Hydra (/ˈhaɪdrə/ HY-drə) is a genus of small freshwater hydrozoans of the phylum Cnidaria. They are native to the temperate and tropical regions.[2][3] The genus was named by Linnaeus in 1758 after the Hydra, which was the many-headed beast of myth defeated by Heracles, as when the animal has a part severed, it will regenerate much like the mythical hydra's heads. Biologists are especially interested in Hydra because of their regenerative ability; they do not appear to die of old age, or to age at all.
| Hydra | |
|---|---|
| |
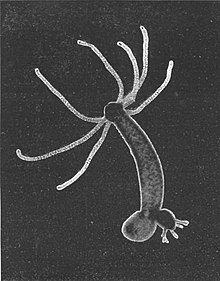
| Hydra budding | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Cnidaria |
| Class: | Hydrozoa |
| Order: | Anthoathecata |
| Family: | Hydridae Dana, 1846 |
| Genus: | Hydra Linnaeus, 1758[1] |
| Species[1] | |
|
List
| |
Morphology
editHydra has a tubular, radially symmetric body up to 10 mm (0.39 in) long when extended, secured by a simple adhesive foot known as the basal disc. Gland cells in the basal disc secrete a sticky fluid that accounts for its adhesive properties.
At the free end of the body is a mouth opening surrounded by one to twelve thin, mobile tentacles. Each tentacle, or cnida (plural: cnidae), is clothed with highly specialised stinging cells called cnidocytes. Cnidocytes contain specialized structures called nematocysts, which look like miniature light bulbs with a coiled thread inside. At the narrow outer edge of the cnidocyte is a short trigger hair called a cnidocil. Upon contact with prey, the contents of the nematocyst are explosively discharged, firing a dart-like thread containing neurotoxins into whatever triggered the release. This can paralyze the prey, especially if many hundreds of nematocysts are fired.
Hydra has two main body layers, which makes it "diploblastic". The layers are separated by mesoglea, a gel-like substance. The outer layer is the epidermis, and the inner layer is called the gastrodermis, because it lines the stomach. The cells making up these two body layers are relatively simple. Hydramacin[4] is a bactericide recently discovered in Hydra; it protects the outer layer against infection. A single Hydra is composed of 50,000 to 100,000 cells which consist of three specific stem cell populations that create many different cell types. These stem cells continually renew themselves in the body column.[5] Hydras have two significant structures on their body: the "head" and the "foot". When a Hydra is cut in half, each half regenerates and forms into a small Hydra; the "head" regenerates a "foot" and the "foot" regenerates a "head". If the Hydra is sliced into many segments then the middle slices form both a "head" and a "foot".[6]
Respiration and excretion occur by diffusion throughout the surface of the epidermis, while larger excreta are discharged through the mouth.[7][8]
Nervous system
editThe nervous system of Hydra is a nerve net, which is structurally simple compared to more derived animal nervous systems. Hydra does not have a recognizable brain or true muscles. Nerve nets connect sensory photoreceptors and touch-sensitive nerve cells located in the body wall and tentacles.
The structure of the nerve net has two levels:
- level 1 – sensory cells or internal cells; and
- level 2 – interconnected ganglion cells synapsed to epithelial or motor cells.
Motion and locomotion
editIf Hydra are alarmed or attacked, the tentacles can be retracted to small buds, and the body column itself can be retracted to a small gelatinous sphere. Hydra generally react in the same way regardless of the direction of the stimulus, and this may be due to the simplicity of the nerve nets.
Hydra are generally sedentary or sessile, but do occasionally move quite readily, especially when hunting. They have two distinct methods for moving – 'looping' and 'somersaulting'. They do this by bending over and attaching themselves to the substrate with the mouth and tentacles and then relocate the foot, which provides the usual attachment, this process is called looping. In somersaulting, the body then bends over and makes a new place of attachment with the foot. By this process of "looping" or "somersaulting", a Hydra can move several inches (c. 100 mm) in a day. Hydra may also move by amoeboid motion of their bases or by detaching from the substrate and floating away in the current.
Reproduction and life cycle
edit- Non-reproducing
- Creating a bud
- Daughter growing out
- Beginning to cleave
- Daughter broken off
- Daughter clone of parent
Most hydra species do not have any gender system. Instead, when food is plentiful, many Hydra reproduce asexually by budding. The buds form from the body wall, grow into miniature adults and break away when mature.
When a hydra is well fed, a new bud can form every two days.[10] When conditions are harsh, often before winter or in poor feeding conditions, sexual reproduction occurs in some Hydra. Swellings in the body wall develop into either ovaries or testes. The testes release free-swimming gametes into the water, and these can fertilize the egg in the ovary of another individual. The fertilized eggs secrete a tough outer coating, and, as the adult dies (due to starvation or cold), these resting eggs fall to the bottom of the lake or pond to await better conditions, whereupon they hatch into nymph Hydra. Some Hydra species, like Hydra circumcincta and Hydra viridissima, are hermaphrodites[11] and may produce both testes and ovaries at the same time.
Many members of the Hydrozoa go through a body change from a polyp to an adult form called a medusa, which is usually the life stage where sexual reproduction occurs, but Hydra do not progress beyond the polyp phase.[12]
Feeding
editHydra mainly feed on aquatic invertebrates such as Daphnia and Cyclops.
While feeding, Hydra extend their body to maximum length and then slowly extend their tentacles. Despite their simple construction, the tentacles of Hydra are extraordinarily extensible and can be four to five times the length of the body. Once fully extended, the tentacles are slowly maneuvered around waiting for contact with a suitable prey animal. Upon contact, nematocysts on the tentacle fire into the prey, and the tentacle itself coils around the prey. Most of the tentacles join in the attack within 30 seconds to subdue the struggling prey. Within two minutes, the tentacles surround the prey and move it into the open mouth aperture. Within ten minutes, the prey is engulfed within the body cavity, and digestion commences. Hydra can stretch their body wall considerably.[citation needed]
The feeding behaviour of Hydra demonstrates the sophistication of what appears to be a simple nervous system.
Some species of Hydra exist in a mutual relationship with various types of unicellular algae. The algae are protected from predators by Hydra; in return, photosynthetic products from the algae are beneficial as a food source to Hydra[13][14], and even help to maintain the Hydra microbiome.[15]
Measuring the feeding response
editThe feeding response in Hydra is induced by glutathione (specifically in the reduced state as GSH) released from damaged tissue of injured prey.[16] There are several methods conventionally used for quantification of the feeding response. In some, the duration for which the mouth remains open is measured.[17] Other methods rely on counting the number of Hydra among a small population showing the feeding response after addition of glutathione.[18] Recently, an assay for measuring the feeding response in hydra has been developed.[19] In this method, the linear two-dimensional distance between the tip of the tentacle and the mouth of hydra was shown to be a direct measure of the extent of the feeding response. This method has been validated using a starvation model, as starvation is known to cause enhancement of the Hydra feeding response.[19]
Predators
editThe species Hydra oligactis is preyed upon by the flatworm Microstomum lineare.[20][21]
Tissue regeneration
editHydras undergo morphallaxis (tissue regeneration) when injured or severed. Typically, Hydras reproduce by just budding off a whole new individual; the bud occurs around two-thirds of the way down the body axis. When a Hydra is cut in half, each half regenerates and forms into a small Hydra; the "head" regenerates a "foot" and the "foot" regenerates a "head". This regeneration occurs without cell division. If the Hydra is sliced into many segments, the middle slices form both a "head" and a "foot".[6] The polarity of the regeneration is explained by two pairs of positional value gradients. There is both a head and foot activation and inhibition gradient. The head activation and inhibition works in an opposite direction of the pair of foot gradients.[22] The evidence for these gradients was shown in the early 1900s with grafting experiments. The inhibitors for both gradients have shown to be important to block the bud formation. The location where the bud forms is where the gradients are low for both the head and foot.[6]
Hydras are capable of regenerating from pieces of tissue from the body and additionally after tissue dissociation from reaggregates.[22] This process takes place not only in the pieces of tissue excised from the body column, but also from re-aggregates of dissociated single cells. It was found that in these aggregates, cells initially distributed randomly undergo sorting and form two epithelial cell layers, in which the endodermal epithelial cells play more active roles in the process. Active mobility of these endodermal epithelial cells forms two layers in both the re-aggregate and the re-generating tip of the excised tissue. As these two layers are established, a patterning process takes place to form heads and feet.[23]
Non-senescence
editDaniel Martinez claimed in a 1998 article in Experimental Gerontology that Hydra are biologically immortal.[24] This publication has been widely cited as evidence that Hydra do not senesce (do not age), and that they are proof of the existence of non-senescing organisms generally. In 2010, Preston Estep published (also in Experimental Gerontology) a letter to the editor arguing that the Martinez data refutes the hypothesis that Hydra do not senesce.[25]
The controversial unlimited lifespan of Hydra has attracted much attention from scientists. Research today appears to confirm Martinez' study.[26] Hydra stem cells have a capacity for indefinite self-renewal. The transcription factor "forkhead box O" (FoxO) has been identified as a critical driver of the continuous self-renewal of Hydra.[26] In experiments, a drastically reduced population growth resulted from FoxO down-regulation.[26]
In bilaterally symmetrical organisms (Bilateria), the transcription factor FoxO affects stress response, lifespan, and increase in stem cells. If this transcription factor is knocked down in bilaterian model organisms, such as fruit flies and nematodes, their lifespan is significantly decreased. In experiments on H. vulgaris (a radially symmetrical member of phylum Cnidaria), when FoxO levels were decreased, there was a negative effect on many key features of the Hydra, but no death was observed, thus it is believed other factors may contribute to the apparent lack of aging in these creatures.[5]
DNA repair
editHydra are capable of two types of DNA repair: nucleotide excision repair and base excision repair.[27] The repair pathways facilitate DNA replication by removing DNA damage. Their identification in hydra was based, in part, on the presence in its genome of genes homologous to ones present in other genetically well studied species playing key roles in these DNA repair pathways.[27]
Genomics
editAn ortholog comparison analysis done within the last decade[as of?] demonstrated that Hydra share a minimum of 6,071 genes with humans. Hydra is becoming an increasingly better model system as more genetic approaches become available.[5] Transgenic hydra have become attractive model organisms to study the evolution of immunity.[28] A draft of the genome of Hydra magnipapillata was reported in 2010.[29]
The genomes of cnidarians are usually less than 500 Mb (megabases) in size, as in the Hydra viridissima, which has a genome size of approximately 300 Mb. In contrast, the genomes of brown hydras are approximately 1 Gb in size. This is because the brown hydra genome is the result of an expansion event involving LINEs, a type of transposable elements, in particular, a single family of the CR1 class. This expansion is unique to this subgroup of the genus Hydra and is absent in the green hydra, which has a repeating landscape similar to other cnidarians. These genome characteristics make Hydra attractive for studies of transposon-driven speciations and genome expansions.[30]
Due to the simplicity of their life cycle when compared to other hydrozoans, hydras have lost many genes that correspond to cell types or metabolic pathways of which the ancestral function is still unknown.
Hydra genome shows a preference towards proximal promoters. Thanks to this feature, many reporter cell lines have been created with regions around 500 to 2000 bases upstream of the gene of interest. Its cis-regulatory elements (CRE) are mostly located less than 2000 base pairs upstream from the closest transcription initiation site, but there are CREs located further away.
Its chromatin has a Rabl configuration. There are interactions between the centromeres of different chromosomes and the centromeres and telomeres of the same chromosome. It presents a great number of intercentromeric interactions when compared to other cnidarians, probably due to the loss of multiple subunits of condensin II. It is organized in domains that span dozens to hundreds of megabases, containing epigenetically co-regulated genes and flanked by boundaries located within heterochromatin.[31]
Transcriptomics
editDifferent Hydra cell types express gene families of different evolutionary ages. Progenitor cells (stem cells, neuron and nematocyst precursors, and germ cells) express genes from families that predate metazoans. Among differentiated cells some express genes from families that date from the base of metazoans, like gland and neuronal cells, and others express genes from newer families, originating from the base of cnidaria or medusozoa, like nematocysts. Interstitial cells contain translation factors with a function that has been conserved for at least 400 million years.[31]
See also
edit- Lernaean Hydra, a Greek mythological aquatic creature after which the genus is named
- Turritopsis dohrnii, another cnidarian (a jellyfish) that scientists believe to be immortal
References
edit- ^ a b Schuchert P (2011). Schuchert P (ed.). "Hydra Linnaeus, 1758". World Hydrozoa database. World Register of Marine Species. Retrieved 20 December 2011.
- ^ Gilberson L (1999). Zoology Lab Manual (4th ed.). Primis Custom Publishing.
- ^ Solomon E, Berg L, Martin D (2002). Biology (6th ed.). Brooks/Cole.
- ^ Jung S, Dingley AJ, Augustin R, Anton-Erxleben F, Stanisak M, Gelhaus C, Gutsmann T, Hammer MU, Podschun R, Bonvin AM, Leippe M, Bosch TC, Grötzinger J (January 2009). "Hydramacin-1, structure and antibacterial activity of a protein from the basal metazoan Hydra". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 284 (3): 1896–905. doi:10.1074/jbc.M804713200. PMID 19019828. S2CID 3887876.
- ^ a b c Tomczyk S, Fischer K, Austad S, Galliot B (January 2015). "Hydra, a powerful model for aging studies". Invertebrate Reproduction & Development. 59 (sup1): 11–16. Bibcode:2015InvRD..59S..11T. doi:10.1080/07924259.2014.927805. PMC 4463768. PMID 26120246.
- ^ a b c Gilbert SF (2000). "Regeneration". Developmental Biology (6th ed.). Sinauer Associates.
- ^ "Olympus Microscopy Resource Center | Pond Life Video Gallery – Hydra (Coelenterata)". olympus.magnet.fsu.edu. Retrieved 21 September 2019.
- ^ Cantor, Marvin H.; Rahat, Menachem (1982). "Regulation of Respiration and Photosynthesis in Hydra viridis and in Its Separate Cosymbionts: Effect of Nutrients". Physiological Zoology. 55 (3). The University of Chicago Press: 281–288. doi:10.1086/physzool.55.3.30157891. ISSN 0031-935X. JSTOR 30157891. S2CID 86961916.
- ^ Ji N, Flavell SW (April 2017). "Hydra: Imaging Nerve Nets in Action". Current Biology. 27 (8): R294 – R295. Bibcode:2017CBio...27.R294J. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2017.03.040. hdl:1721.1/114954. PMID 28441559.
- ^ Patton WK (August 2014). "Hydra (coelenterate)". Grolier Multimedia Encyclopedia. Grolier Online.
- ^ Holstein T, Emschermann P (1995). Cnidaria: Hydrozoa Süsswasserfauna von Mitteleuropa. Bd 1/2+ 3. Stuttgart: Spektrum Akademischer Verlag. ISBN 978-3-8274-0836-5.
- ^ Hickman, Cleveland P. Jr. (2019). Integrated principles of zoology (Eighteenth ed.). New York, NY. ISBN 978-1-260-20519-0. OCLC 1097367369.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Thorington, Glyne; Margulis, Lynn (1981). "Hydra viridis; transfer of metabolites between Hydra and symbiotic algae". The Biological Bulletin. 160 (1): 175–188. doi:10.2307/1540911. ISSN 0006-3185. JSTOR 1540911. PMID 6164406. S2CID 21008864.
- ^ Muscatine, Leonard; Lenhoff, Howard M. (15 November 1963). "Symbiosis: On the Role of Algae Symbiotic with Hydra". Science. 142 (3594): 956–958. Bibcode:1963Sci...142..956M. doi:10.1126/science.142.3594.956. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 17753799. S2CID 28578967.
- ^ Bathia, Jay; Schröder, Katja; Fraune, Sebastian; Lachnit, Tim; Rosenstiel, Philip; Bosch, Thomas C. G. (6 June 2022). "Symbiotic Algae of Hydra viridissima Play a Key Role in Maintaining Homeostatic Bacterial Colonization". Front. Microbiol. 13: 869666. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2022.869666. PMC 9207534. PMID 35733963.
- ^ Loomis WF (October 1955). "Glutathione control of the specific feeding reactions of hydra". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 62 (9): 211–27. Bibcode:1955NYASA..62..211L. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1955.tb35372.x. S2CID 85570550.
- ^ Bellis SL, Laux DC, Rhoads DE (November 1994). "Affinity purification of Hydra glutathione binding proteins". FEBS Letters. 354 (3): 320–4. Bibcode:1994FEBSL.354..320B. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(94)01154-0. PMID 7957948. S2CID 29262166.
- ^ Venturini G (1987). "The hydra GSH receptor. Pharmacological and radioligand binding studies". Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. C, Comparative Pharmacology and Toxicology. 87 (2): 321–4. doi:10.1016/0742-8413(87)90015-6. PMID 2888575.
- ^ a b Kulkarni R, Galande S (November 2014). "Measuring glutathione-induced feeding response in hydra". Journal of Visualized Experiments (93): e52178. doi:10.3791/52178. PMC 4354099. PMID 25490534.
- ^ Krohne, Georg (2018). "Organelle survival in a foreign organism: Hydra nematocysts in the flatworm Microstomum lineare". European Journal of Cell Biology. 97 (4): 289–299. doi:10.1016/j.ejcb.2018.04.002. ISSN 1618-1298. PMID 29661512.
- ^ Krohne, Georg (2020). "Hydra nematocysts in the flatworm Microstomum lineare: in search for alterations preceding their disappearance from the new host". Cell and Tissue Research. 379 (1): 63–71. doi:10.1007/s00441-019-03149-w. ISSN 1432-0878. PMID 31848750. S2CID 209380951.
- ^ a b Fujisawa T (February 2003). "Hydra regeneration and epitheliopeptides". Developmental Dynamics. 226 (2): 182–9. doi:10.1002/dvdy.10221. PMID 12557197. S2CID 26953455.
- ^ Fujisawa, Toshitaka (29 January 2003). "Hydra regeneration and epitheliopeptides". Developmental Dynamics. 226 (2). American Association for Anatomy (Wiley): 182–189. doi:10.1002/dvdy.10221. ISSN 1058-8388. PMID 12557197. S2CID 26953455.
- ^ Martínez DE (May 1998). "Mortality patterns suggest lack of senescence in hydra". Experimental Gerontology. 33 (3): 217–25. doi:10.1016/S0531-5565(97)00113-7. PMID 9615920. S2CID 2009972.
- ^ Estep PW (September 2010). "Declining asexual reproduction is suggestive of senescence in hydra: comment on Martinez, D., "Mortality patterns suggest lack of senescence in hydra." Exp Gerontol 33, 217–25". Experimental Gerontology. 45 (9): 645–6. doi:10.1016/j.exger.2010.03.017. PMID 20398746. S2CID 35408542.
- ^ a b c Boehm AM, Khalturin K, Anton-Erxleben F, Hemmrich G, Klostermeier UC, Lopez-Quintero JA, Oberg HH, Puchert M, Rosenstiel P, Wittlieb J, Bosch TC (November 2012). "FoxO is a critical regulator of stem cell maintenance in immortal Hydra". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 109 (48): 19697–702. Bibcode:2012PNAS..10919697B. doi:10.1073/pnas.1209714109. PMC 3511741. PMID 23150562.
- ^ a b Barve, Apurva; Galande, Alisha A.; Ghaskadbi, Saroj S.; Ghaskadbi, Surendra (2021). "DNA Repair Repertoire of the Enigmatic Hydra". Frontiers in Genetics. 12: 670695. doi:10.3389/fgene.2021.670695. PMC 8117345. PMID 33995496.
- ^ "Transgenic Hydra Facility, University of Kiel (Germany)".
- ^ Chapman JA, Kirkness EF, Simakov O, Hampson SE, Mitros T, Weinmaier T, et al. (March 2010). "The dynamic genome of Hydra". Nature. 464 (7288): 592–6. Bibcode:2010Natur.464..592C. doi:10.1038/nature08830. PMC 4479502. PMID 20228792.
- ^ Wong, WY; Simakov, O; Bridge, DM; Cartwright, P; Bellantuono, AJ; Kuhn, A; Holstein, TW; David, CN; Steele, RE; Martínez, DE (2019). "Expansion of a single transposable element family is associated with genome-size increase and radiation in the genus Hydra". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 116 (46): 22915–22917. Bibcode:2019PNAS..11622915W. doi:10.1073/pnas.1910106116. PMC 6859323. PMID 31659034.
- ^ a b J. F., Cazet; S., Siebert; H. M., Little; P., Bertemes; A. S., Primack; P., Ladurner; M., Achrainer; M. T., Fredriksen; R. T., Moreland; S., Singh; S., Zhang; T. G., Wolfsberg; T. G., Schnitzler; A. D., Baxevanis; O., Simakov; B., Hobmayer; C. E., Juliano (2023). "A chromosome-scale epigenetic map of the Hydra genome reveals conserved regulators of cell state". Genome Research. 33 (2): 283–298. doi:10.1101/gr.277040.122. PMC 10069465. PMID 36639202.