[7]
- Lucas Rodríguez (born 1986), soccer midfielder[37]
- Paul Rudd, (born 1969), actor[38]
- William Shaw (born 1955), biochemist, autism researcher[39]
- Grace VanderWaal (born 2004), winner of the eleventh season of the NBC TV competition show America's Got Talent[40]
- Jason Wiles (born 1970), actor, director, producer.[41] Starred as Maurice 'Bosco' Boscorelli (1999–2005) in the television series Third Watch.
- Ron Worley (born 1945), Kansas state legislator[42]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ a b c d e U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Lenexa, Kansas
- ^ "2019 U.S. Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 24, 2020.
- ^ a b c "Profile of Lenexa, Kansas in 2020". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on November 23, 2022. Retrieved November 22, 2022.
- ^ a b c "QuickFacts; Lenexa, Kansas; Population, Census, 2020 & 2010". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on August 24, 2021. Retrieved August 23, 2021.
- ^ "PRINCIPAL CITIES OF METROPOLITAN AND MICROPOLITAN STATISTICAL AREAS, MARCH 2020".
- ^ "The Demographic Statistical Atlas of the United States - Statistical Atlas". Archived from the original on December 9, 2015.
- ^ a b "The Lenexa Police Department History". Archived from the original on June 24, 2009. Retrieved June 24, 2009.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link). - ^ "US Gazetteer files 2010". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on July 2, 2012. Retrieved July 6, 2012.
- ^ United States Census Bureau. "Census of Population and Housing". Retrieved November 29, 2014.
- ^ "US Census Bureau, Table P16: HOUSEHOLD TYPE". data.census.gov. Retrieved January 3, 2024.
- ^ a b c d e "US Census Bureau, Table DP1: PROFILE OF GENERAL POPULATION AND HOUSING CHARACTERISTICS". data.census.gov. Retrieved January 3, 2024.
- ^ "Gazetteer Files". Census.gov. Retrieved December 30, 2023.
- ^ "US Census Bureau, Table P1: RACE". data.census.gov. Retrieved January 3, 2024.
- ^ "US Census Bureau, Table P2: HISPANIC OR LATINO, AND NOT HISPANIC OR LATINO BY RACE". data.census.gov. Retrieved January 3, 2024.
- ^ "US Census Bureau, Table S1101: HOUSEHOLDS AND FAMILIES". data.census.gov. Retrieved January 3, 2024.
- ^ "US Census Bureau, Table S1501: EDUCATIONAL ATTAINMENT". data.census.gov. Retrieved January 3, 2024.
- ^ "US Census Bureau, Table S1903: MEDIAN INCOME IN THE PAST 12 MONTHS (IN 2020 INFLATION-ADJUSTED DOLLARS)". data.census.gov. Retrieved January 3, 2024.
- ^ "US Census Bureau, Table S2001: EARNINGS IN THE PAST 12 MONTHS (IN 2020 INFLATION-ADJUSTED DOLLARS)". data.census.gov. Retrieved January 3, 2024.
- ^ "US Census Bureau, Table S1701: POVERTY STATUS IN THE PAST 12 MONTHS". data.census.gov. Retrieved January 3, 2024.
- ^ "US Census Bureau, Table S1702: POVERTY STATUS IN THE PAST 12 MONTHS OF FAMILIES". data.census.gov. Retrieved January 3, 2024.
- ^ "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 6, 2012.
- ^ "Kansas: 2000" (PDF). 2000 Census of Population and Housing. March 2003.
- ^ "Garmin". Companieshistory.com. January 15, 2014. Retrieved June 24, 2019.
- ^ "Lenexa gives green light to new 6-story regional headquarters building for Kiewit Corp". shawneemissionpost.com. Archived from the original on December 30, 2018. Retrieved January 13, 2022.
- ^ "City of Lenexa, Kansas Comprehensive Annual Financial Report" (PDF). February 28, 2017. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 28, 2017. Retrieved June 24, 2019.
- ^ "The National Archives in Lenexa, Kansas". National Archives. Archived from the original on December 17, 2009. Retrieved November 20, 2009.
- ^ Keen, Judy (November 20, 2009). "JFK Relics Stir Strong Emotions". USA Today. Retrieved November 20, 2009.
- ^ "Mayor Julie Sayers - City of Lenexa". City of Lenexa. Retrieved March 20, 2024.
- ^ "City Manager's Office - City of Lenexa". City of Lenexa. Retrieved January 21, 2020.
- ^ Brackman, Barbara (1997). Kansas Trivia. Thomas Nelson Inc. p. 10. ISBN 9781418553814.
- ^ Koch, Makenzie; Stowell, Kerri (April 14, 2023). "AdventHealth breaks ground on new Lenexa hospital". FOX 4. Retrieved May 6, 2023.
- ^ "Warren Ault dies; Baker grad was oldest Rhodes scholar". The Lawrence Journal-World. May 15, 1989. Retrieved March 25, 2016.
- ^ Grathoff, Pete (July 24, 2015). "After losing bout, Lenexa's Cam F. Awesome says he's been called the Taylor Swift of boxing". The Kansas City Star. Retrieved March 25, 2016.
- ^ "Behind WWE superstar villain Baron Corbin is an ornery, edgy Lenexa native". Kansascity.com. Retrieved November 23, 2016.
- ^ "Madison Desch". USA Gymnastics. Retrieved March 25, 2016.
- ^ "Drake Dunsmore". NU Sports. Retrieved March 25, 2016.
- ^ "Midfielder Lucas Rodriguez Returns to Comets for 2015/16 MASL Season". Our Sports Central. November 4, 2015. Retrieved March 25, 2016.
- ^ Freeman, Hadley (July 9, 2015). "Paul Rudd on Ant-Man, being Hollywood's go-to nice guy and growing up with English parents in Kansas". The Guardian. London, UK. Archived from the original on February 12, 2018. Retrieved February 10, 2021.
- ^ Tsouderos, Trine; Callahan, Patricia (December 7, 2009). "Chelation based on faulty premise". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved March 25, 2016.
- ^ "America's Got Talent 11th Season Contestants". Retrieved December 2, 2016.
- ^ "Jason Wiles". IMDb. Retrieved March 25, 2016.
- ^ "Ron Worley's Biography". Vote Smart. Retrieved March 25, 2016.
