This article needs to be updated. (May 2022) |
Jiashan County (simplified Chinese: 嘉善县; traditional Chinese: 嘉善縣; pinyin: Jiāshàn Xiàn) is a county in the north of Zhejiang Province, bordering Shanghai to the northeast and Jiangsu province to the north. It is administered by the prefecture-level city of Jiaxing. Jiashan is nicknamed "The Land of Fish and Rice", and is 80 km (50 mi) southwest of central Shanghai, 95 km (59 mi) east of Hangzhou, and 90 km (56 mi) south of Suzhou. The county seat is located on 126 People Avenue, Weitang Town.
Jiashan
嘉善县 Kashan | |
|---|---|
 Jiashan | |
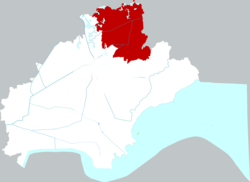 Location of Jiashan County within Jiaxing | |
| Coordinates: 30°49′52″N 120°55′34″E / 30.831°N 120.926°E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Zhejiang |
| Prefecture-level city | Jiaxing |
| Area | |
| • Total | 506.88 km2 (195.71 sq mi) |
| Population (2020) | |
| • Total | 648,160 |
| • Density | 1,300/km2 (3,300/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
The second campus of Sanda University, known as Guangbiao Institute, is located in Jiashan County.
History
editJiashan formerly was part of Jiaxing. In 1430, Jiashan was established.
On 1 November 2022, the county was named by a guideline of the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) as a "leading trial area" for common prosperity.[1]
Administration divisions
editJiashan County consists of six towns, three subdistricts, 11 communities, 16 residential zones and 164 administrative villages.
Subdistricts
editTowns
editClimate
edit| Climate data for Jiashan (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 22.5 (72.5) |
27.4 (81.3) |
30.2 (86.4) |
33.7 (92.7) |
35.6 (96.1) |
38.1 (100.6) |
40.0 (104.0) |
40.2 (104.4) |
36.6 (97.9) |
33.3 (91.9) |
29.4 (84.9) |
23.7 (74.7) |
40.2 (104.4) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 8.4 (47.1) |
10.6 (51.1) |
14.8 (58.6) |
20.8 (69.4) |
25.8 (78.4) |
28.4 (83.1) |
33.0 (91.4) |
32.4 (90.3) |
28.4 (83.1) |
23.4 (74.1) |
17.6 (63.7) |
11.2 (52.2) |
21.2 (70.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 4.5 (40.1) |
6.3 (43.3) |
10.2 (50.4) |
15.7 (60.3) |
20.9 (69.6) |
24.4 (75.9) |
28.8 (83.8) |
28.4 (83.1) |
24.3 (75.7) |
18.9 (66.0) |
13.1 (55.6) |
6.9 (44.4) |
16.9 (62.4) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 1.4 (34.5) |
2.9 (37.2) |
6.5 (43.7) |
11.7 (53.1) |
17.0 (62.6) |
21.4 (70.5) |
25.6 (78.1) |
25.4 (77.7) |
21.2 (70.2) |
15.3 (59.5) |
9.4 (48.9) |
3.4 (38.1) |
13.4 (56.2) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −7.6 (18.3) |
−6.6 (20.1) |
−3.9 (25.0) |
0.3 (32.5) |
8.5 (47.3) |
13.2 (55.8) |
18.4 (65.1) |
18.1 (64.6) |
12.4 (54.3) |
2.4 (36.3) |
−2.3 (27.9) |
−8.9 (16.0) |
−8.9 (16.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 76.6 (3.02) |
73.0 (2.87) |
107.6 (4.24) |
90.0 (3.54) |
106.0 (4.17) |
212.8 (8.38) |
138.0 (5.43) |
176.1 (6.93) |
98.6 (3.88) |
59.2 (2.33) |
61.5 (2.42) |
54.3 (2.14) |
1,253.7 (49.35) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 11.7 | 11.2 | 13.6 | 12.4 | 12.2 | 15.1 | 11.6 | 12.8 | 10.2 | 7.8 | 10.1 | 9.1 | 137.8 |
| Average snowy days | 2.7 | 1.9 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | 1.0 | 6.5 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 77 | 76 | 76 | 74 | 75 | 82 | 79 | 79 | 79 | 77 | 78 | 75 | 77 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 115.5 | 116.9 | 143.1 | 167.0 | 177.5 | 140.7 | 219.1 | 216.8 | 173.7 | 166.1 | 132.0 | 130.8 | 1,899.2 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 36 | 37 | 38 | 43 | 42 | 33 | 51 | 53 | 47 | 47 | 42 | 42 | 43 |
| Source: China Meteorological Administration[2][3] | |||||||||||||
Economy
editTransportation
editRoad
edit- G320
- Shen-Jia-Hu High Way
- Hu-Hang High Way
- Ping-Li County Road
- Chang-Jia High Way
Railway
edit- Hu-Kun Railway
- Hu-Hang High Railway
Water
edit- Hongqitang Canel
- Luxutang Canel
- Taipu River
Industry
editAgriculture
editTourism
editCulture
editEducation
edit- Jiashan Senior High School
- Jiashan Second Senior High School
- Jiashan High School
Notable people
edit- Wu Zhen, a painter in Yuan Dynasty
- Qian Nengxun, a premier of the Republic of China
- Sun Daolin, a renowned Chinese actor
- Huang Ju, Mayor and Party chief of Shanghai, Vice-Premier of the People's Republic of China
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Wang, Orange (2022-11-03). "China names model county in inequality reduction campaign". South China Morning Post. Retrieved 2022-11-04.
- ^ 中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 25 June 2023.
- ^ 中国气象数据网 (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 25 June 2023.