The perineal membrane is an anatomical term for a fibrous membrane in the perineum. The term "inferior fascia of urogenital diaphragm", used in older texts, is considered equivalent to the perineal membrane.
| Perineal membrane | |
|---|---|
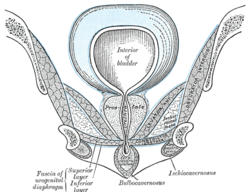 Coronal section of anterior part of pelvis, through the pubic arch. Seen from in front. (Inferior layer labeled at bottom left.) | |
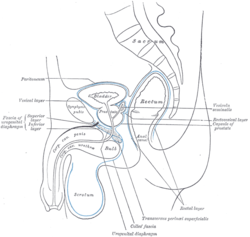 Median sagittal section of male pelvis, showing arrangement of fasciæ. (Inferior layer labeled at center left.) | |
| Details | |
| Location | Perineum |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | membrana perinei |
| TA98 | A09.5.03.002 |
| TA2 | 2444 |
| FMA | 30514 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
It is the superior border of the superficial perineal pouch, and the inferior border of the deep perineal pouch.
Structure
editThe perineal membrane is triangular in shape.[1] It attaches to both ischiopubic rami of the pelvis. It also attaches to the perineal body.
Female
editThe perineal membrane has two distinct portions that span the opening of the anterior pelvic outlet.[2]
The ventral (anterior) portion is associated with the compressor urethra and urethrovaginal sphincter muscles (previously called deep transverse perineal muscles), and is continuous with the insertion of the arcus tendineus fascia pelvis.[3] The apex is separated from the arcuate pubic ligament by an oval opening for the transmission of the deep dorsal vein of the clitoris.
The dorsal (posterior) portion consists of a sheet of dense fibrous tissue that attaches laterally to the ishiopubic rami and medially to the distal third of the vagina and to the perineal body.[3]
The perineal membrane provides support to the distal vagina and urethra by attaching these structures to the bony pelvis.
Male
editIts apex is directed forward, and is separated from the arcuate pubic ligament by an oval opening for the transmission of the deep dorsal vein of the penis
Its lateral margins are attached on either side to the inferior rami of the pubis and ischium, above the crus penis.
Its base is directed toward the rectum, and connected to the central tendinous point of the perineum. The base is fused with both the pelvic fascia and Colle's fascia.
Relations
editIt is continuous with the deep layer of the superficial fascia behind the superficial transverse perineal muscle, and with the inferior layer of the diaphragmatic part of the pelvic fascia.
Perforations
editFemales
editThe vagina, including the opening of the urethra, divides the perineal membrane into two halves.[2] The artery to the bulb of the vestibule originates from the perineal artery and pierces the perineal membrane to travel towards the vestibule of the vagina.[4] The deep and dorsal artery of clitoris are the two terminal branches of the internal pudendal artery which pierce the perineal membrane to supply the clitoris.[5]
Males
editIn males, it is perforated, about 2-3 cm below the pubic symphysis, by the urethra.[6] The bulbourethral glands are present on either side of the membranous urethra and their ducts pierce the perineal membrane posterolateral to the urethra. The deep and dorsal artery of the penis arises from the internal pudendal artery and penetrates the perineal membrane to enter the corpora cavernosa in the crus of the penis.[7]
Contents
editIf the inferior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm is detached on either side, the following structures will be seen between it and the superior fascia:
- the deep dorsal vein of the penis and deep dorsal vein of the clitoris
- the urethra (membranous portion in males)
- the deep transverse perineal muscle and the urethral sphincter muscles
- the bulbourethral glands and their ducts
- the pudendal arteries, dorsal nerves of the penis, dorsal nerves of the clitoris
- the arteries and nerves of the vestibular bulbs and urethral bulb
- a plexus of veins
Additional images
edit-
The constituent cavernous cylinders of the penis.
References
editThis article incorporates text in the public domain from page 428 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Peschers, U; DeLancey, J. O. L. (2007). J. Laycock, J. Haslam (ed.). Therapeutic Management of Incontinence and Pelvic Pain: Pelvic Organ Disorders (2 ed.). London: Springer. pp. 9–20.
- ^ a b Stein, Tamara A.; DeLancey, John O.L. (March 2008). "Structure of the Perineal Membrane in Females: Gross and Microscopic Anatomy". Obstetrics and Gynecology. 111 (3): 686–693. doi:10.1097/AOG.0b013e318163a9a5. ISSN 0029-7844. PMC 2775042. PMID 18310372.
- ^ a b Corton, Marlene M. (2009-09-01). "Anatomy of Pelvic Floor Dysfunction". Obstetrics and Gynecology Clinics of North America. Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery. 36 (3): 401–419. doi:10.1016/j.ogc.2009.09.002. ISSN 0889-8545. PMID 19932407.
- ^ "Artery of Bulb of Vestibule (Right) | Complete Anatomy". www.elsevier.com. Retrieved 2024-06-15.
- ^ "Dorsal Artery of Clitoris (Right) | Complete Anatomy". www.elsevier.com. Retrieved 2024-06-15.
- ^ Bolla, Srinivasa Rao; Hoare, Brittany S.; Varacallo, Matthew (2024), "Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis: Deep Perineal Space", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 30855860, retrieved 2024-06-15
- ^ "Deep Artery of Penis | Complete Anatomy". www.elsevier.com. Retrieved 2024-06-15.
External links
edit- perineum at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (maleugtriangle3, maleugtriangle4)