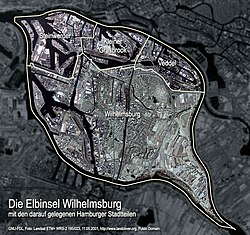
Wilhelmsburg () (Low German: Willemsborg) is a quarter (Stadtteil) of Hamburg, Germany within the borough (Bezirk) of Hamburg-Mitte. It is situated on several islands between the Northern and Southern branches of the Elbe river (Norderelbe and Süderelbe), together with the other quarters of Steinwerder, Veddel and Kleiner Grasbrook. The latter almost exclusively consists of facilities of the port of Hamburg. In 2020 the population was 53,064.
Wilhelmsburg | |
|---|---|
 Aerial photo of Wilhelmsburg | |
| Coordinates: 53°29′42″N 10°00′40″E / 53.49500°N 10.01111°E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Hamburg |
| City | Hamburg |
| Borough | Hamburg-Mitte |
| Area | |
| • Total | 35.3 km2 (13.6 sq mi) |
| Population (2023-12-31)[1] | |
| • Total | 54,662 |
| • Density | 1,500/km2 (4,000/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Dialling codes | 040 |
| Vehicle registration | HH |
History
editIn 1642, George William, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg acquired three islets in the river Elbe and connected them by means of dams. The resultant island was named Wilhelmsburg in his honour.
In 1705, the Principality of Lüneburg passed on to the Electorate of Hanover, and Wilhelmsburg became part of the Hanoverian state, which then subsequently became the Prussian Province of Hanover in 1866. In 1925, the Prussian authorities designated Wilhelmsburg as a city district, and merged it with nearby Harburg two years later to form the city of Harburg-Wilhelmsburg.
In 1937, Harburg-Wilhelmsburg, along with the cities from the Prussian Province of Schleswig-Holstein, Altona and Wandsbek, was annexed to Hamburg in the Greater Hamburg Act.[2]
During World War II, the port of Hamburg and therefore Wilhelmsburg were targets of the air raids of the so-called Operation Gomorrah. A subcamp to the Neuengamme concentration camp existed in Wilhelmsburg.[3]
On the night of February 16–17, 1962, Wilhelmsburg was widely flooded and seriously damaged by the North Sea flood.
On March 1, 2008, Wilhelmsburg was transferred from the borough Harburg to the borough Hamburg-Mitte by a Hamburg law.[4]
Geography
editIn 2006, according to the statistical office of Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein, the quarter Wilhelmsburg has a total area of 35.3 km2 (14 sq mi). Wihelmsburg borders in the north to the quarters Steinwerder, Kleiner Grasbrook and Veddel. In the east are the quarters Spadenland and Ochsenwerder of the Bergedorf borough. In the south are the quarters Neuland and Harburg of the Harburg borough and the state of Lower Saxony and in the east are the quarters Moorburg and Altenwerder of the Harburg borough.
Demographics
editIn 2006, Wilhelmsburg had 49,132 inhabitants. The population density was 1,394/km2 (3,610/sq mi). 22.6% of the population were under the age of 18, and 14.6% were 65 years of age or older. 33.7% were resident aliens. 4,298 people were registered as unemployed.[5] In 1999 there were 21,345 households, out of which 26.8% had children under the age of 18 living with them and 39.9% of all households were made up of individuals. The average household size was 2.18.[6]
Population by year[5]
| 1987 | 1988 | 1989 | 1990 | 1991 | 1992 | 1993 | 1994 | 1995 | 1996 | 1997 | 1998 | 1999 |
| 44,047 | 44,477 | 45,636 | 46,686 | 46,876 | 47,523 | 47,729 | 47,670 | 47,772 | 47,604 | 47,256 | 46,280 | 46,110 |
| 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 |
| 46,125 | 47,180 | 47,857 | 47,847 | 48,322 | 48,957 | 49,132 |
In 2006, there were 7,204 criminal offences (147 crimes per 1,000 people).[7]
There were 8 elementary schools and 6 secondary schools in the quarter Wilhelmsburg and 52 physicians in private practice and 11 pharmacies.[8]
Economy
editParts of the port of Hamburg are located in Wilhelmsburg.
Infrastructure
editThe hospital Wilhelmsburger Krankenhaus Groß Sand has 257 beds and a day care center for geriatrics.[9]
Transportation
editWilhelmsburg is serviced by the rapid transit system of the city train with the Wilhelmsburg station.
The islands of Wilhelmsburg, Steinwerder, Veddel and Kleiner Grasbrook are connected via numerous bridges. The main connections to other parts of Hamburg are the Hamburger Elbbrücken (Hamburg Elbe Bridges) which consist of the Norder- und Süderelbbrücken (Northern and Southern Elbe Bridges), that connect Wilhelmsburg with the City Center of Hamburg in the north and with the quarter of Harburg in the south, the Kattwyk-Bridge (world's largest vertical lift bridge) in the southwest and the Köhlbrand Bridge which is a major connection from Wilhelmsburg to the nearby motorway 7 and the New Elbe Tunnel in the northwest.
According to the Department of Motor Vehicles (Kraftfahrt-Bundesamt), in the quarter Wilhelmsburg were 13,714 private cars registered (280 cars/1,000 people).[8]
Culture
editSince 2007, the music and art festival Dockville takes place every year in summer.
Notes
edit- ^ "Bevölkerung in Hamburg am 31.12.2023 nach Stadtteilen". Statistisches Amt für Hamburg und Schleswig-Holstein. May 2024.
- ^ Text of the law (in German)
- ^ The camp is listed as No. 556 Hamburg-Wilhelmsburg, Jung-Öl industry in the official German list Archived 2009-04-23 at the Wayback Machine (in German)
- ^ Act of the areal organisation
- ^ a b Residents registration office, source: statistical office Nord of Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein (2006)
- ^ Source: statistical office Nord of Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein (1999)
- ^ State Investigation Bureaux (Landeskriminalamt), source: statistical office Nord of Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein (2006)
- ^ a b Source: statistical office Nord of Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein (2006)
- ^ List of Hospitals, p. 18
References
edit- Act of the areal organisation, July 6, 2006 Gesetz über die räumliche Gliederung der Freien und Hansestadt Hamburg (RäumGiG) (in German)
- Statistical office Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein Statistisches Amt für Hamburg und Schleswig-Holstein, official website (in German)
- List of hospitals Krankenhaus-Verzeichnis Hamburg 2006 Ministry of Social Affairs, Family Affairs, Health and Consumer Protection Behörde für Soziales, Familie, Gesundheit und Verbraucherschutz (in German)